Energy spectrum nuclide recognition method based on long short-term memory neural network
-
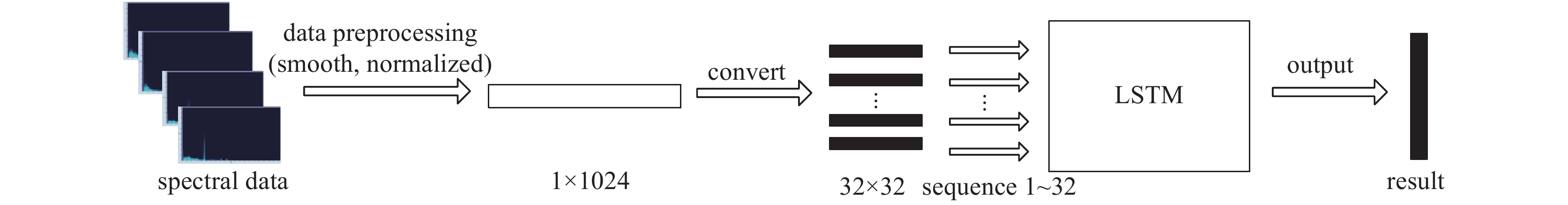
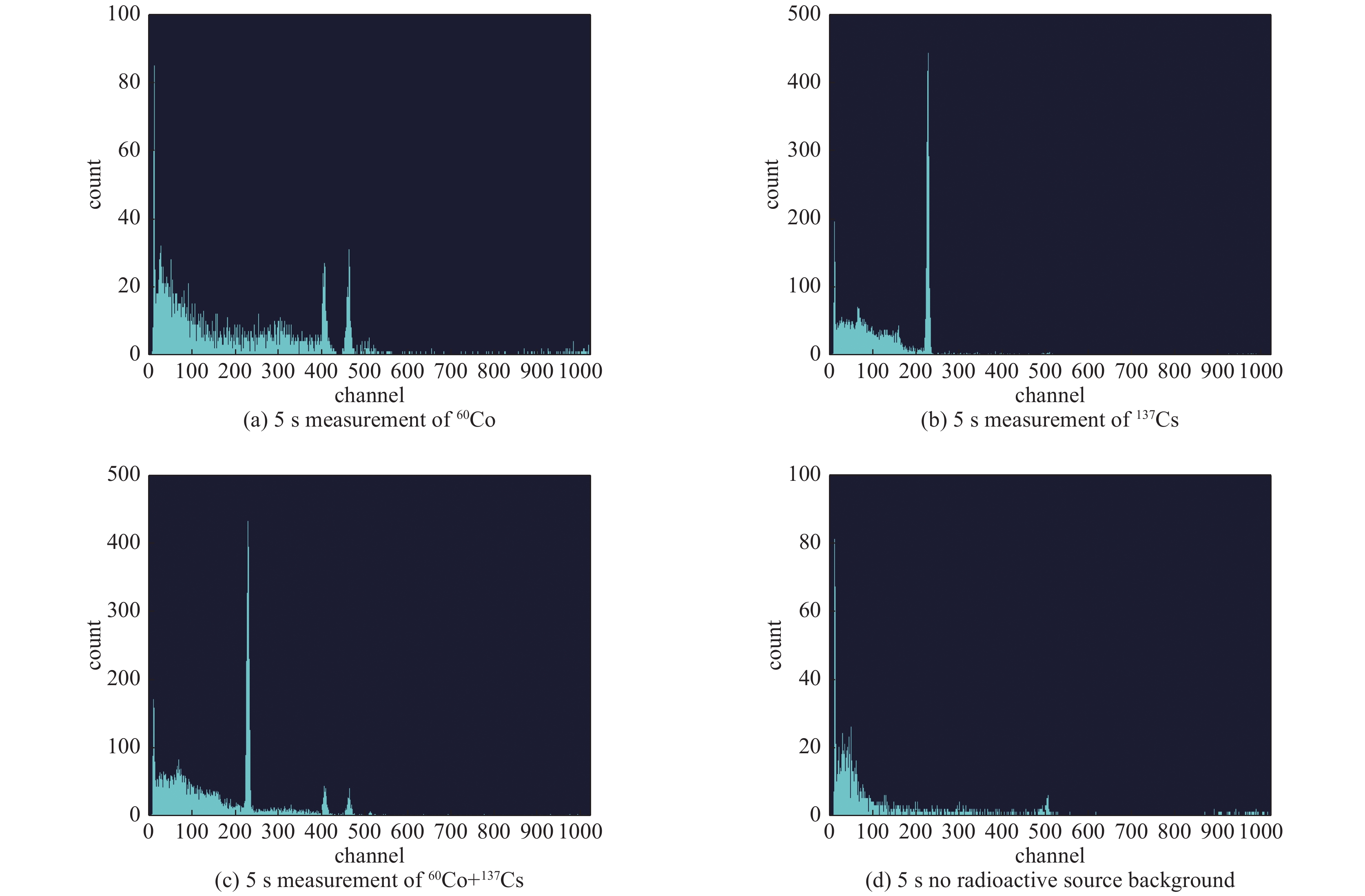
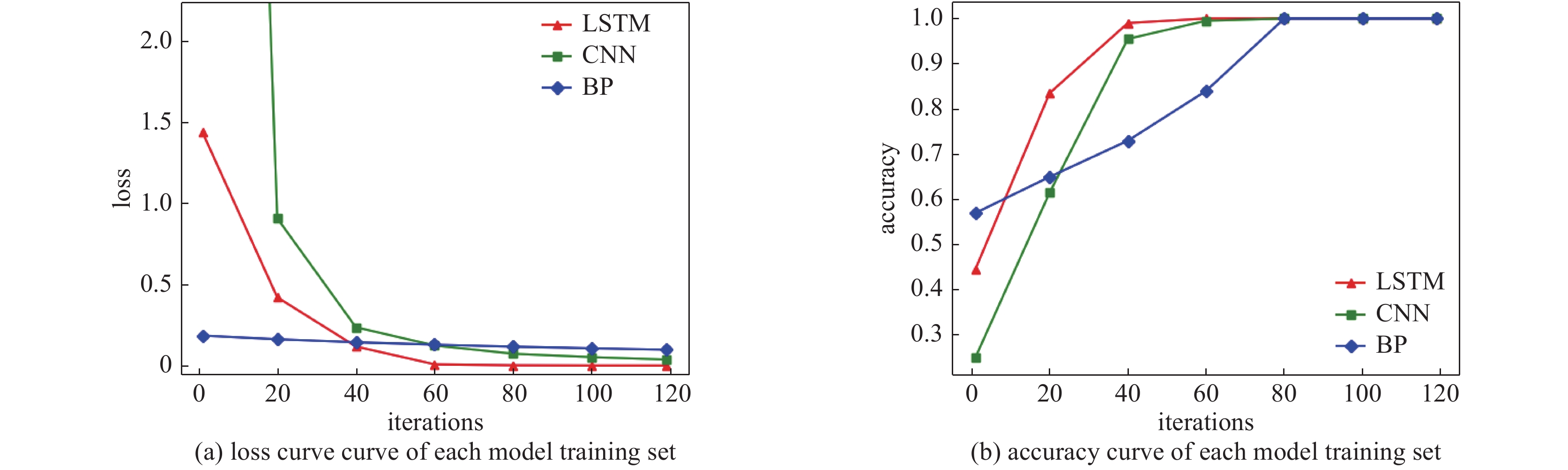
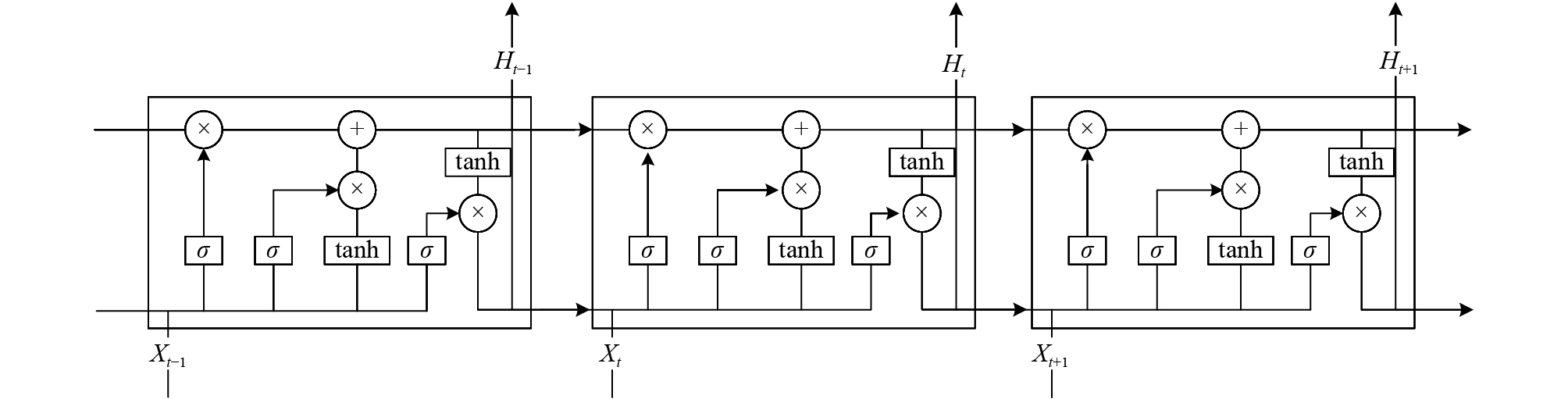
摘要: 针对新兴的能谱核素识别方法在混合放射性核素的噪声环境中存在识别速度慢、准确率较低等问题,提出了基于长短时记忆神经网络(LSTM)的能谱核素识别方法。实验使用溴化镧(LaBr3)晶体探测器,分别对环境中60Co、137Cs放射性源分组测量得到能谱数据集,首先使用数据平滑方法和归一化方法进行数据预处理,然后将能谱数据按时间序列分组以获得可用的输入序列数组,最后训练LSTM模型得到预测结果。通过基于BP神经网络和卷积神经网络(CNN)的两个能谱识别模型进行对比,得到在测试集中平均识别率分别为83.45%和86.21%,而LSTM能谱识别模型平均识别率为93.04%,实验结果表明,该能谱模型在核素识别效果中表现较好,可用于快速的能谱核素识别设备上。Abstract: Energy spectrum data analysis is the main source of nuclide identification. Aiming at the slow recognition speed and low accuracy of the emerging energy spectrum nuclide identification method in the noisy environment of mixed radionuclides, an energy spectrum nuclide recognition method based on long short-term memory neural network (LSTM) is proposed. In the experiment, a LaBr3 crystal detector was used to measure the 60Co and 137Cs radioactive sources in the environment to obtain a gamma spectrum data set. First, the experiment used data smoothing and normalization methods for data preprocessing. Then, the energy spectrum data was grouped in time series to obtain a usable input sequence array. Finally, the prediction results were obtained through the LSTM model. By comparing two energy spectrum recognition models based on BP neural network and convolutional neural network (CNN), the average recognition rates in the test set are 83.45% and 86.21% respectively, while the average recognition rate of the LSTM model is 93.04%. The experimental results show that the energy spectrum model has performed well in the nuclide identification and can be used in fast energy spectrum nuclide identification equipment.
-
Key words:
- energy spectrum data /
- long short-term memory /
- nuclide identification /
- data smoothing /
- normalization
-
表 1 LSTM最后一个时间节点的能谱预测结果
Table 1. Energy spectrum prediction results of the last time node of LSTM
sample prediction 60Co 137Cs 60Co+137Cs no radioactive source 60Co 17.25354004 −13.38463688 5.48915672 −8.59954166 137Cs −3.00819635 6.40356064 0.29465187 2.9503994 60Co+137Cs 0.48095784 2.74640751 8.61173725 −5.41806173 no radioactive source −0.71746081 −1.06083262 −3.47033572 8.91043949 表 2 相同测量时间的训练集和相同测量时间的测试集结果
Table 2. Results of the training set with the same measurement time and the test set with the same measurement time
sample measurement time/s size of training set data size of test set data average accuracy/% 5 160 40 90.15 10 160 40 92.26 20 160 40 92.66 表 3 混合测量时间的训练集和混合测量时间的测试集结果
Table 3. Results of training set and mixed measurement time test set with mixed measurement time
sample measurement time/s size of training set data size of test set data average accuracy/% 5 s,10 s and 20 s mixed 480 120 92.37 360 120 89.60 240 120 90.96 表 4 混合测量时间的训练集和连续测量时间的测试集结果
Table 4. Results of mixed measurement time training set and continuous measurement time test set
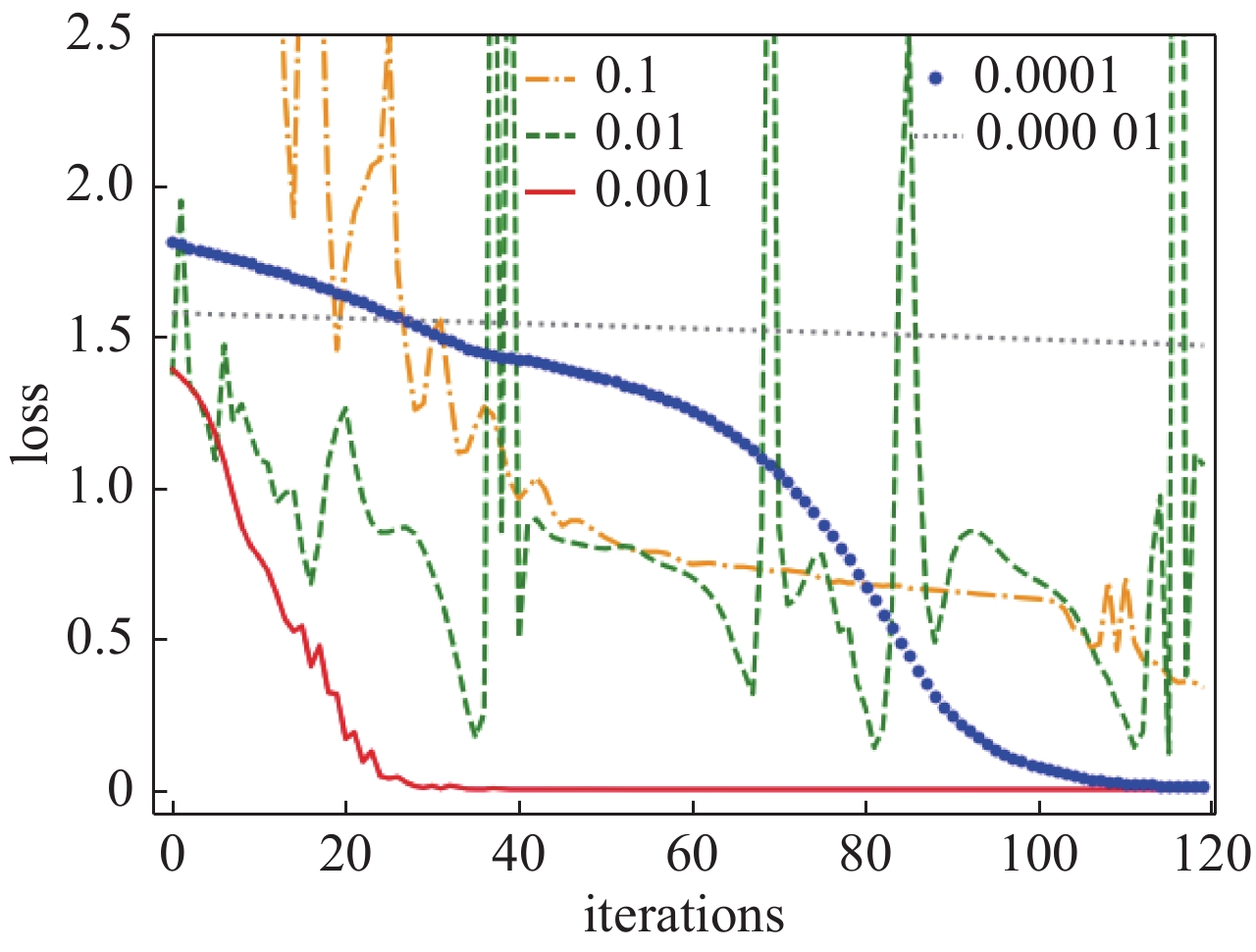
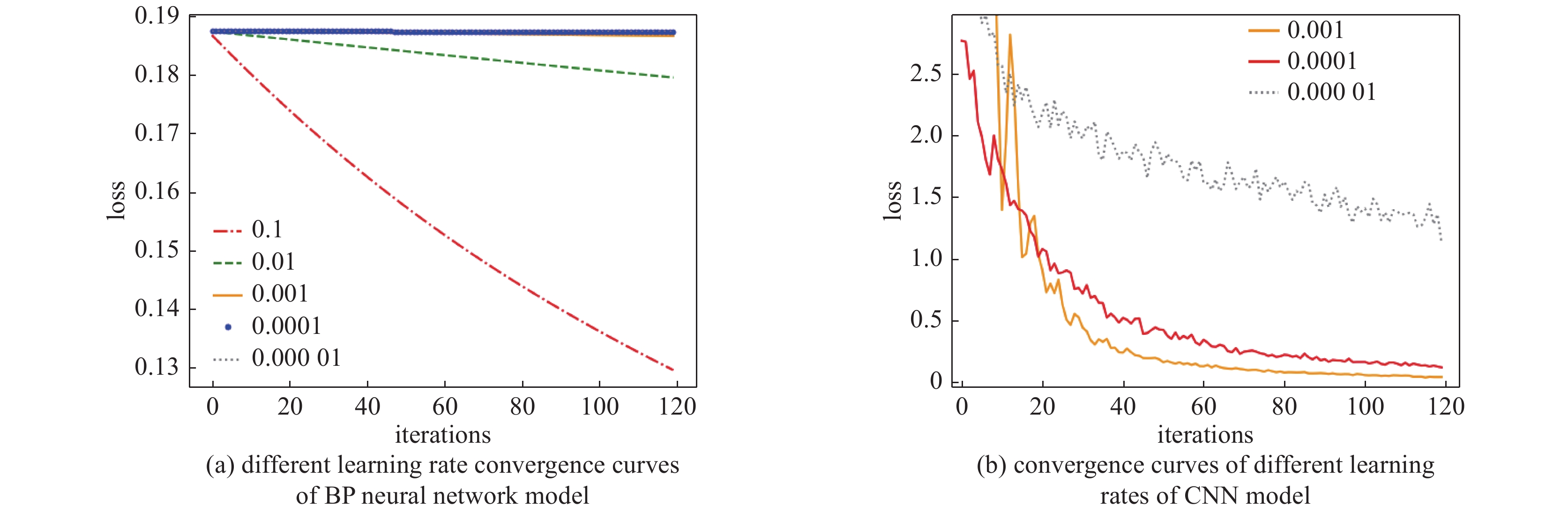
sample measurement time/s size of training set data size of test set data average accuracy/% 5 s,10 s and 20 s mixed 480 40 92.07 360 40 91.57 240 40 88.05 表 5 准确率达到100%所需训练步数和训练时长
Table 5. Training steps and training time required to achieve 100% accuracy
model name training steps training time /min BP 67 73.10 CNN 66 72.78 LSTM 40 35.26 表 6 各模型识别准确率
Table 6. Recognition accuracy of each model
model name accuracy of data set 1/% accuracy of data set 2/% accuracy of data set 3/% BP 83.74 83.59 83.04 CNN 86.05 85.83 86.73 LSTM 93.56 92.13 93.44 -
[1] Liang Chen, Yi Xiangwei. Nuclide identification algorithm based on K–L transform and neural networks[J]. Nuclear Inst and Methods in Physics Research A, 2009, 598(2): 450-453. [2] 王一鸣, 魏义祥. 基于模糊逻辑的γ能谱核素识别[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 52(12):1736-1740. (Wang Yiming, Wei Yixiang. Fuzzy logic based nuclide identification for γ ray spectra[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2012, 52(12): 1736-1740 [3] 问斯莹, 王百荣, 肖刚, 等. 基于序贯贝叶斯方法的核素识别算法研究[J]. 核电子学与探测术, 2016, 36(2):179-183. (Wen Siying, Wang Bairong, Xiao Gang, et al. The study on nuclide identification algorithm based on sequential Bayesian analysis[J]. Nuclear Electronics and Detection Technology, 2016, 36(2): 179-183 [4] 张江梅, 季海波, 冯兴华, 等. 基于稀疏表示的核素能谱特征提取及核素识别[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30:046003. (Zhang Jiangmei, Ji Haibo, Feng Xinghua, et al. Nuclide spectrum feature extraction and nuclide identification based on sparse representation[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 046003 [5] 胡浩行, 张江梅, 王坤朋, 等. 卷积神经网络在复杂核素识别中的应用[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2019, 38(10):154-156, 160. (Hu Haohang, Zhang Jiangmei, Wang Kunpeng, et al. Application of convolutional neural networks in identification of complex nuclides[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2019, 38(10): 154-156, 160 [6] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9: 1735-1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [7] Graves A, Jaitly N, Mohamed A. Hybrid speech recognition with deep bidirectional LSTM[C]//IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding. 2013. [8] Hayashi T, Watanabe S, Toda T, et al. Duration-controlled LSTM for polyphonic sound event detection[J]. IEEE ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 2017, 25(11): 2059-2070. [9] 任智慧, 徐浩煜, 封松林, 等. 基于LSTM网络的序列标注中文分词法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2017, 34(5):1321-1324, 1341. (Ren Zhihui, Xu Haoyu, Feng Songlin, et al. Sequence labeling Chinese word segmentation method based on LSTM networks[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2017, 34(5): 1321-1324, 1341 [10] Ran J. A self-attention based LSTM network for text classification[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019, 1207: 12008. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1207/1/012008 [11] 梁军, 柴玉梅, 原慧斌, 等. 基于极性转移和LSTM递归网络的情感分析[J]. 中文信息学报, 2015, 29(5):152-159. (Liang Jun, Chai Yumei, Yuan Huibin, et al. Polarity shifting and LSTM based recursive networks for sentiment analysis[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2015, 29(5): 152-159 [12] 季学武, 费聪, 何祥坤, 等. 基于LSTM网络的驾驶意图识别及车辆轨迹预测[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(6):34-42. (Ji Xuewu, Fei Cong, He Xiangkun, et al. Intention recognition and trajectory prediction for vehicles using LSTM network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(6): 34-42 [13] 祝强, 李少康, 徐臻. LM算法求解大残差非线性最小二乘问题研究[J]. 中国测试, 2016, 42(3):12-16. (Zhu Qiang, Li Shaokang, Xu Zhen. Study of solving nonlinear least squares under large residual based on Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm[J]. China Measurement and Test, 2016, 42(3): 12-16 [14] 高伟伟, 王广龙, 陈建辉, 等. 多尺度变步长最小均方自适应算法在光纤陀螺数据处理中的应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:071002. (Gao Weiwei, Wang Guanglong, Cheng Jianhui, et al. Application of multiple-scale variable step least mean square adaptive algorithm to fiber optic gyroscope data processing[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 071002 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142607.71002 [15] Li Q, Huang Y, Song X, et al. Moving window smoothing on the ensemble of competitive adaptive reweighted sampling algorithm[J]. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular And Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2019, 214: 129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.02.023 [16] Bolstad B M, Irizarry R A, Astrand M, et al. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias[J]. Bioinformatics, 2003, 19(2): 185-193. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/19.2.185 -




 下载:
下载: