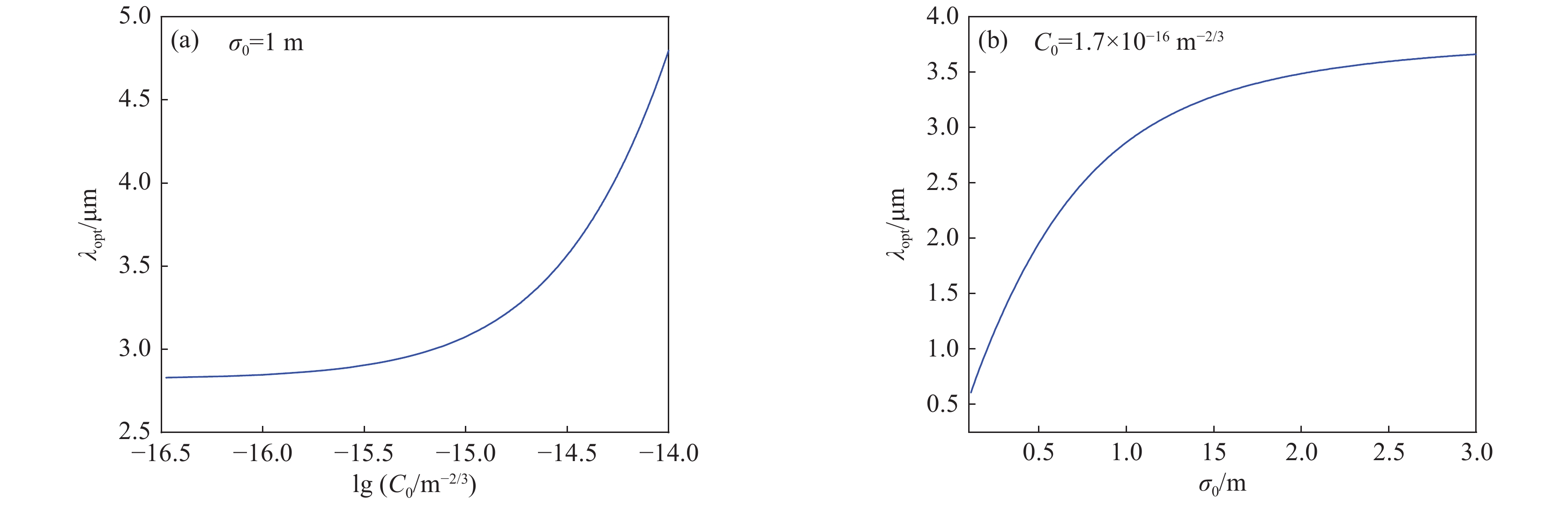
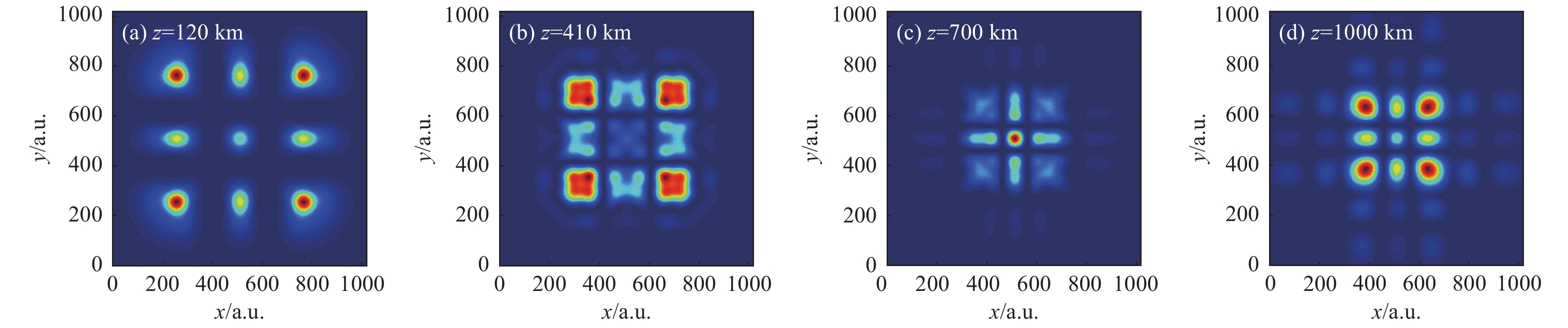
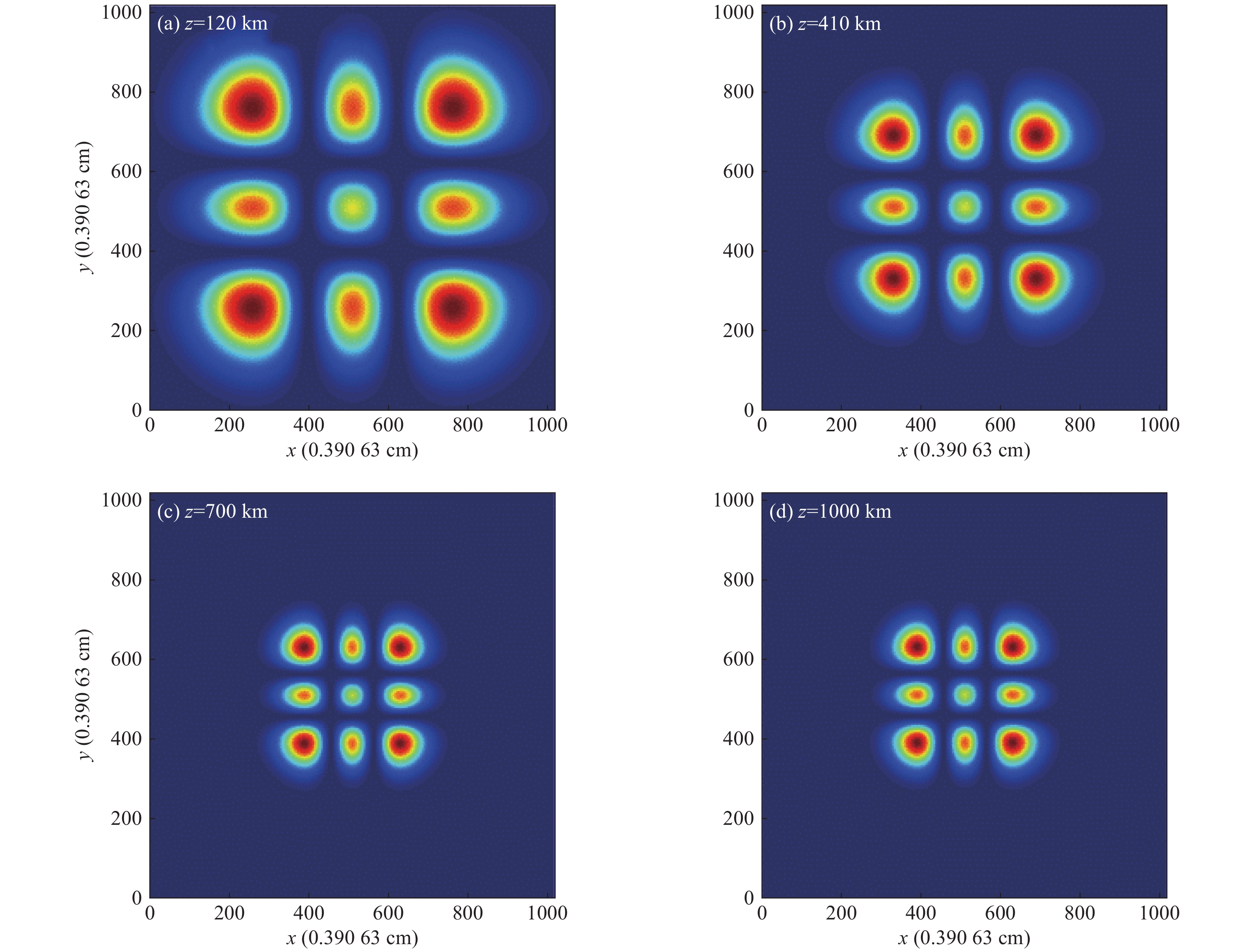
Research progress on self-focusing effect of high-power laser beams propagating in inhomogeneous atmosphere
-
摘要:
地基激光空间碎片清除和利用激光辐射把转换的太阳能从空间轨道输运到地面等应用中,不可避免地遇到高功率激光在非均匀大气中的传输问题。由于激光功率已远远超过大气非线性自聚焦临界功率,大气自聚焦效应是影响光束质量的一个重要物理因素。概述了近年来国内外高功率激光在非均匀大气中上行或下行传输的自聚焦效应研究进展,主要介绍了高功率激光在非均匀大气中的传输模型、理论基础、数值和解析研究方法,着重介绍了自聚焦效应对激光传输特性和光束质量的影响,并总结了优化靶面光束质量的方案。此外,还介绍了大气群速度色散效应和大气湍流效应等物理因素对激光光束质量的影响。最后,还提出了该领域值得进一步深入研究的一些问题。
Abstract:The problem of high-power laser beams propagating through the atmosphere will be encountered in applications, such as the ground-based laser space-debris cleaning, and transportation of the laser radiation produced by solar power from space orbits to the ground. In such applications, the laser power is well above the critical power for self-focusing in air. Therefore, it is important to study the self-focusing effect of high-power laser beams propagating through the inhomogeneous atmosphere. This paper reviews the research progress on self-focusing effect of high-power laser beams propagating upwards or downwards in the inhomogeneous atmosphere. The laser beam propagation model, the theoretical model, and the numerical and analytical methods are introduced. The influence of the self-focusing on the beam propagation characteristics and the beam quality is introduced, and the methods of optimizing the beam quality on the target are summarized. Furthermore, the effects of group-velocity dispersion and atmospheric turbulence on the beam quality are also introduced. Finally, some interesting questions for further research are put forward.
-
-
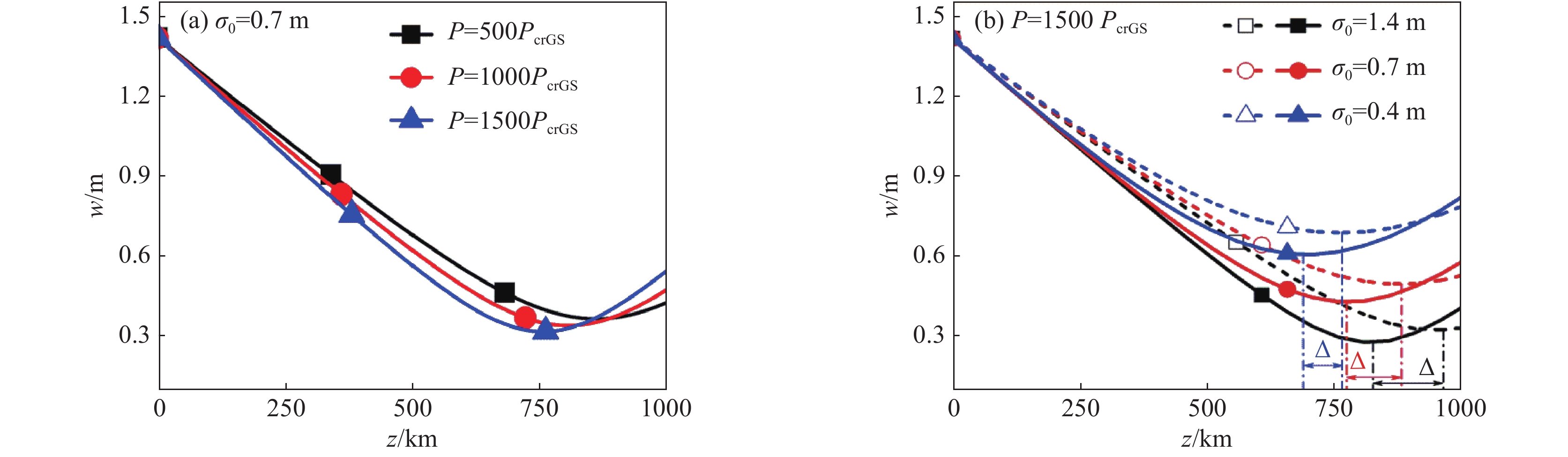
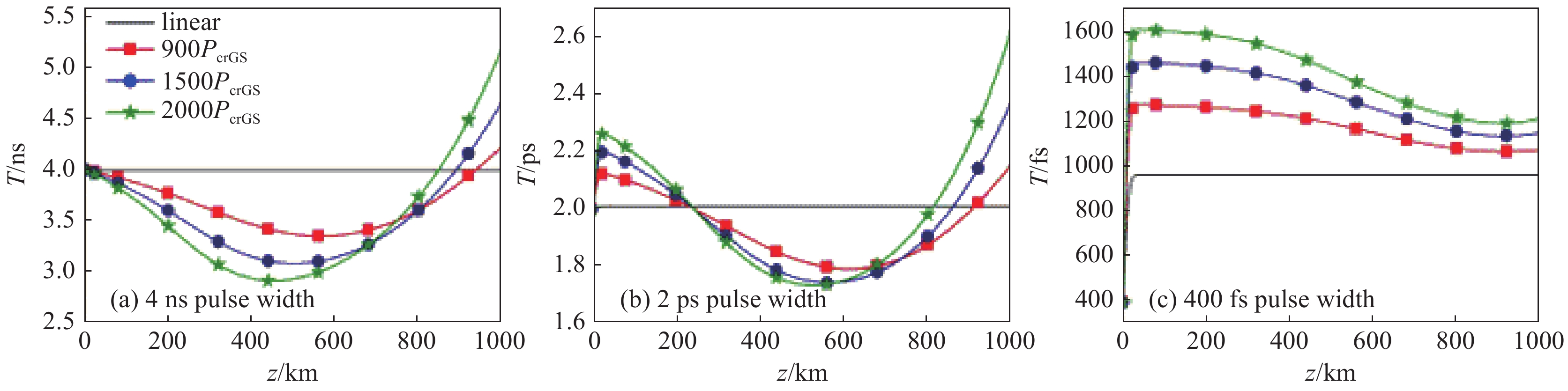
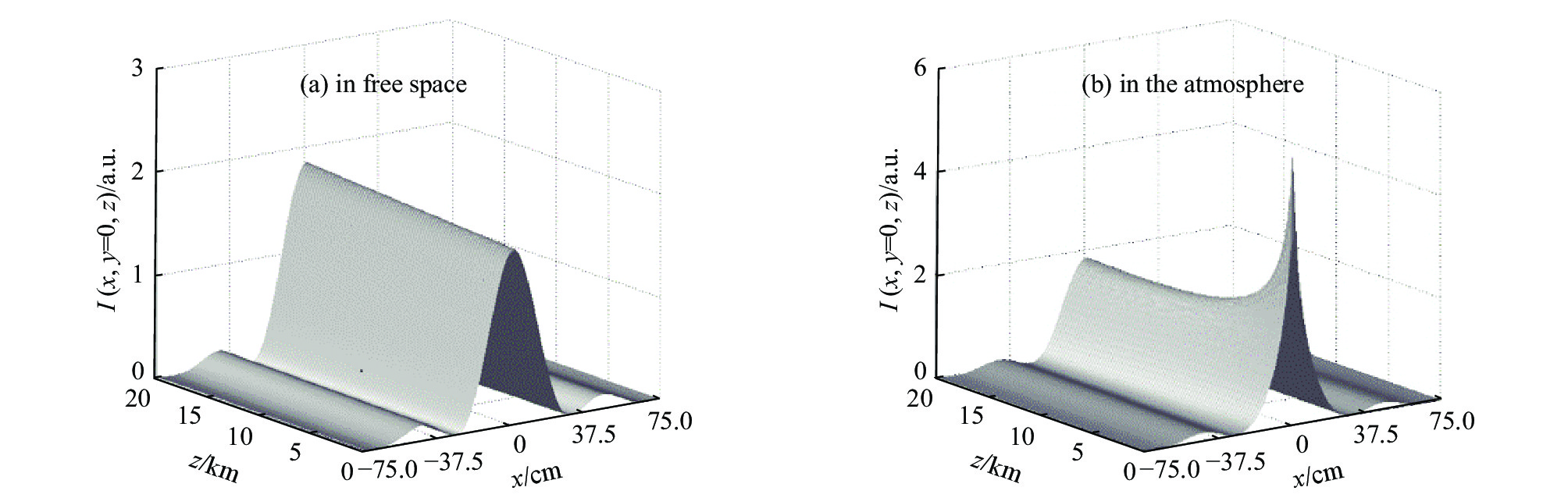
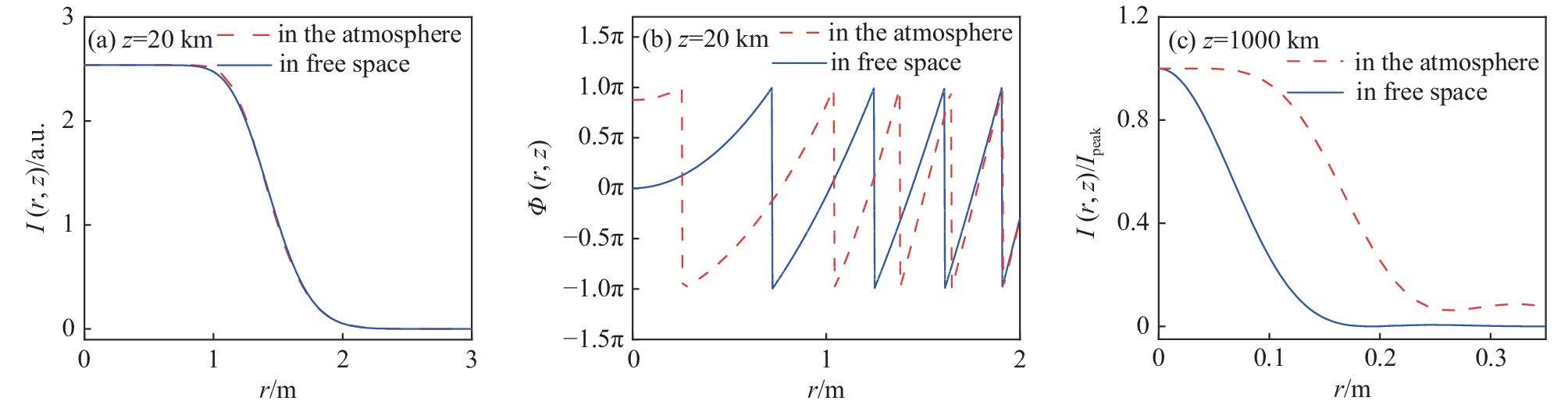
[1] Klinkrad K. Space debris–models and risk analysis[M]. Chichester: Praxis Publishing, 2006. [2] Campbell J W. Project Orion: Orbital debris removal using ground-based sensors and lasers[R]. NASA Technical Memorandum 108522, 1996. [3] Early J T, Bibeau C, Phipps C. Space debris de-orbiting by vaporization impulse using short pulse laser[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2004, 702(1): 190-204. [4] Rubenchik A M, Barty C P J, Beach R J, et al. Laser systems for orbital debris removal[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2010, 1278(1): 347-353. [5] Phipps C R, Baker K L, Libby S B, et al. Removing orbital debris with lasers[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2012, 49(9): 1283-1300. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2012.02.003 [6] Phipps C R. Laser ablation propulsion and its applications in space[M]//Ossi P M. Advances in the Application of Lasers in Materials Science. Cham: Springer, 2018: 217-246. [7] Esmiller B, Jacquelard C, Eckel H A, et al. Space debris removal by ground-based lasers: main conclusions of the European project CLEANSPACE[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(31): I45-I54. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.000I45 [8] Lorbeer R A, Zwilich M, Zabic M, et al. Experimental verification of high energy laser-generated impulse for remote laser control of space debris[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 8453. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26336-1 [9] Phipps C R, Albrecht G, Friedman H, et al. ORION: Clearing near-Earth space debris using a 20-kW, 530-nm, Earth-based, repetitively pulsed laser[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 1996, 14(1): 1-44. doi: 10.1017/S0263034600009733 [10] Phipps C R Jr, Turner T P, Harrison R F, et al. Impulse coupling to targets in vacuum by KrF, HF, and CO2 single-pulse lasers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1988, 64(3): 1083-1096. doi: 10.1063/1.341867 [11] 张品亮, 龚自正, 杨武霖, 等. 激光移除空间碎片过程的三维仿真与建模[J]. 宇航学报, 2017, 38(3):323-330. (Zhang Pinliang, Gong Zizheng, Yang Wulin, et al. Three-dimensional simulation and modeling on removing orbital debris with lasers[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2017, 38(3): 323-330 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.03.014 [12] 洪延姬, 金星, 王广宇, 等. 激光清除空间碎片方法[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013.Hong Yanji, Jin Xing, Wang Guangyu, et al. Laser space-debris cleaning method[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013 [13] 温泉, 马赛, 杨丽薇, 等. 湍流作用下地基激光清除空间碎片的影响规律[J]. 激光与红外, 2017, 47(3):277-283. (Wen Quan, Ma Sai, Yang Liwei, et al. Research on influence law of space debris removed by ground-based laser under atmospheric turbulence[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2017, 47(3): 277-283 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2017.03.004 [14] 朱文越, 钱仙妹, 饶瑞中, 等. 高能激光大气传输性能评估技术[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48:1203002. (Zhu Wenyue, Qian Xianmei, Rao Ruizhong, et al. Evaluation technology of high energy laser atmospheric propagation performance[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48: 1203002 doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.1203002 [15] 饶瑞中. 现代大气光学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.Rao Ruizhong. Modern atmospheric optics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012 [16] 王英俭, 范承玉, 魏合理. 激光在大气和海水中传输及应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2015.Wang Yingjian, Fan Chengyu, Wei Heli. Laser beam propagation and applications through the atmosphere and sea water[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2015 [17] Andrews L C, Phillips R L. Laser beam propagation through random media[M]. 2nd ed. Bellingham: SPIE Optical Engineering Press, 2005. [18] 魏平, 李新阳, 罗曦, 等. 部分子孔径缺光对夏克-哈特曼波前传感器波前复原的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47:0409002. (Wei Ping, Li Xinyang, Luo Xi, et al. Influence of lack of light in partial subapertures on wavefront reconstruction for Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47: 0409002 doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0409002 [19] Rubenchik A M, Fedoruk M P, Turitsyn S K. The effect of self-focusing on laser space-debris cleaning[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3: e159. [20] Vaseva I A, Fedoruk M P, Rubenchik A M, et al. Light self-focusing in the atmosphere: thin window model[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 30697. doi: 10.1038/srep30697 [21] Zhang Yuqiu, Ji Xiaoling, Zhang Hao, et al. Self-focusing and group-velocity dispersion of pulsed laser beams in the inhomogeneous atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(11): 14617-14625. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.014617 [22] Deng Yu, Ji Xiaoling, Yu Hong, et al. Uniform irradiation generated by beam self-focusing in the inhomogeneous atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(10): 14585-14593. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.014585 [23] Wang Huan, Ji Xiaoling, Deng Yu, et al. Effect of spatial coherence on laser space-debris removal in the inhomogeneous atmosphere[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2019, 235: 244-249. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2019.07.009 [24] Fan Xiaoli, Ji Xiaoling, Wang Huan, et al. Self-focusing effect on the beam quality of Hermite-Gaussian beams propagating upwards through the inhomogeneous atmosphere[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2021, 38(2): 168-173. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.412506 [25] Deng Yu, Wang Huan, Ji Xiaoling, et al. Characteristics of high-power partially coherent laser beams propagating upwards in the turbulent atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(19): 27927-27939. doi: 10.1364/OE.399401 [26] Rubenchik A M, Fedoruk M P, Turitsyn S K. Laser beam self-focusing in the atmosphere[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102: 233902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.233902 [27] Miller R I, Roberts T G. Laser self-focusing in the atmosphere[J]. Applied Optics, 1987, 26(21): 4570-4575. doi: 10.1364/AO.26.004570 [28] Talanov V I. Self focusing of wave beams in nonlinear media[J]. ZhETF Pisma Redaktsiiu, 1965, 2: 218. [29] Kelley P L. Self-focusing of optical beams[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1965, 15(26): 1005-1008. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.15.1005 [30] Chiao R Y, Garmire E, Townes C H. Self-trapping of optical beams[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1964, 13(15): 479-482. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.13.479 [31] Deng Hanling, Ji Xiaoling, Li Xiaoqing, et al. Effect of spherical aberration on laser beam self-focusing in the atmosphere[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(16): 3881-3884. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.003881 [32] Deng Hanling, Ji Xiaoling, Li Xiaoqing, et al. Effect of spatial coherence on laser beam self-focusing from orbit to the ground in the atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(13): 14429-14437. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.014429 [33] Zhang Yuqiu, Ji Xiaoling, Li Xiaoqing, et al. Self-focusing effect of annular beams propagating in the atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(18): 21329-21341. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.021329 [34] Chekalin S V, Kandidov V P. From self-focusing light beams to femtosecond laser pulse filamentation[J]. Physics-Uspekhi, 2013, 56(2): 123-140. doi: 10.3367/UFNe.0183.201302b.0133 [35] Rothenberg J E. Pulse splitting during self-focusing in normally dispersive media[J]. Optics Letters, 1992, 17(8): 583-585. doi: 10.1364/OL.17.000583 [36] Stassinakis A N, Nistazakis H E, Peppas K P, et al. Improving the availability of terrestrial FSO links over log normal atmospheric turbulence channels using dispersive chirped Gaussian pulses[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2013, 54: 329-334. [37] Agrawal G P. Nonlinear fiber optics[M]//Christiansen P L, Sørensen M P, Scott A C. Nonlinear Science at the Dawn of the 21st Century. Berlin: Springer, 2000: 195-211. [38] Taha T R, Ablowitz M I. Analytical and numerical aspects of certain nonlinear evolution equations. III. Numerical, Korteweg-de Vries equation[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1984, 55(2): 231-253. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(84)90004-4 [39] Wang Huan, Ji Xiaoling, Zhang Hao, et al. Propagation formulae and characteristics of partially coherent laser beams in nonlinear media[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(4): 743-746. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.000743 [40] Fan Xiaoli, Ji Xiaoling, Yu Hong, et al. Kerr effect on propagation characteristics of Hermite-Gaussian beams[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(16): 23112-23123. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.023112 [41] Couairon A, Mysyrowicz A. Femtosecond filamentation in transparent media[J]. Physics Reports, 2007, 441(2/4): 47-189. [42] Dickey F M. Laser beam shaping: theory and techniques[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014. [43] Dickey F M, Holswade S C, Shealy D L. Laser beam shaping applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2006. [44] Shealy D L. Historical perspective of laser beam shaping[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 4770, Laser Beam Shaping III. 2002: 28-47. [45] Pfalzner S. An introduction to inertial confinement fusion[M]. New York: CRC Press, 2006. [46] ITU-R. On propagation data and prediction methods required for the design of space-to-earth and earth-to-space optical communication systems[R]. Document 3J/31-E, 2001. [47] Ribak E N. Laser guide star projection for large telescopes[C]//Proceedings of SPIE, Advances in Adaptive Optics II. 2006: 62724E. [48] Holzlöhner R, Rochester S M, Calia D B, et al. Optimization of CW sodium laser guide star efficiency[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2010, 510: A20. [49] 鲁燕华, 黄园芳, 张雷, 等. 钠导星激光器研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2011, 48:071406. (Lu Yanhua, Huang Yuanfang, Zhang Lei, et al. Research progress of sodium guide star lasers[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2011, 48: 071406 -




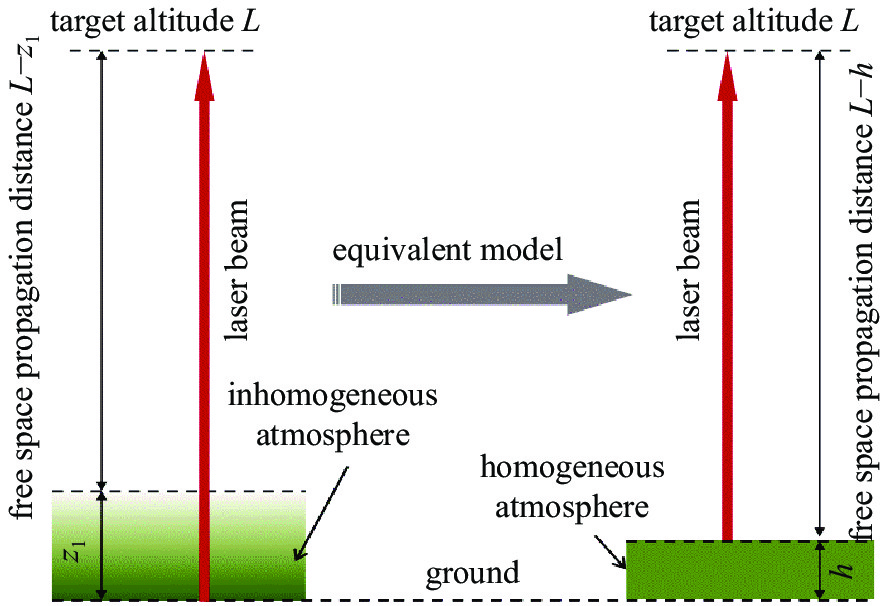
 下载:
下载: