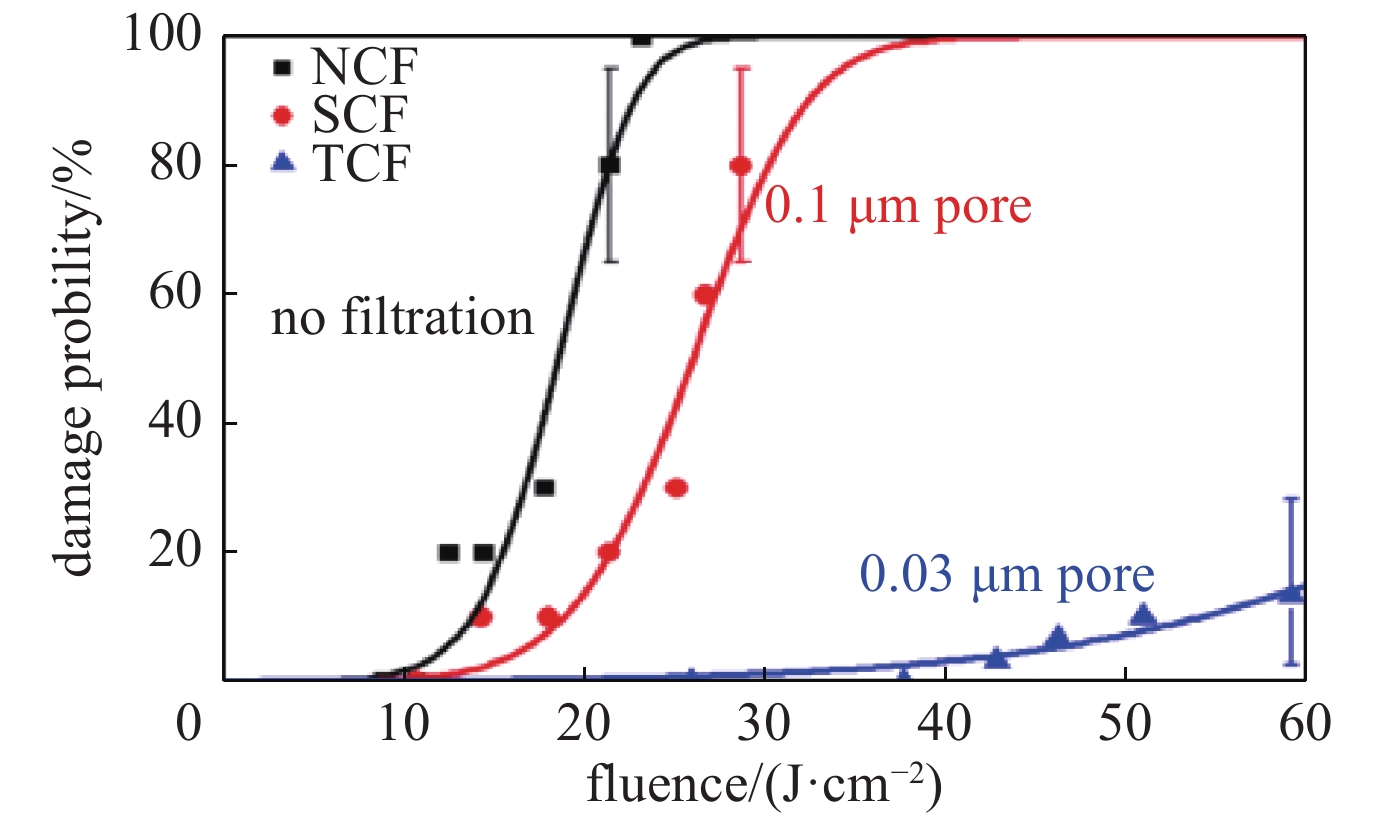
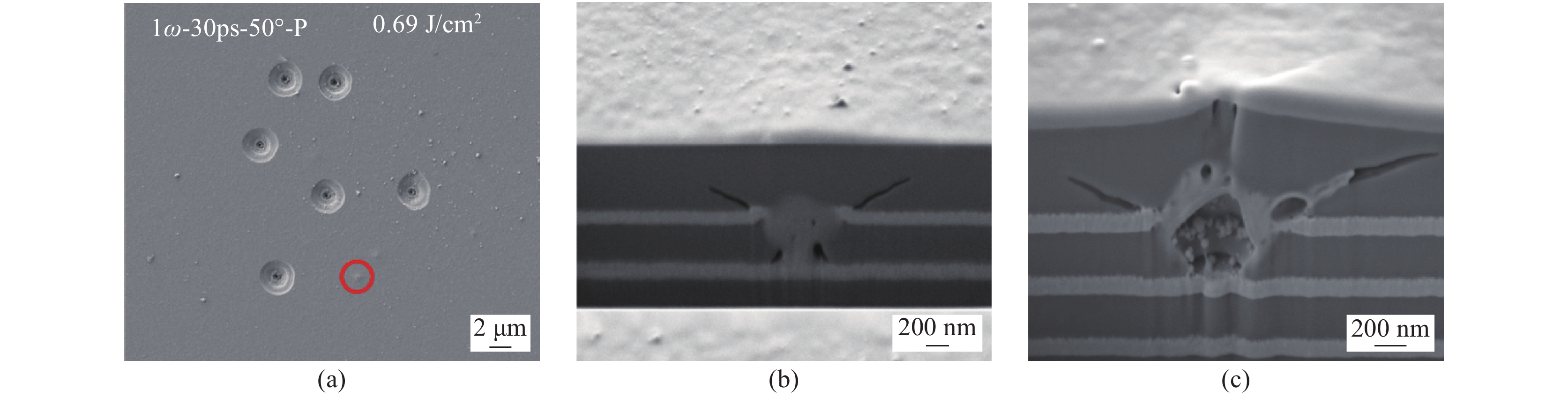
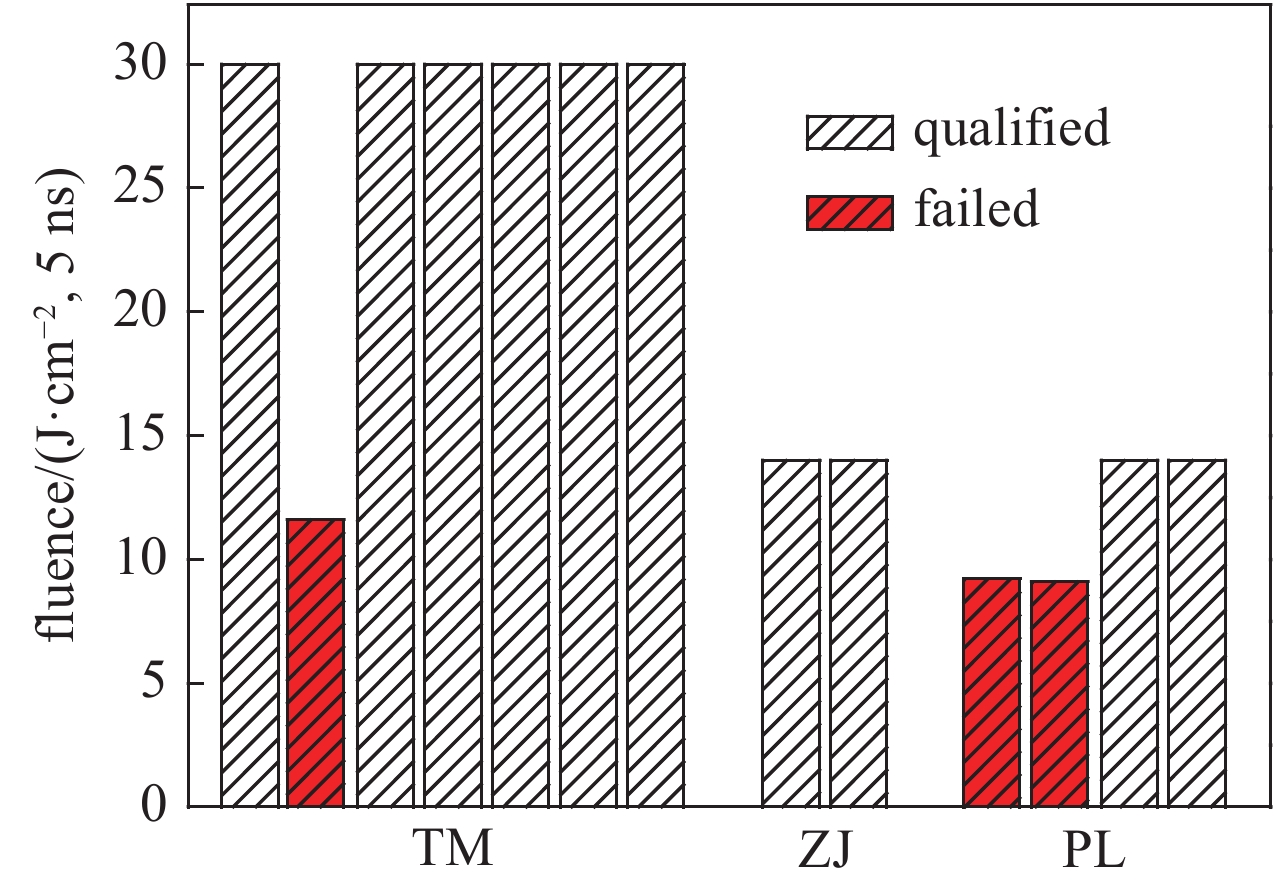
Tracking and understanding laser damage events in optics
-
摘要: 光学元件是各类激光系统不可或缺的光学功能实现部件,其性能决定了激光系统的输出能力和光束质量。光学元件的激光损伤问题从激光发明起就一直伴随着激光技术的发展,随着激光新技术的发展和激光新应用的牵引,激光的波段、脉冲宽度以及重复频率等参数不断拓宽,使得激光损伤问题更加复杂,但万变不离其宗,激光损伤问题的核心是光学元件或光学材料对激光的吸收机制问题。从激光与光学材料相互作用的基本原理出发,以惯性约束聚变(ICF)激光驱动器应用的典型光学材料和光学元件为研究对象,回顾了针对光学元件的激光损伤问题开展的科研工作,总结了在此期间形成的关键技术和里程碑进展,同时也对依然困扰该领域的几类光学元件存在的问题瓶颈以及进一步研究发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: Optics are indispensable components for realizing optical functions of various laser systems, and their performances determine the output capability and beam quality of the laser system. Laser damage of optics have accompanied the developments of laser technologies since the invention of laser. With the development of new laser technologies and tractions of new laser applications, laser parameters such as the wavelength, pulse width and repetition frequency have been expanded, making laser damage more complicated. However, remaining essentially the same, the core of laser damage is the absorption mechanism of optics or optical materials. Starting from the basic principles of the interaction between laser and optical materials, this paper focuses on the typical optical materials and optics used in domestic inertial confinement fusion (ICF) laser drivers, and reviews the scientific research on laser damage of optics. Then, it summarizes the key technologies and milestone progress formed during this period. At last, it predicts several types of bottleneck optics that still plagued this field as well as the development of further research.
-
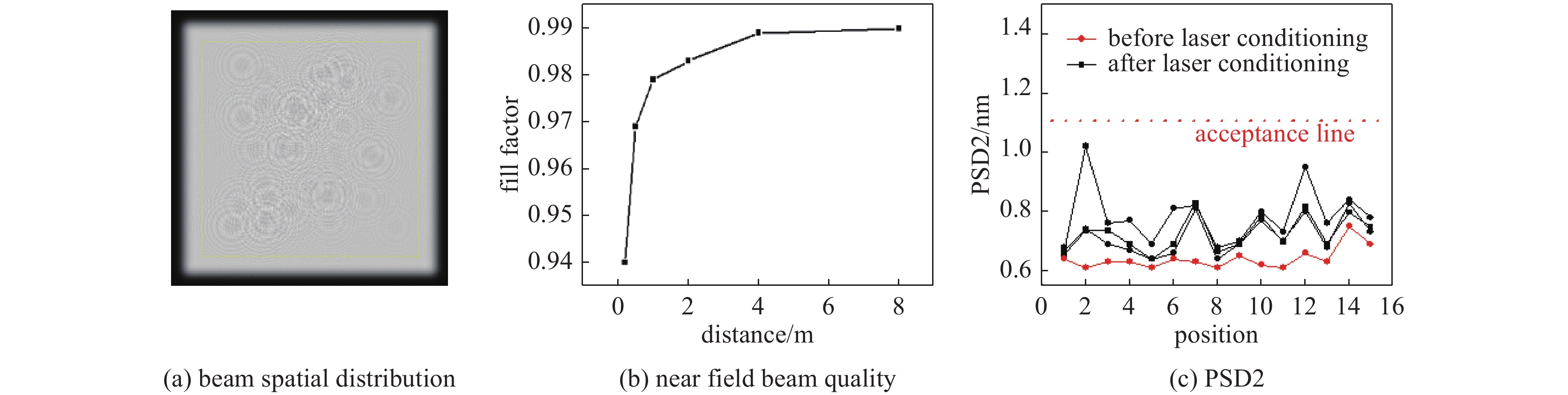
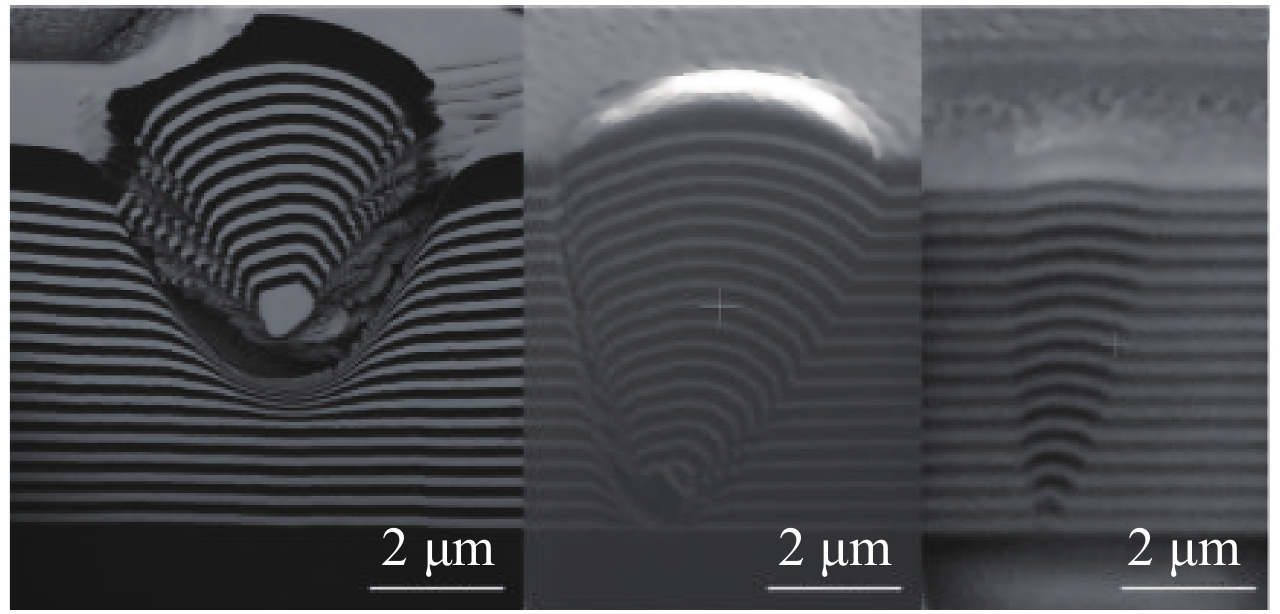
图 14 大口径光学元件激光预处理平台[35]
Figure 14. Laser conditioning platforms for large optics[35]
-
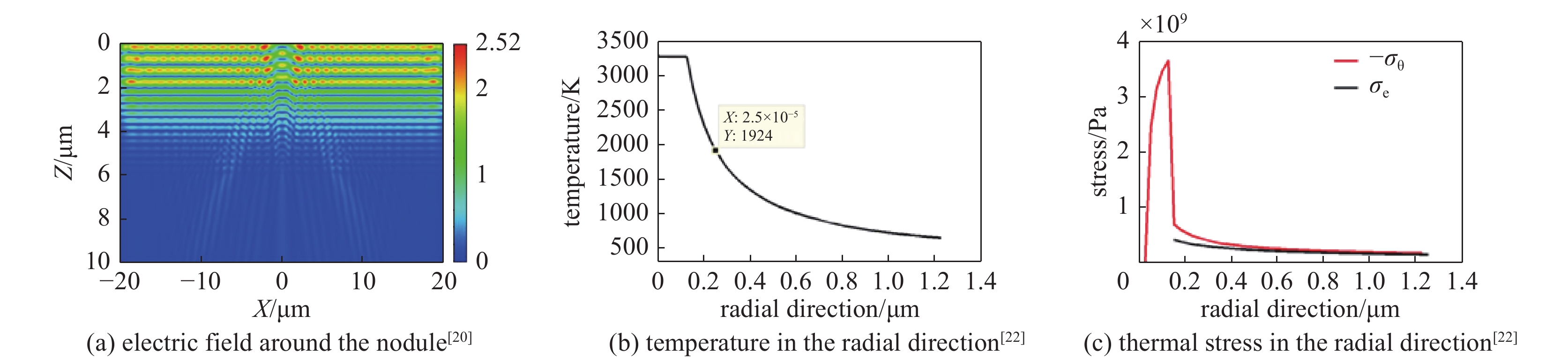
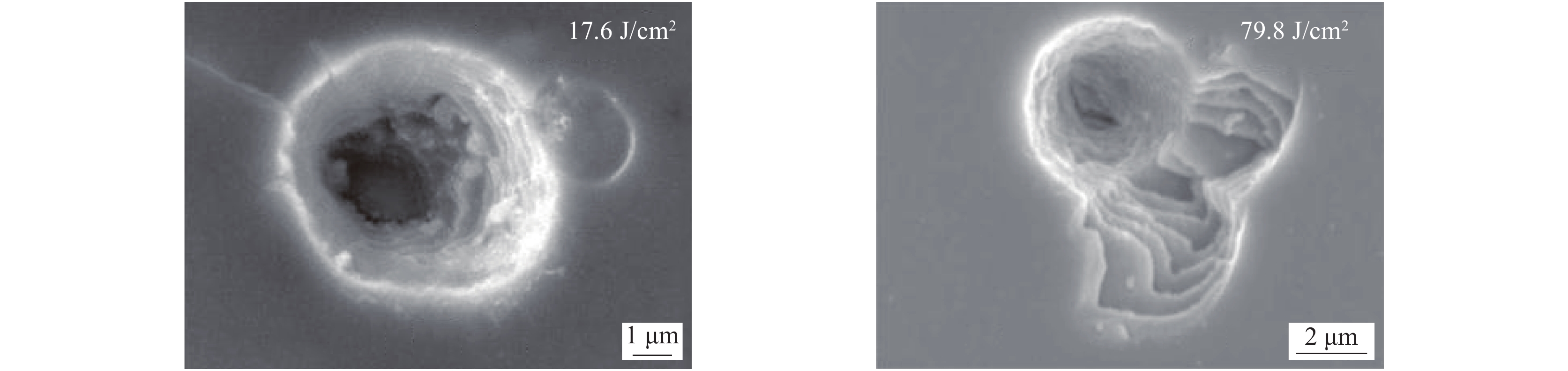
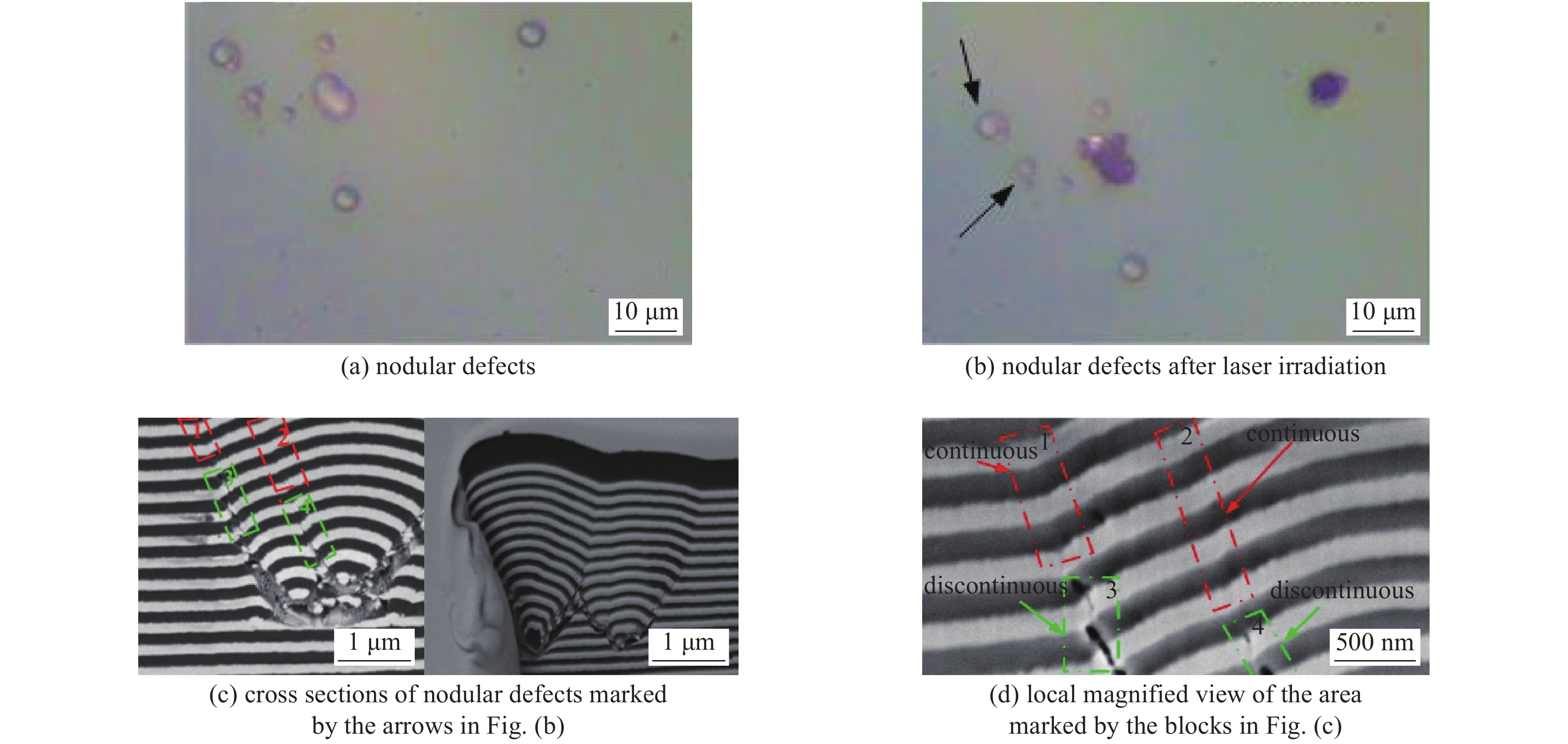
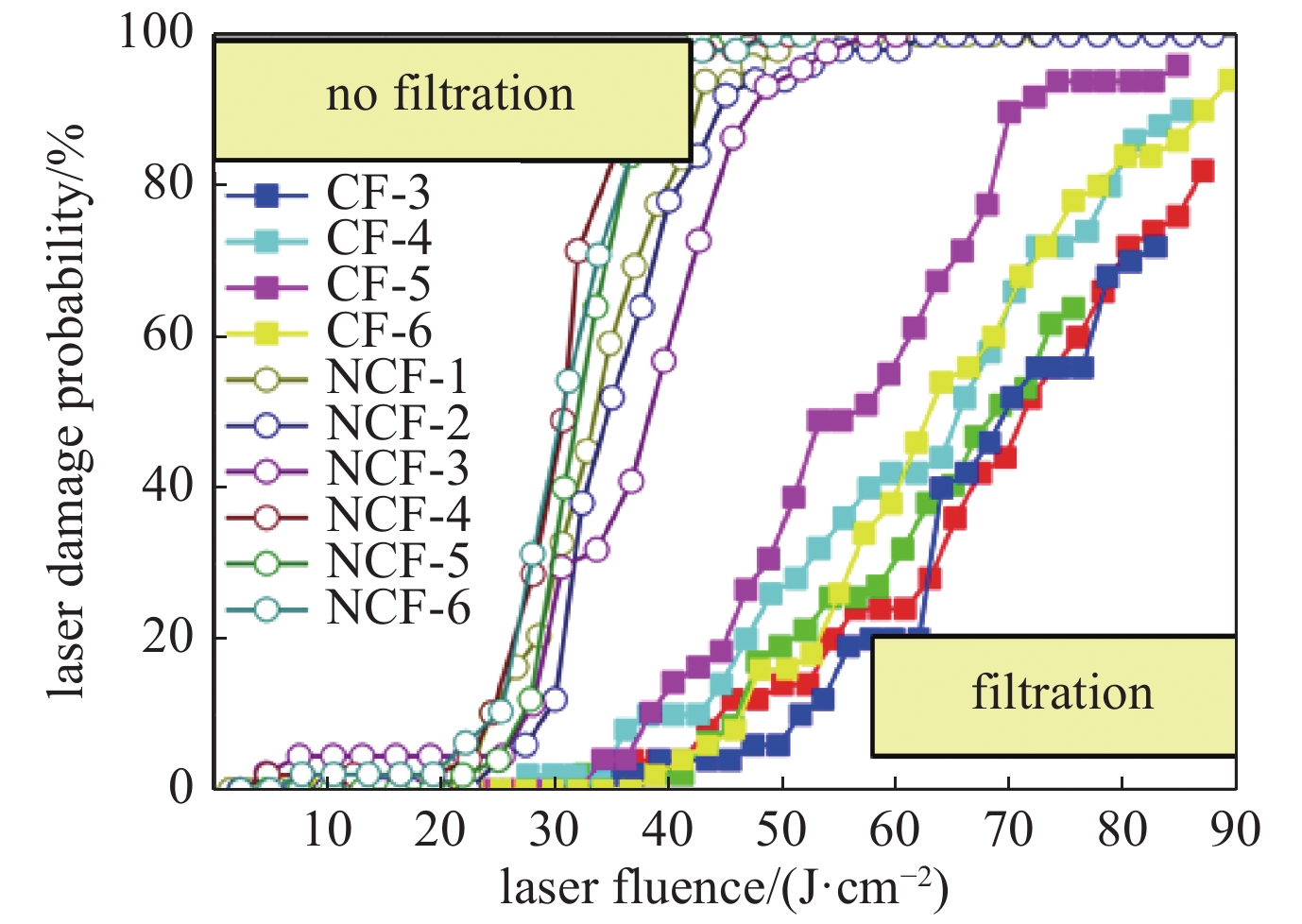
[1] McClung F J, Hellwarth R W. Giant optical pulsations from ruby[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1962, 33(3): 828-829. doi: 10.1063/1.1777174 [2] Hopper R W, Uhlmann D R. Mechanism of inclusion damage in laser glass[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1970, 41(10): 4023-4037. doi: 10.1063/1.1658407 [3] Carr C W, Bude J D, Demange P. Laser-supported solid-state absorption fronts in silica[J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 82: 184304. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.184304 [4] Bloembergen N. Laser-induced electric breakdown in solids[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1974, 10(3): 375-386. doi: 10.1109/JQE.1974.1068132 [5] Epifanov A S, Manenkov A A, Prokhorov A M. Theory of avalanche ionization induced in transparent dielectrics by an electromagnetic field[J]. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics, 1976, 43(2): 377-382. [6] Schaffer C B, Brodeur A, Mazur E. Laser-induced breakdown and damage in bulk transparent materials induced by tightly focused femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2001, 12(11): 1784-1794. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/12/11/305 [7] Deng Hongxiang, Guo Wenli, Gao Huanhuan, et al. A numerical approach for femtosecond laser-induced photoionization in solids and its application[J]. Journal of Optics, 2019, 21: 075501. doi: 10.1088/2040-8986/ab2357 [8] Jing Xufeng, Tian Ying, Zhang Junchao, et al. Modeling validity of femtosecond laser breakdown in wide bandgap dielectrics[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(10): 4741-4749. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.01.070 [9] Dijon J, Poulingue M, Hue J. Thermomechanical model of mirror laser damage at 1.06 μm: I. Nodule ejection[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 3578 Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials. 1999: 387-397. [10] Liu Xiaofeng, Li Dawei, Zhao Yuan’an, et al. Characteristics of nodular defect in HfO2/SiO2 multilayer optical coatings[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 256(12): 3783-3788. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.01.026 [11] Papernov S. Mechanisms of near-ultraviolet, nanosecond-pulse–laser damage in HfO2/SiO2-based multilayer coatings[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2013, 11: S10703. [12] Li Cheng, Zhao Yuan’an, Cui Yun, et al. Comparison of 355-nm nanosecond and 1064-nm picosecond laser-induced damage in high-reflective coatings[J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 57: 121908. [13] Borden M R, Folta J A, Stolz C J, et al. Improved method for laser damage testing coated optics[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5991, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials. 2005: 59912A. [14] Taniguchi J, Lebarron N E, Howe J, et al. Functional damage thresholds of hafnia/silica coating designs for the NIF laser[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 4347, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials. 2001: 109-117. [15] Stolz C J. Status of NIF mirror technologies for completion of the NIF facility[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 7101, Advances in Optical Thin Films III. 2008: 710115. [16] Spaeth M L, Manes K R, Kalantar D H, et al. Description of the NIF Laser[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 25-145. doi: 10.13182/FST15-144 [17] Suratwala T I, Miller P E, Bude J D, et al. HF-based etching processes for improving laser damage resistance of fused silica optical surfaces[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(2): 416-428. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04112.x [18] Bude J, Miller P, Baxamusa S, et al. High fluence laser damage precursors and their mitigation in fused silica[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(5): 5839-5851. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.005839 [19] Liu Xiaofeng, Li Dawei, Zhao Yuan’an, et al. Further investigation of the characteristics of nodular defects[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(10): 1774-1779. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.001774 [20] Shan Yongguang, He Hongbo, Wei Chaoyang, et al. Geometrical characteristics and damage morphology of nodules grown from artificial seeds in multilayer coating[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(22): 4290-4295. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.004290 [21] 潘顺民, 卫耀伟, 安晨辉, 等. 45°高反膜中节瘤缺陷的电场增强效应及损伤特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:071006. (Pan Shunmin, Wei Yaowei, An Chenhui, et al. Electric field enhancement effect and damage characteristics of nodular defect in 45° high-reflection coating[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 071006 [22] Shan Yongguang, He Hongbo, Wei Chaoyang, et al. Thermomechanical analysis of nodule damage in HfO2/SiO2 multilayer coatings[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2011, 9: 103101. doi: 10.3788/COL201109.103101 [23] Stolz C J. Engineering high-damage-threshold NIF polarizers and mirrors [R]. ICF Quarterly Report, 1999, 9(2): 151-162. [24] Demange P P, Negres R A, Radousky H B, et al. Differentiation of defect populations responsible for bulk laser-induced damage in potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals[J]. Optical Engineering, 2010, 45: 104205. [25] Demos S G, Demange P, Negres R A, et al. Investigation of the electronic and physical properties of defect structures responsible for laser-induced damage in DKDP crystals[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(13): 13788-13804. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.013788 [26] Reyné S, Duchateau G, Natoli J Y, et al. Laser-induced damage of KDP crystals by 1ω nanosecond pulses: influence of crystal orientation[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(24): 21652-21665. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.021652 [27] Baisden P A, Atherton L J, Hawley R A, et al. Large optics for the National Ignition Facility[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 295-351. doi: 10.13182/FST15-143 [28] Wang Yueliang, Zhao Yuan’an, Xie Xiaoyi, et al. Laser damage dependence on the size and concentration of precursor defects in KDP crystals: view through differently sized filter pores[J]. Optics Letter, 2016, 41(7): 1534-1537. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001534 [29] Demange P, Negres R A, Carr C W, et al. Laser-induced defect reactions governing damage initiation in DKDP crystals[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(12): 5313-5328. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.005313 [30] Duchateau G. Simple models for laser-induced damage and conditioning of potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals by nanosecond pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(13): 10434-10456. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.010434 [31] 李成. 纳观尺度缺陷诱导多层介质膜激光损伤动力学研究[D].上海: 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 2020: 79-87Li Cheng. Dynamics of nanoscale defects induced laser damage of multilayer dielectric coatings[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020: 79-87 [32] De Yoreo J J, Burnham A K, Whitman P K. Developing KH2PO4 and KD2PO4 crystals for the world's most power laser[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2002, 47(3): 113-152. doi: 10.1179/095066001225001085 [33] Sheehan L M, Kozlowski M R, Tench R J. Full-aperture laser conditioning of multilayer mirrors and polarizers[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 2633, Solid State Lasers for Application to Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF). 1995: 457-463. [34] Hunt J T, Manes K R, Renard P A. Hot images from obscurations[J]. Applied Optics, 1993, 32(30): 5973-5982. doi: 10.1364/AO.32.005973 [35] 赵元安, 胡国行, 刘晓凤, 等. 激光预处理技术及其应用[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(12):2938-2947. (Zhao Yuan’an, Hu Guohang, Liu Xiaofeng, et al. Laser conditioning technology and its applications[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(12): 2938-2947 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162412.2938 [36] Sheehan L M, Schwartz S, Battersby C L, et al. Automated damage test facilities for materials development and production optic quality assurance at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 3578, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials. 1999: 302-313. [37] Liao Z M, Spaeth M L, Manes K, et al. Predicting laser-induced bulk damage and conditioning for deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals using an absorption distribution model[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(15): 2538-2540. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.002538 [38] Peng Xiaocong, Zhao Yuan’an, Wang Yueliang, et al. Variation of the band structure in DKDP crystal excited by intense sub-picosecond laser pulses[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2018, 6: 03000e41. [39] 王岳亮. I类KDP和II类DKDP晶体激光损伤机理及激光预处理特性研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 2017: 53-66Wang Yueliang. Laser damage mechanisms and laser conditioning properties in I-type KDP and II-type DKDP crystals[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017: 53-66 -




 下载:
下载: