Modal analysis and mid-spatial-frequency errors suppression of 6-DOF bonnet polishing robot
-
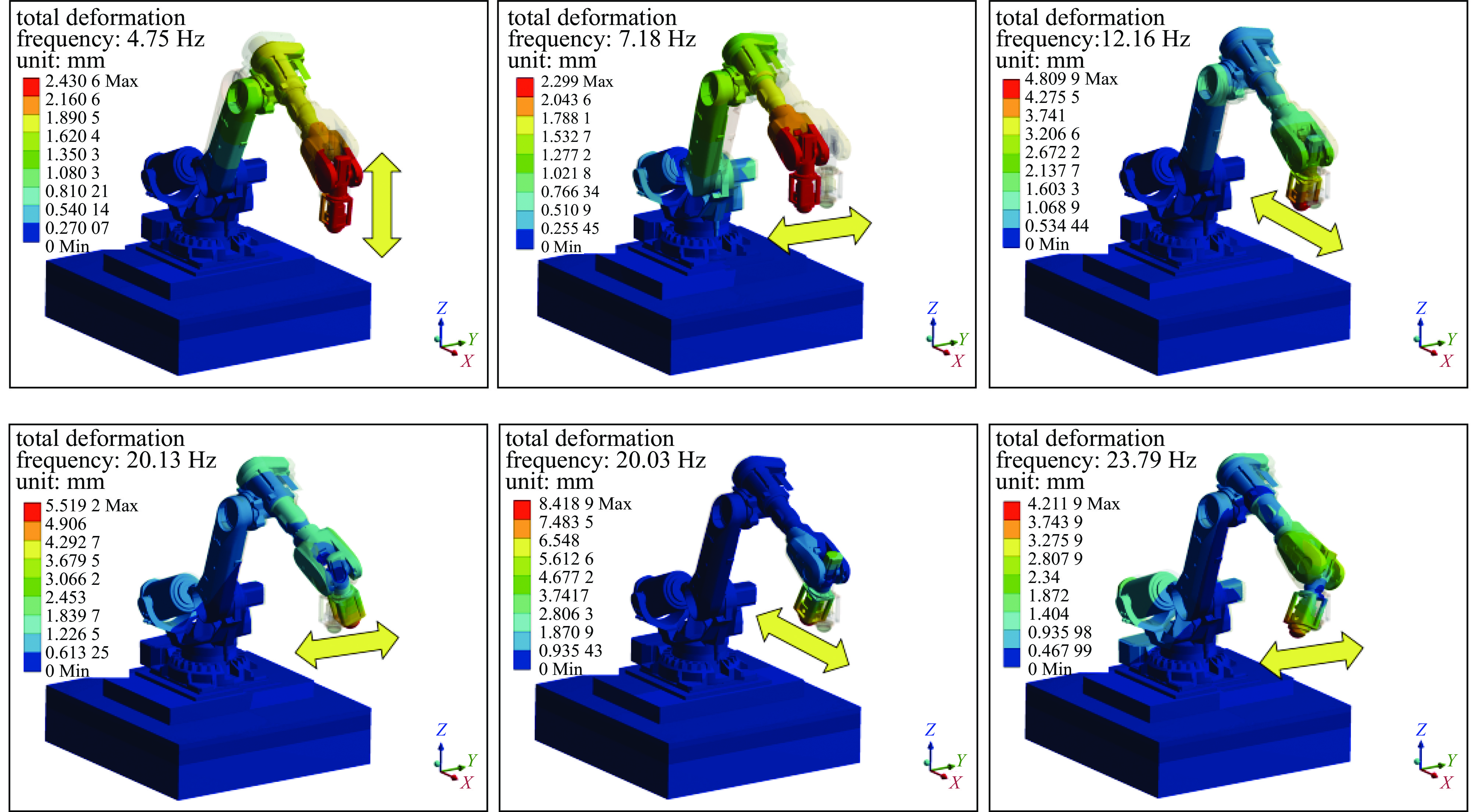
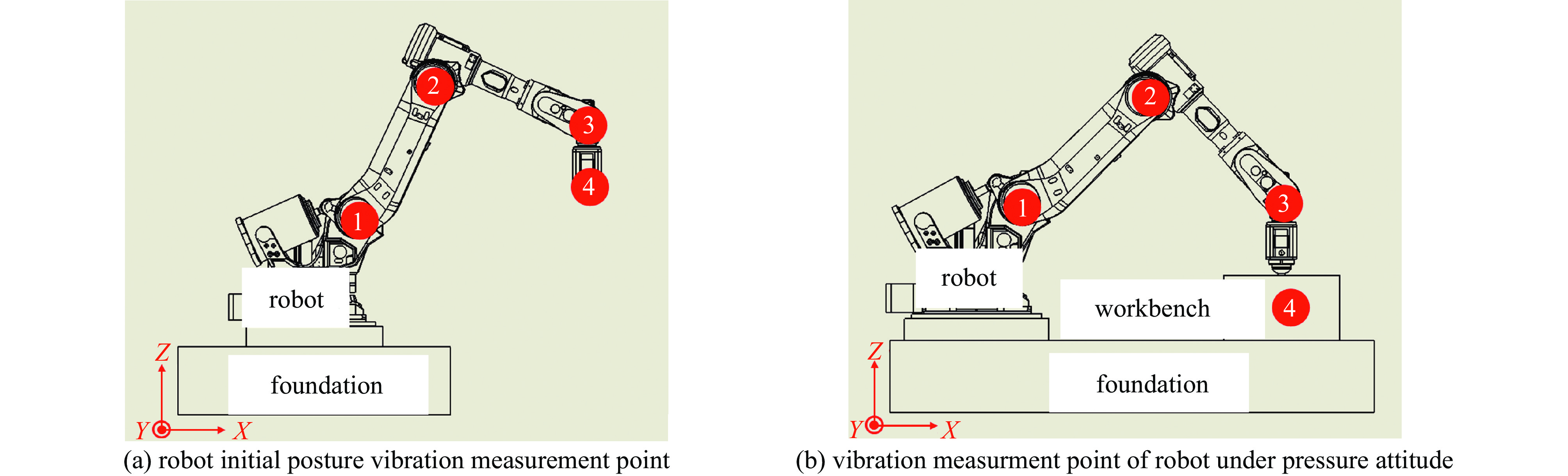
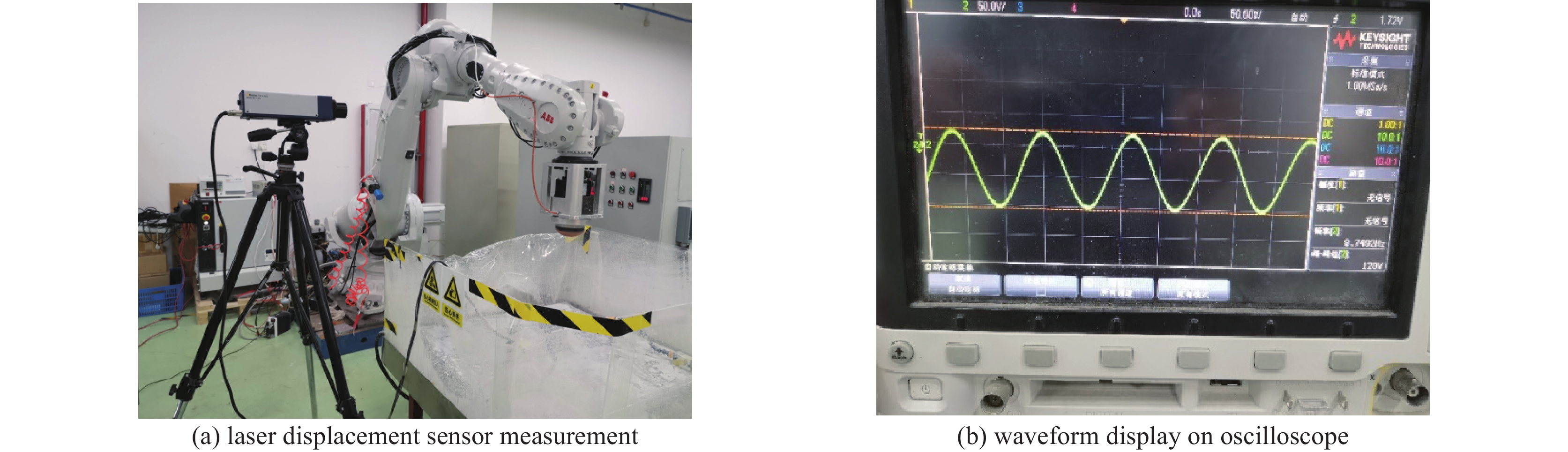
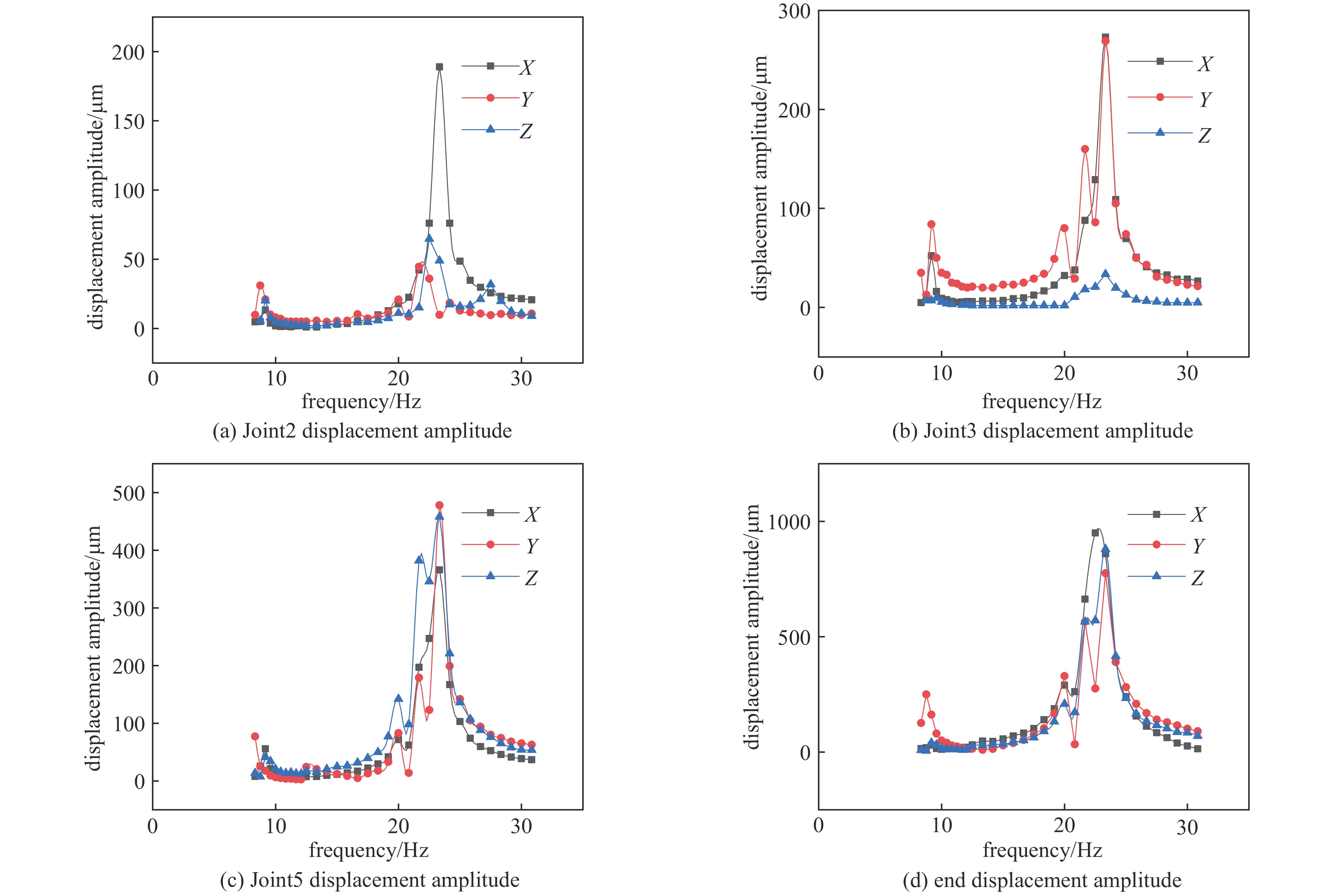
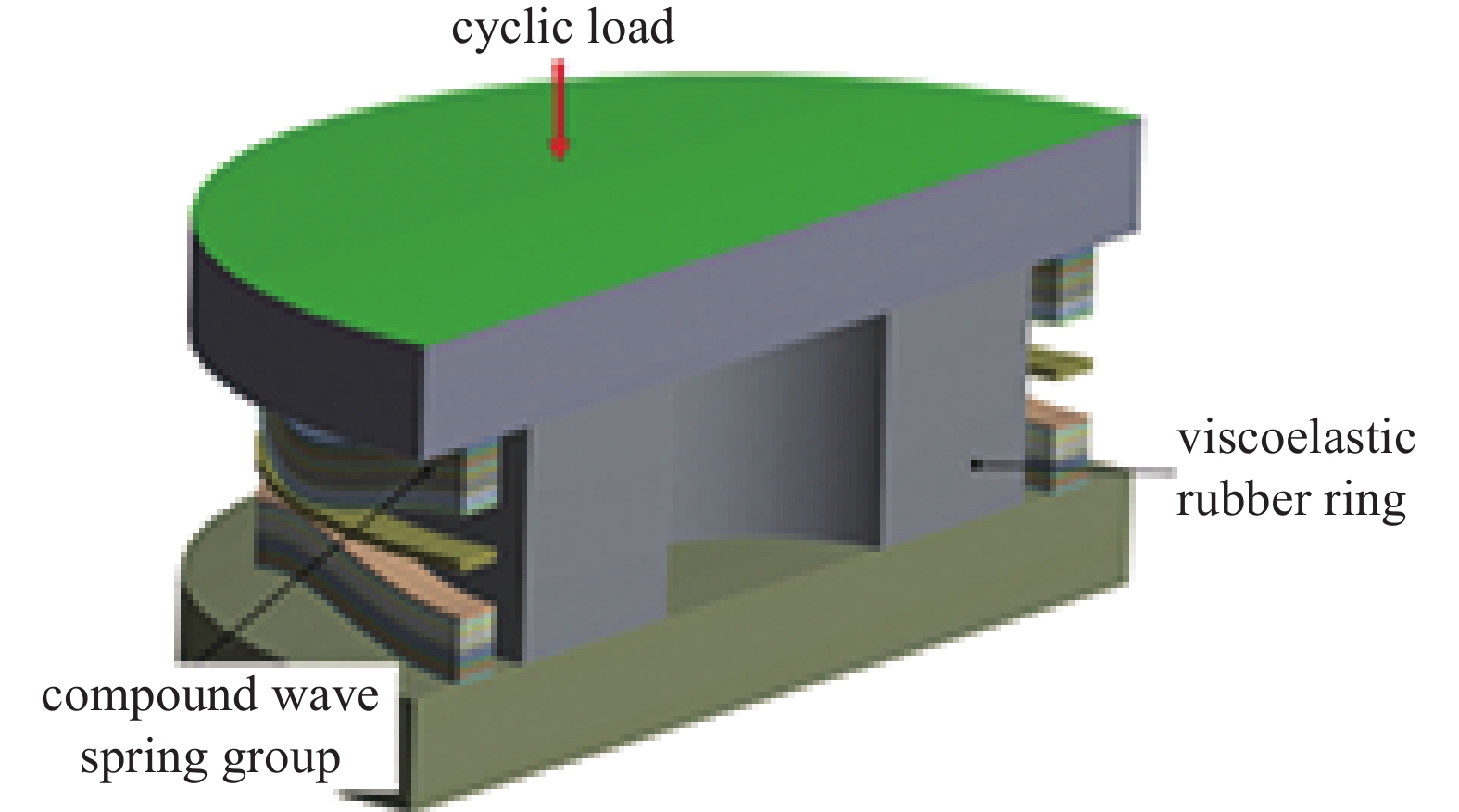
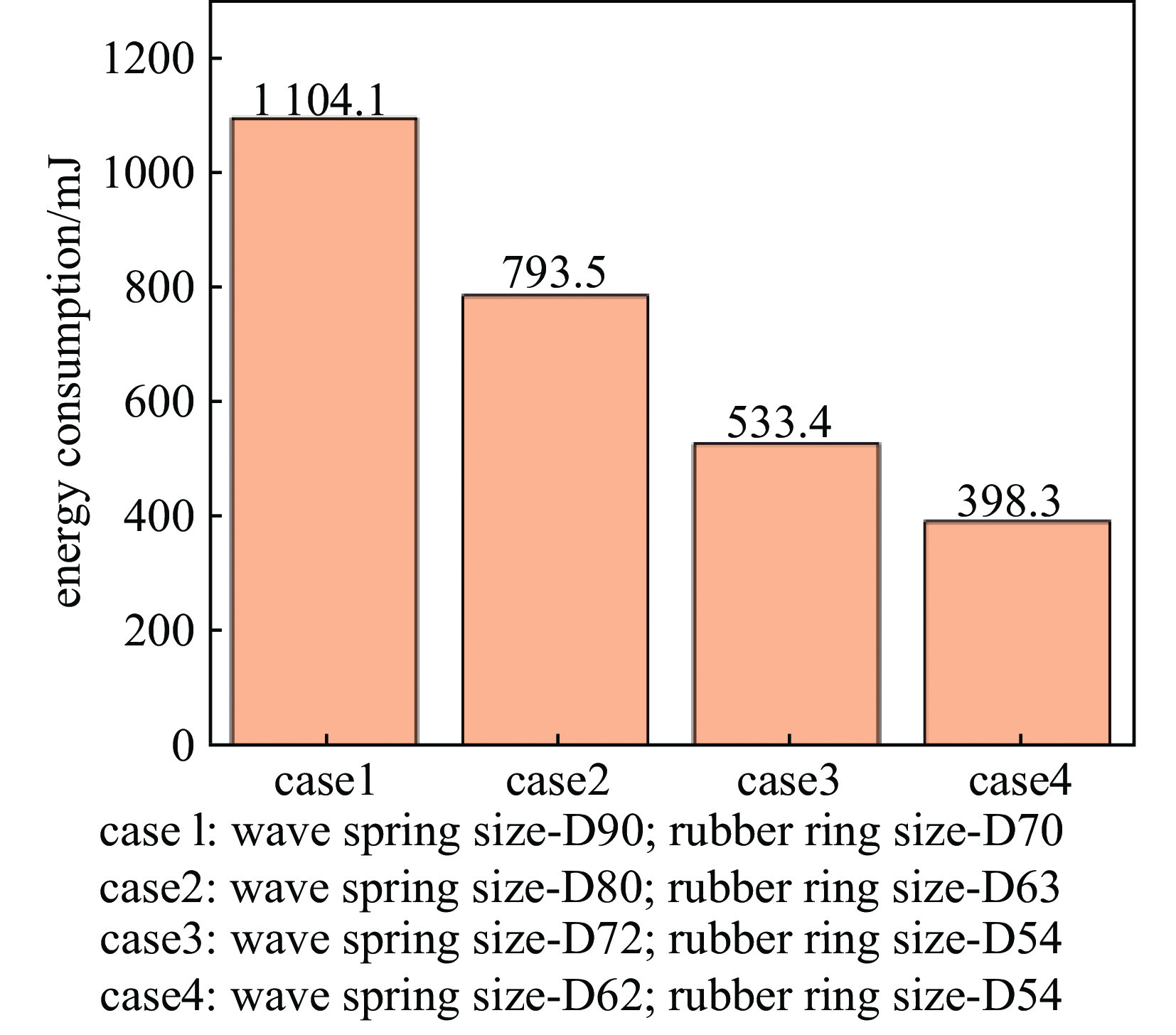
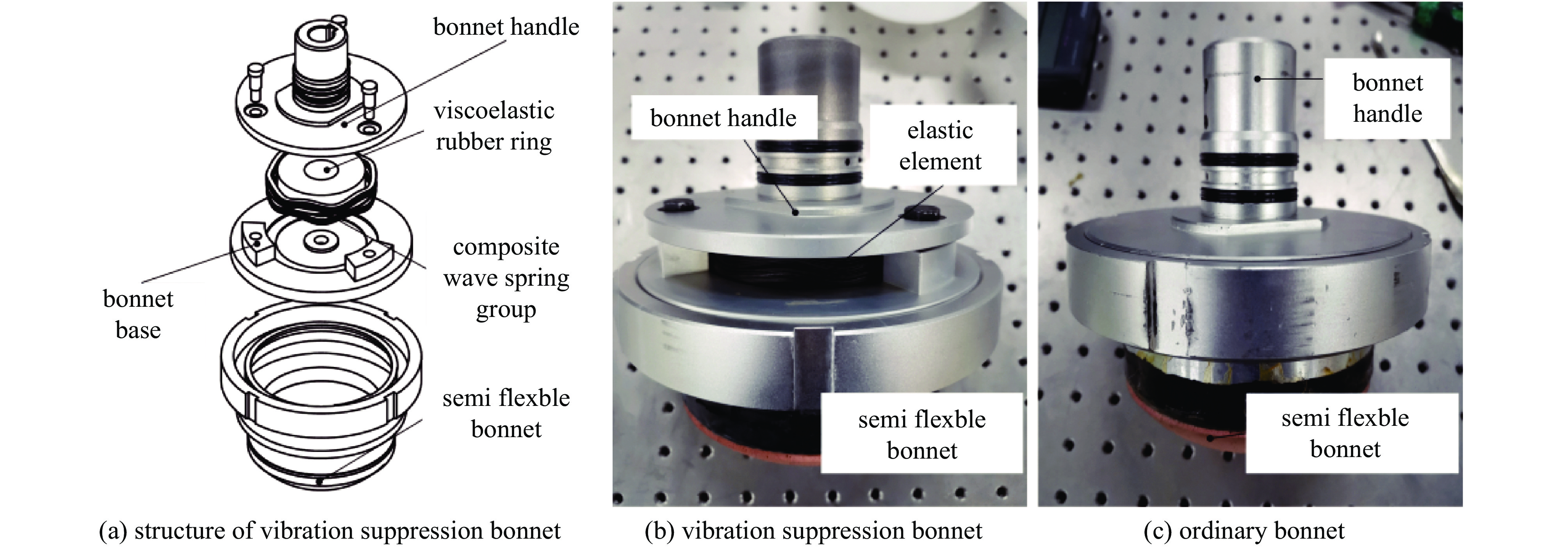
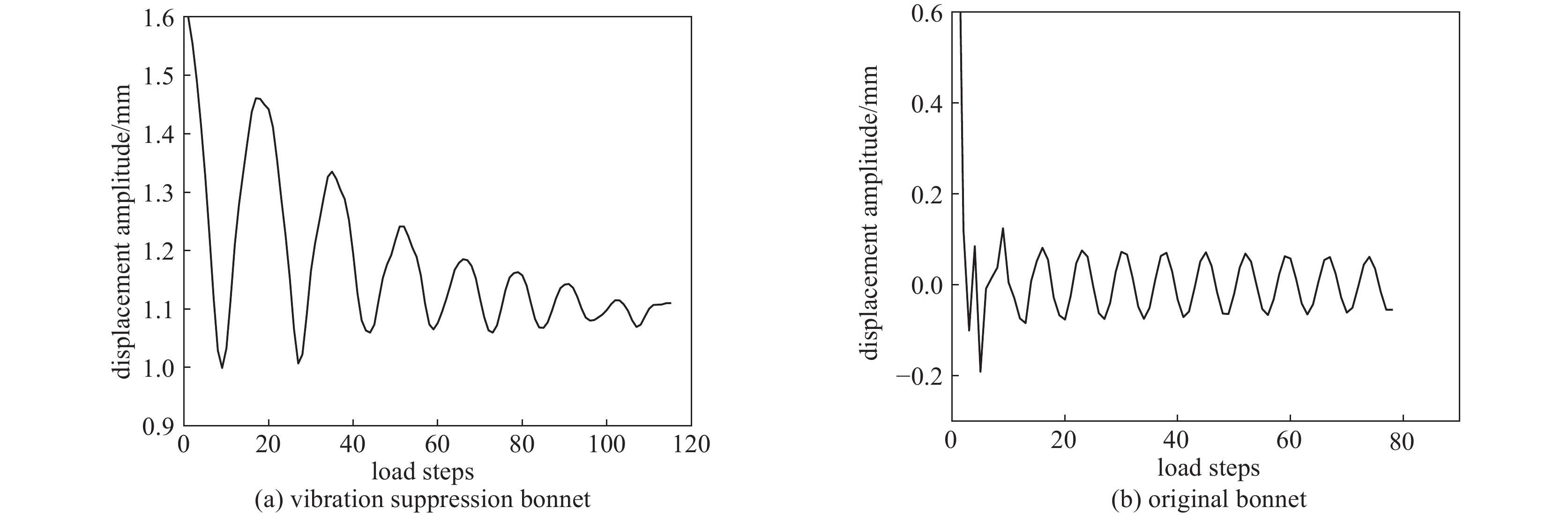
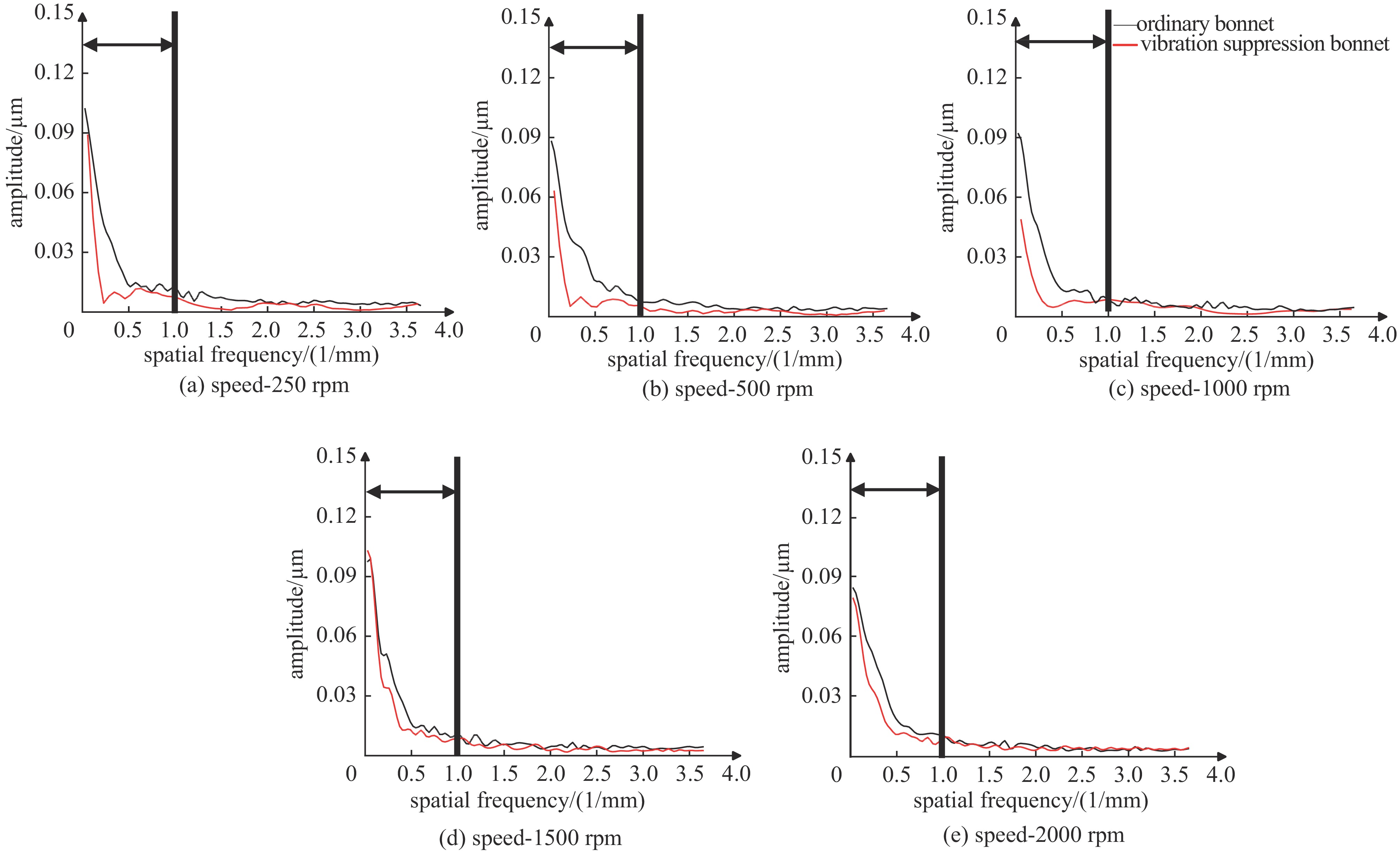
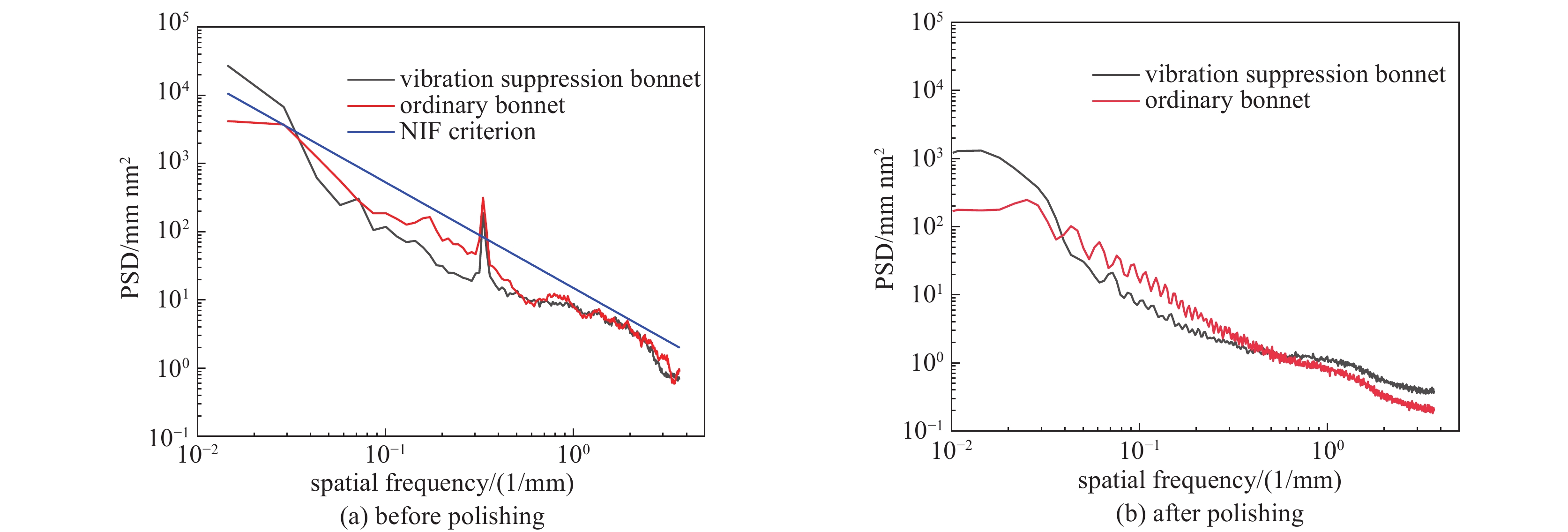
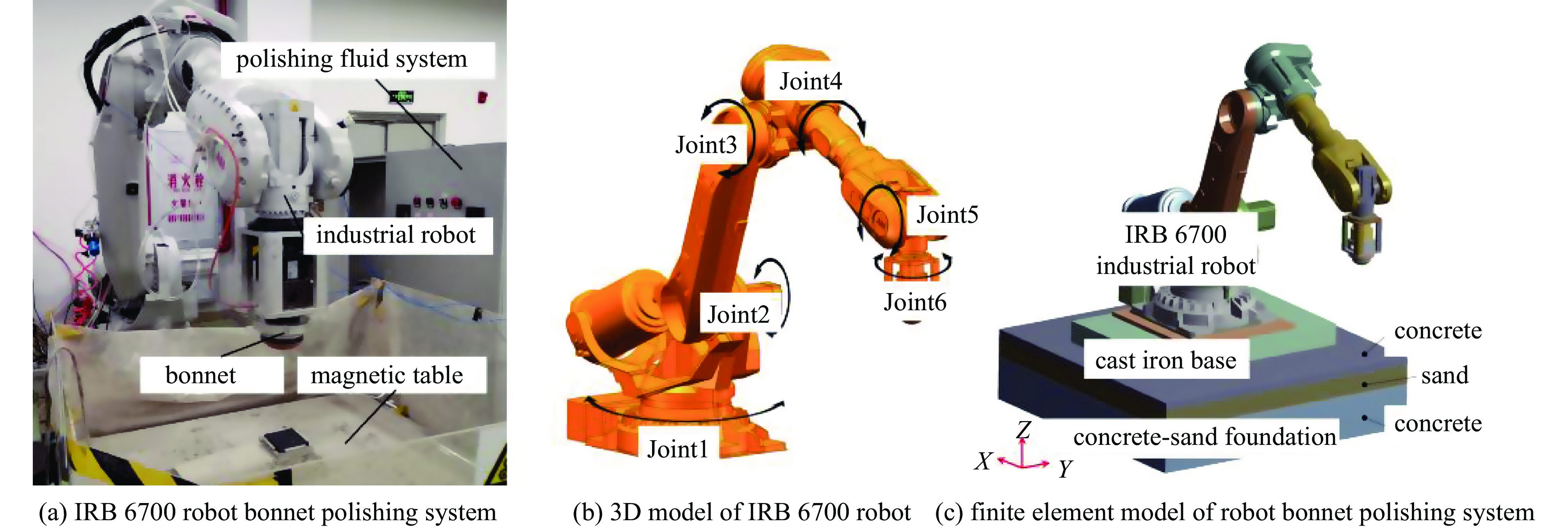
摘要: 针对六自由度串联式关节机器人气囊抛光系统因刚度不足引起的加工振动以及引入中频误差的问题,以IRB 6700机器人作为研究对象,基于Ansys Workbench建立模态分析模型,并结合实验分析机器人气囊抛光系统工况频带内动态特性,实验与仿真结果共同表明,机器人气囊抛光系统在工况频带至少存在5阶模态,且共振时机器人末端抖动幅值为mm级,机器人加工严重受限。同时针对机器人气囊抛光系统先进光学元件抛光工艺应用,设计一种阻尼抑振气囊工具头,与普通气囊工具头进行定点抛光与整面抛光对比实验。结果表明:抑振气囊头定点抛光斑粗糙度与频谱幅值普遍低于普通气囊工具头,引入的中频误差较一般气囊工具头低40%,抛光优化效果显著。Abstract: Aiming at the insufficient stiffness of the bonnet polishing system of the six-degree-of-freedom tandem joint robot, which may cause vibration and further mid-spatial-frequency errors, used we the IRB 6700 robot as the research object, established the modal analysis model based on Ansys Workbench and combined experiment to analyze the dynamic characteristics of the robot bonnet polishing system in the working condition frequency range. The experimental and simulation results together show that the robot bonnet polishing system has at least 5 modes in the working condition frequency range, and the jitter amplitude at the end of the robot is millimeter-level when the resonance occurs. Robot processing is severely restricted. In addition, for the application of advanced optical component polishing technology in the robotic bonnet polishing system, a vibration suppression bonnet tool was designed, and the fixed-point polishing and whole-surface polishing comparison experiments were carried out with the ordinary bonnet tool. The results show that the RMS and spectral amplitude of the fixed-point polishing spot of the vibration suppression bonnet are generally lower than that of the ordinary bonnet, and the introduced mid-spatial-frequency errors PSD is 40% lower than that of general bonnet polishing.
-
表 1 气囊抛光系统参数
Table 1. Bonnet polishing system parameters
scope of work/m carrying capacity/kg repeatability/mm repeat path accuracy/mm total mass/kg 2.6 200 0.05 0.10 1170 表 2 仿真材料参数
Table 2. Simulation material parameters
material density/(kg/m3) Young’s modulus/MPa Poisson’s ratio gray cast iron 7200 1.1×1011 0.28 aluminum alloy 2770 7.1×1010 0.33 concrete 2300 3×1010 0.18 sand 2000 1×108 0.25 60Si2MnA 7740 2.06×1011 0.29 表 3 IRB 6700关节刚度
Table 3. IRB 6700 joint stiffness
joint1 joint2 joint3 joint4 joint5 joint6 joint stiffness/(mm∙N/rad) 2.53×109 9.31×108 6.52×108 9.12×107 4.36×107 2.34×107 表 5 Mooney-Rivilin超弹性本构模型
Table 5. Mooney-Rivilin hyperelastic constitutive model
material constant/Pa C10 C01 2.45×106 −9.58×105 表 6 3阶广义麦克斯韦粘弹性本构模型
Table 6. The third-order generalized Maxwell viscoelastic constitutive model
dimensionless material constant relaxation time/s g1 g2 g3 τ1 τ2 τ3 0.10293 0.57067 0.05479 0.02905 0.00082 0.78611 表 7 原始气囊工具头与抑振气囊工具头抛光效果对比
Table 7. Comparison of the polishing effect of the original bonnet tool and the vibration suppression bonnet tool
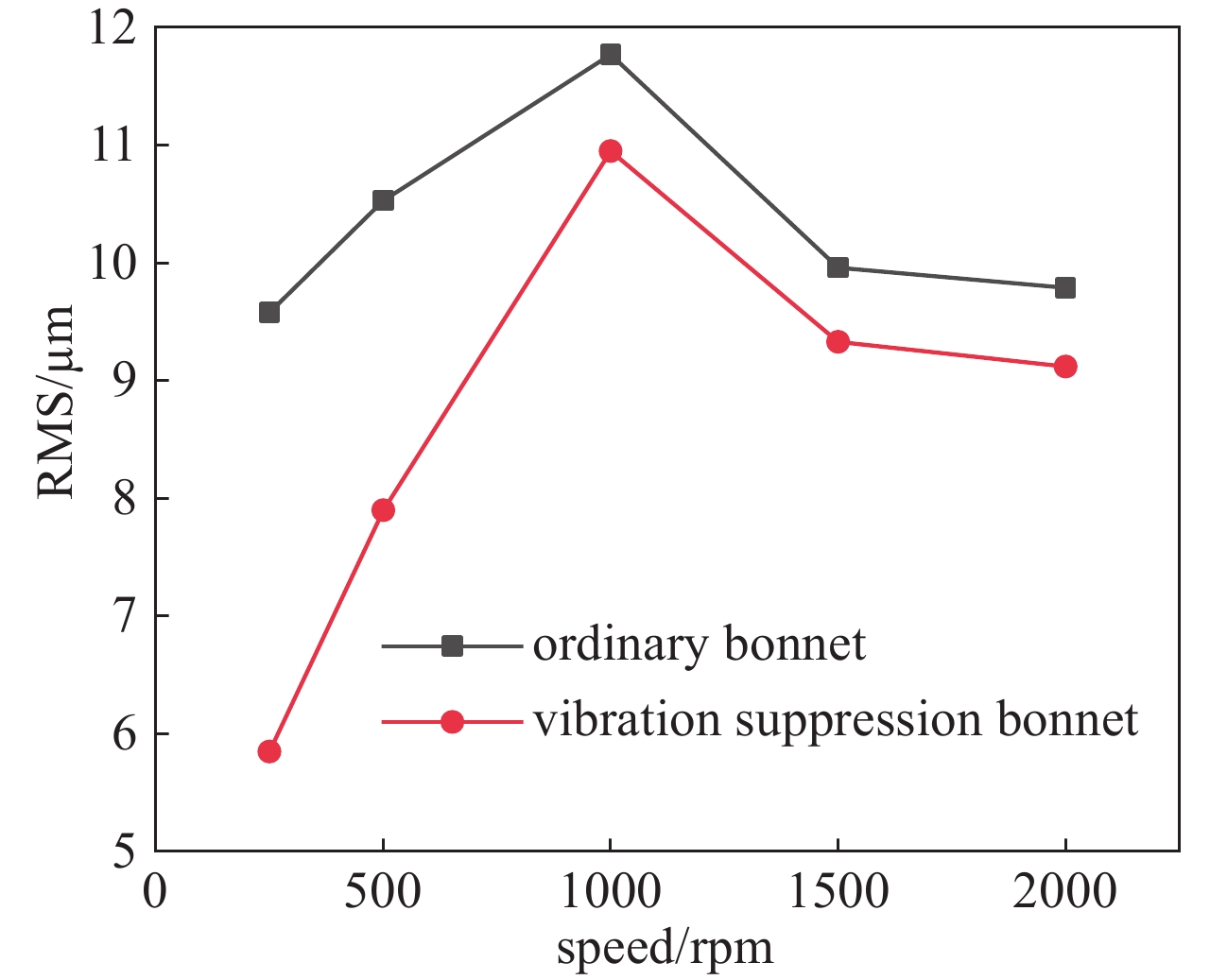
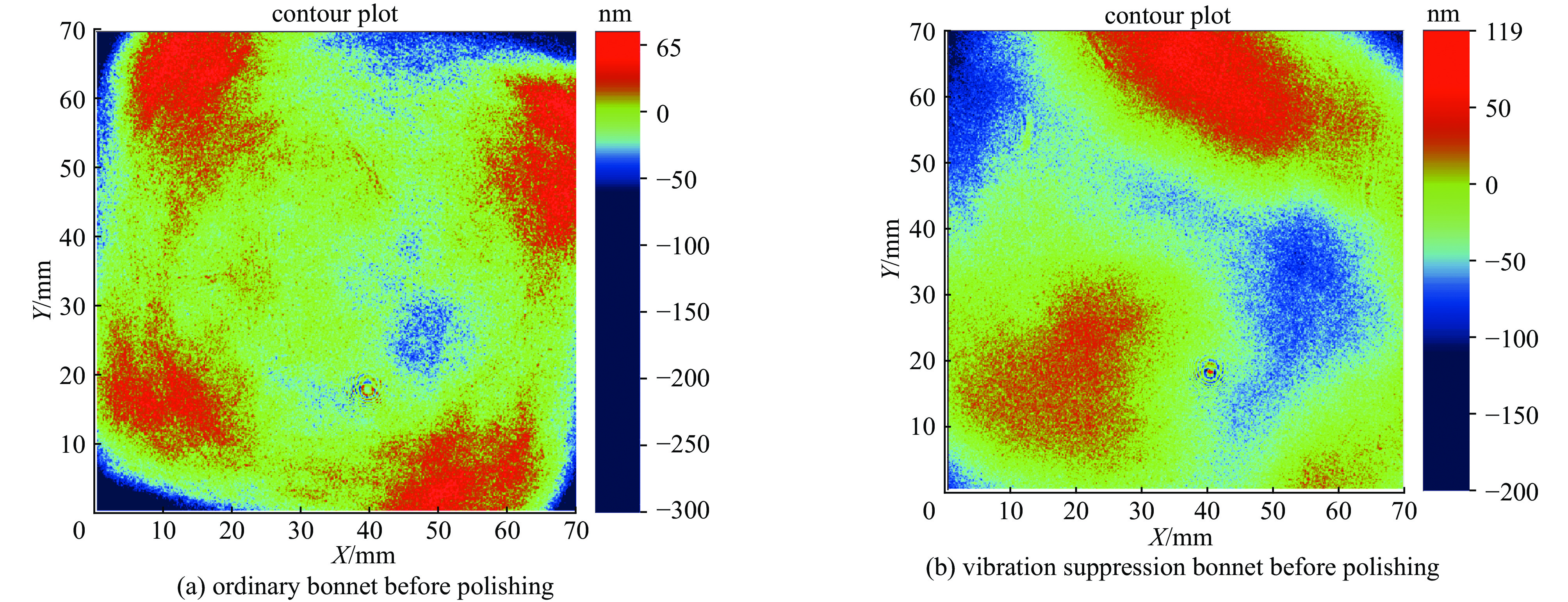
comparison parameters originary bonnet vibration suppression bonnet relative reduction rate PV/μm before polishing 2.866 2.000 — after polishing 2.809 1.948 PSD/(mm·nm2) before polishing — — 40% after polishing 316.9 187.5 RMS/nm before polishing 540.773 395.562 — after polishing 534.043 382.256 -
[1] Cheng Haobo. Independent variables for optical surfacing systems[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 11-20. [2] 王振忠, 施晨淳, 张鹏飞, 等. 先进光学制造技术最新进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(8):23-56 doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.08.023Wang Zhenzhong, Shi Chenchun, Zhang Pengfei, et al. Recent progress of advanced optical manufacturing technology[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(8): 23-56 doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.08.023 [3] 樊非, 徐曦, 许乔, 等. 大口径强激光光学元件超精密制造技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47:200135Fan Fei, Xu Xi, Xu Qiao, et al. Progress on ultra precision manufacturing technology of large-aperture high-power laser optics[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2020, 47: 200135 [4] 徐德衍. NIF的光学加工现状[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2004, 41(12):13-14,12Xu Deyan. Optical processing status of NIF[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2004, 41(12): 13-14,12 [5] 计时鸣, 陈伟强, 金明生, 等. 气囊连续进动抛光运动模型的研究[J]. 机电工程, 2012, 29(4):377-380,416 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2012.04.002Ji Shiming, Chen Weiqiang, Jin Mingsheng, et al. Research on motion model for gasbag polishing with continuous precession process[J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, 2012, 29(4): 377-380,416 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2012.04.002 [6] 计时鸣, 金明生, 张宪, 等. 应用于模具自由曲面的新型气囊抛光技术[J]. 机械工程学报, 2007, 43(8):2-6 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2007.08.001Ji Shiming, Jin Mingsheng, Zhang Xian, et al. Novel gasbag polishing technique for free-form mold[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 43(8): 2-6 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2007.08.001 [7] 黄智, 周涛, 吴湘, 等. 机器人气囊抛光SiC光学元件加工特性研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(12):22-29Huang Zhi, Zhou Tao, Wu Xiang, et al. SiC optical element processing properties under robot bonnet polishing[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(12): 22-29 [8] 林泽文, 王振忠, 黄雪鹏, 等. 机器人气囊抛光去除函数稳定性分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:051001Lin Zewen, Wang Zhenzhong, Huang Xuepeng, et al. Influence of robotic structural deformation on bonnet polishing removal function[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 051001 [9] Campbell J H, Hawley-Fedder R A, Stolz C J, et al. NIF optical materials and fabrication technologies: an overview[C]//Proceedings of the SPIE 5341, Optical Engineering at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory II: The National Ignition Facility. 2004: 84-101. [10] 李爱民. 计算机控制小工具研抛的去除特性及工艺研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2003: 21-30Li Aimin. Research on the removal characteristics and process of computer-controlled gadget polishing[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2003: 21-30 [11] 陈伟. 光学元件表面频谱分布影响因素的分析方法[J]. 应用光学, 2011, 32(5):967-970 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2011.05.030Chen Wei. Analysis of impact factors on frequency distribution of optic surface[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2011, 32(5): 967-970 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2011.05.030 [12] 姜涛. 气囊抛光机床精度及元件面形中频控制研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2015: 25-35Jiang Tao. Research on the precision of bonnet polishing machine tool and the intermediate frequency control of the component surface[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2015: 25-35 [13] Yu Guoyu, Walker D, Li Hongyu. Implementing a grolishing process in Zeeko IRP machines[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(27): 6637-6640. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.006637 [14] Dunn C R, Walker D D. Pseudo-random tool paths for CNC sub-aperture polishing and other applications[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(23): 18942-18949. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.018942 [15] Wang Chunjin, Wang Zhenzhong, Wang Quanjin, et al. Improved semirigid bonnet tool for high-efficiency polishing on large aspheric optics[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 88(5): 1607-1617. [16] 潘日. 大口径非球面高效可控气囊抛光技术研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2014: 7-100Pan Ri. Research on polishing technology of large-aperture aspheric surface and high-efficiency controllable airbag[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2014: 7-100 [17] 王春锦. 大口径光学元件的半柔性气囊高效抛光技术研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2015: 20-50Wang Chunjin. Research on high-efficiency polishing technology for semi-flexible bonnet of large-aperture optical components[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2015: 20-50 [18] Ahmadian H, Mottershead J E, James S, et al. Modelling and updating of large surface-to-surface joints in the AWE-MACE structure[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2006, 20(4): 868-880. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.05.005 [19] Pan Zengxi, Zhang Hui. Analysis and suppression of chatter in robotic machining process[C]//2007 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems. 2007: 595-600. [20] 陈永刚, 樊开夫, 谭晶晶, 等. 工业六轴机器人末端抖动的研究[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2019, 38(12):44-47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2019.12.011Chen Yonggang, Fan Kaifu, Tan Jingjing, et al. Research on jitter of industrial six-axis robot terminal[J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 2019, 38(12): 44-47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2019.12.011 [21] 王战玺, 张晓宇, 李飞飞, 等. 机器人加工系统及其切削颤振问题研究进展[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(14):147-155,188Wang Zhanxi, Zhang Xiaoyu, Li Feifei, et al. Review on the research developments of robot machining systems and cutting chatter behaviors[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(14): 147-155,188 [22] 方强, 李超, 费少华, 等. 机器人镗孔加工系统稳定性分析[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(2):727-737Fang Qiang, Li Chao, Fei Shaohua, et al. Stability analysis of robot boring system[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 727-737 [23] Pan Ri, Zhao Wanying, Wang Zhenzhong, et al. Research on an evaluation model for the working stiffness of a robot-assisted bonnet polishing system[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 65: 134-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.03.013 [24] Alberts T E, Dickerson S L, Book W J. On the transfer function modeling of flexible structures with distributed damping[J]. Georgia Institute of Technology, 1986. [25] 贺兴书. 机械振动学[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1985He Xingshu. Mechanical vibration[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 1985 [26] 伍魏明. 环形橡胶—硅油组合式减振器刚度与阻尼特性研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2018: 40-60Wu Weiming. Study on the stiffness and damping characteristics of annular rubber-silicone oil damper[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018: 40-60 -




 下载:
下载: