Simulation and experiment study on a horizontally polarized bounded-wave electromagnetic pulse simulator
-
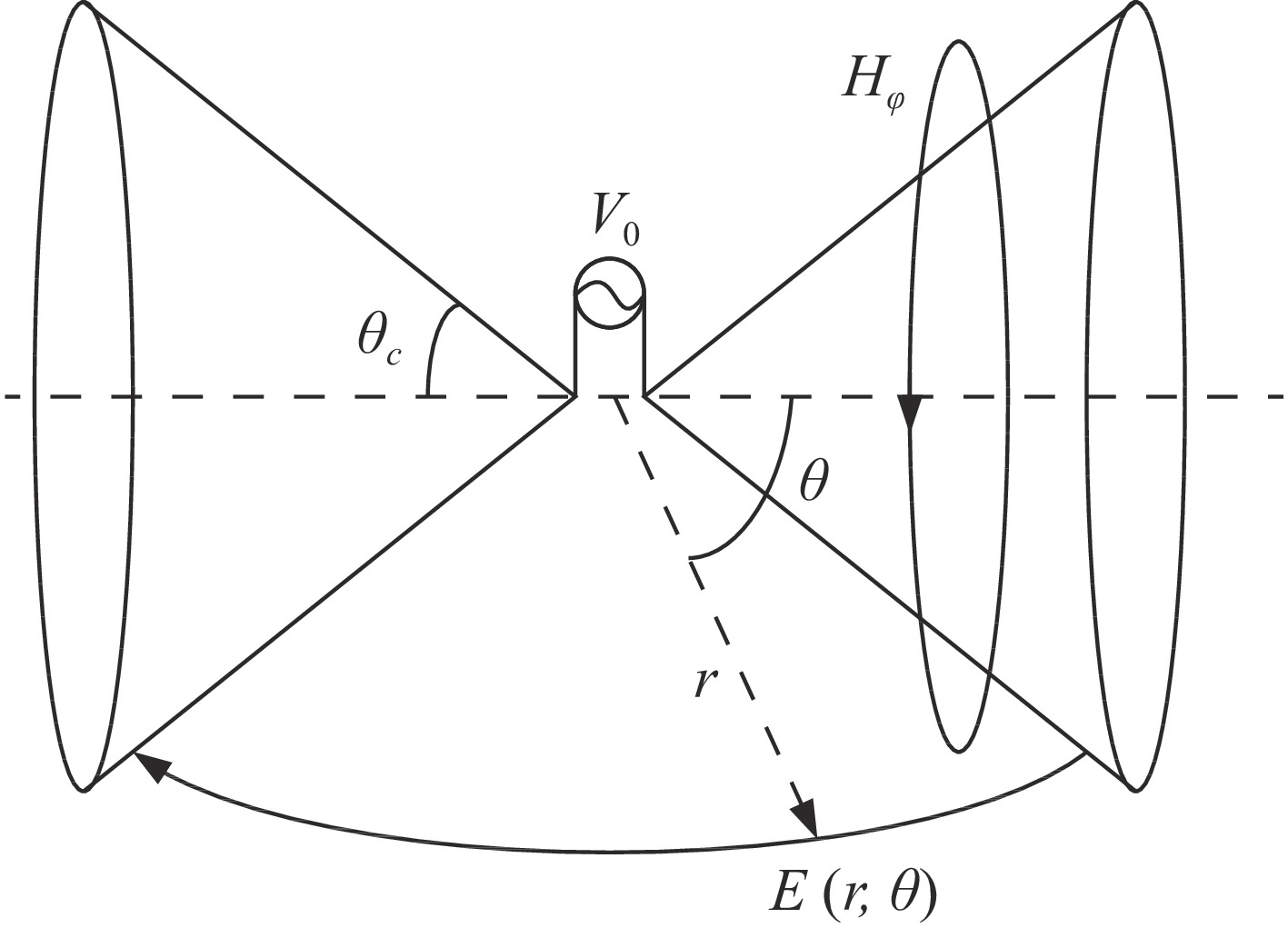
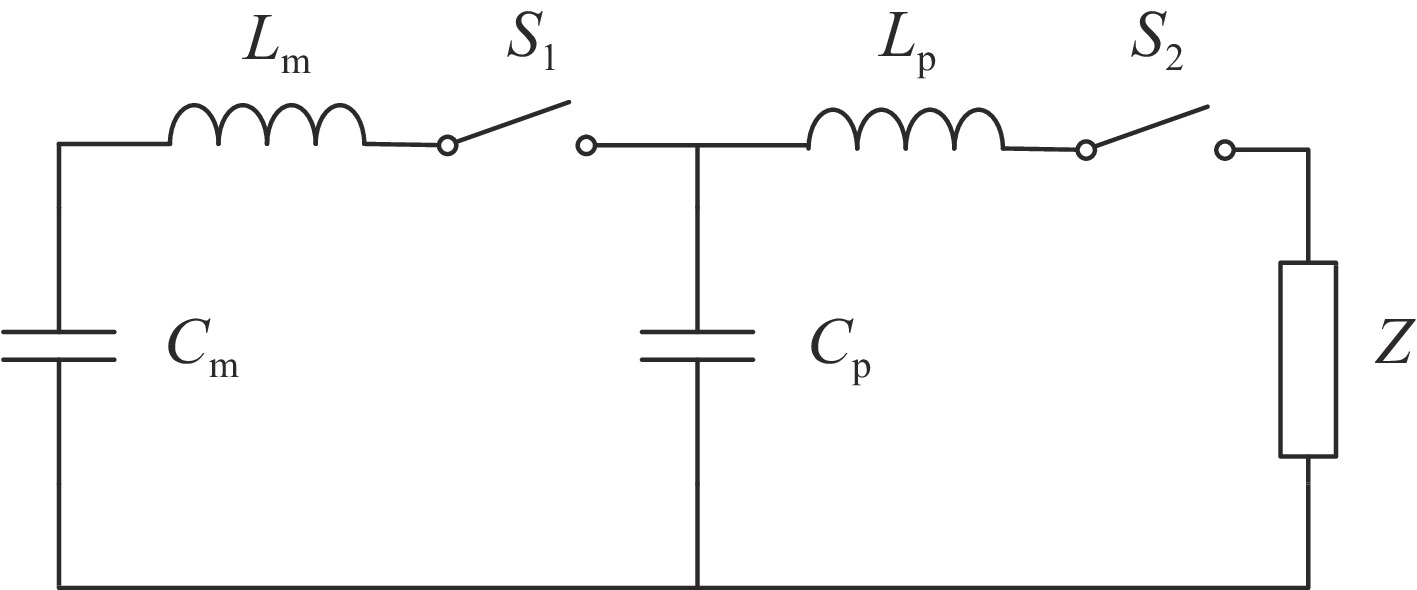
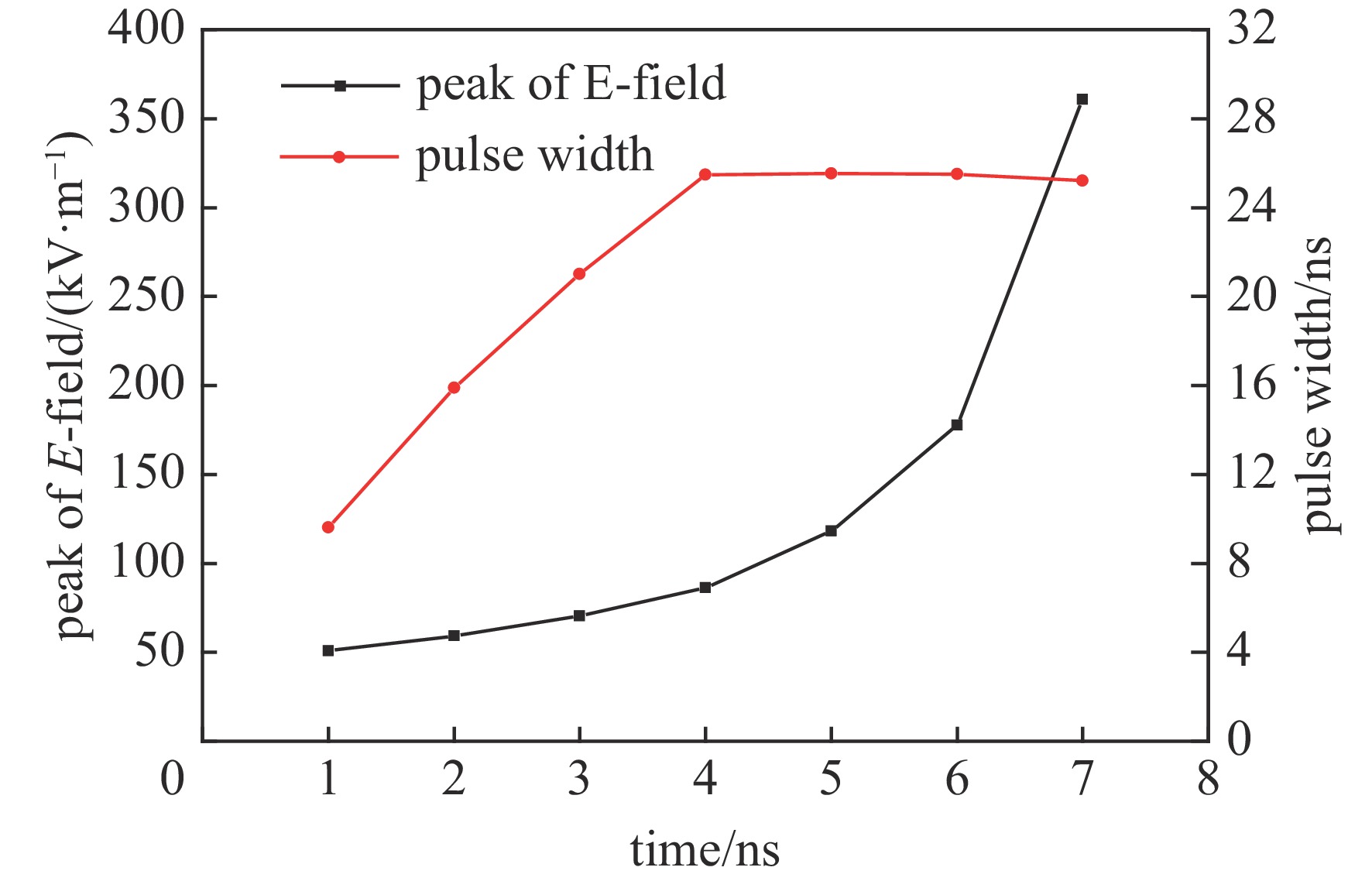
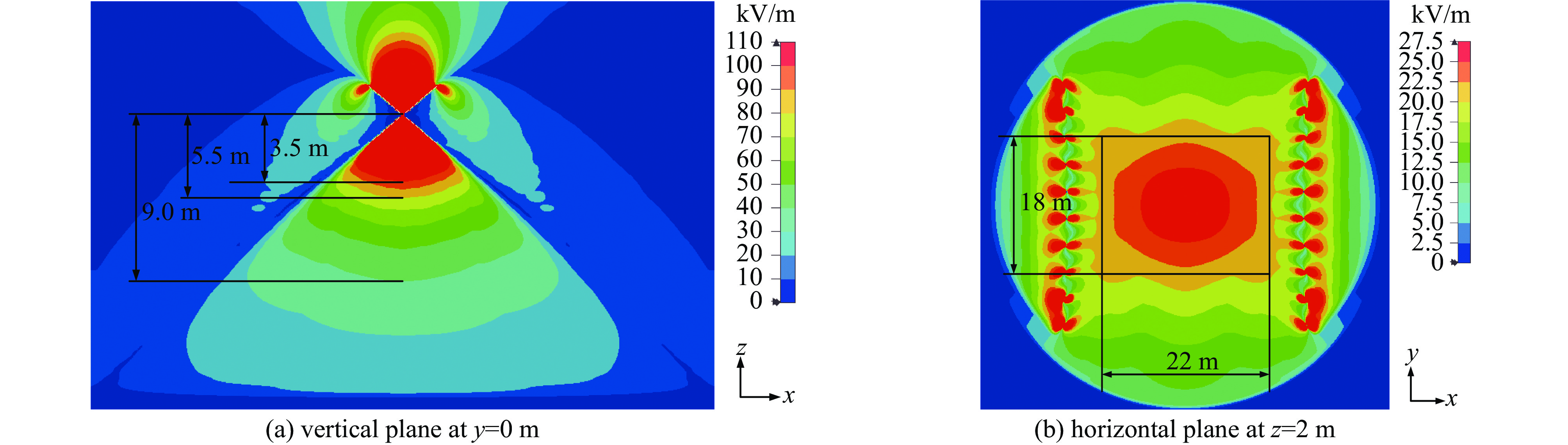
摘要: 结合传统有界波模拟器和辐射波模拟器的特点,采用新型双锥-线栅型平板天线结构,设计了一台水平极化有界波电磁脉冲模拟器。通过电磁仿真和实验测试,对模拟器的辐射特性和场均匀性进行了研究。仿真结果和实测结果基本一致。结果表明,模拟器能产生包含地面反射的水平极化电磁脉冲环境,波形满足上升沿(2.5±0.5) ns、半高宽(23±5) ns的高空电磁脉冲标准要求。模拟器使用灵活机动,能在不小于5 m×3 m×2 m工作空间内产生峰值场强不小于50 kV/m的6 dB均匀场,也能在降低测试场强时提供更大的工作空间。Abstract: EMP simulators are used to test and harden electronic systems in an intense electromagnetic pulse. A horizontally polarized bounded-wave EMP simulator is designed based on a bicone-plate antenna structure, which combines the strengths of traditional bounded-wave simulators and radiating-wave simulators. Simulation and experiments are conducted to study the characteristics and the distribution of the radiation field. The results show that the simulator can generate horizontally polarized electromagnetic pulse and the waveform is double-exponential with a rise time of (2.5±0.5) ns and a pulse width of (23±5) ns. The simulator has a working volume of 5 m×3 m×2 m in which the electric field is no less than 50 kV/m within a 6 dB tolerance. Moreover, the simulator is flexible to increase the working volume while decreasing the field intensity.
-
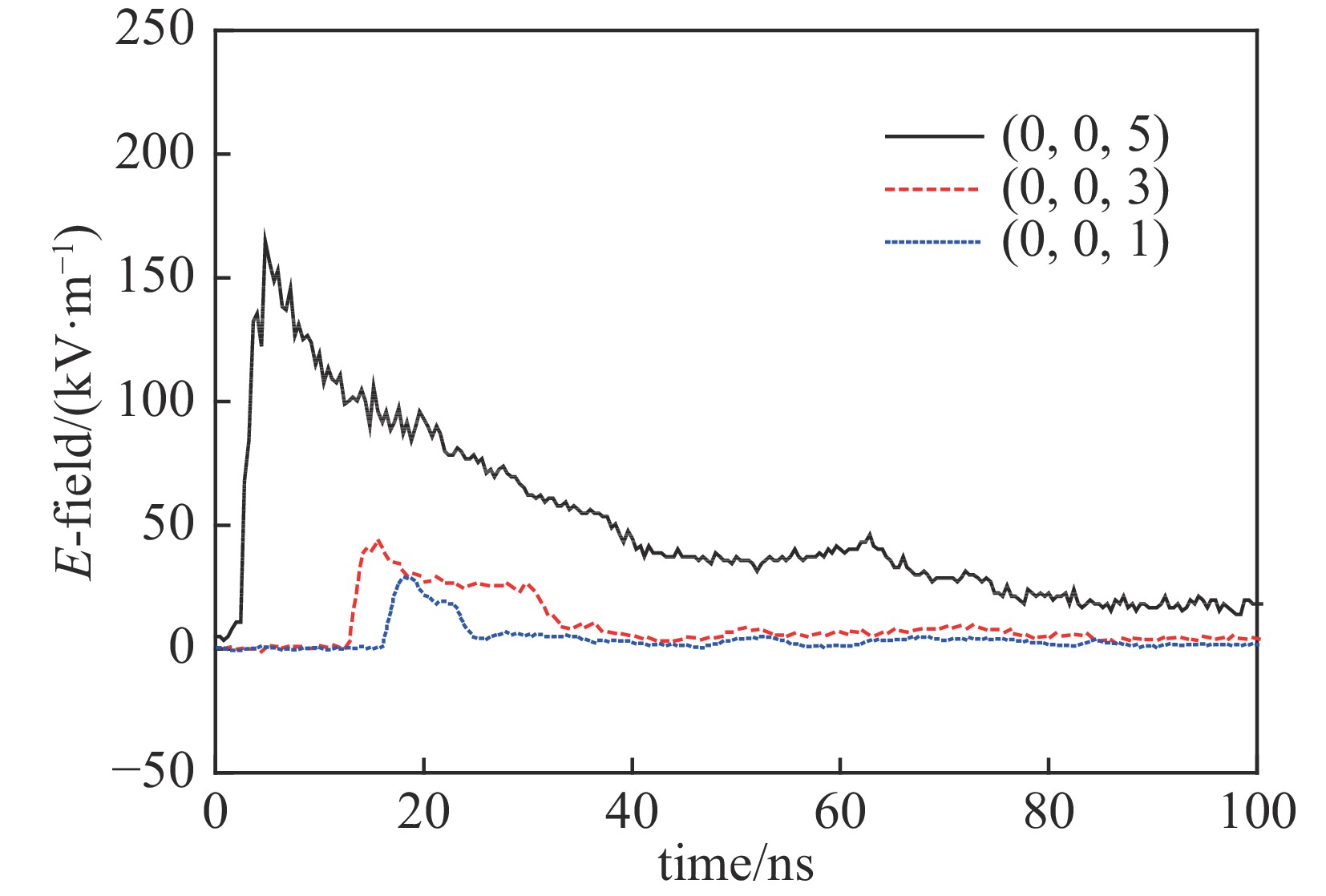
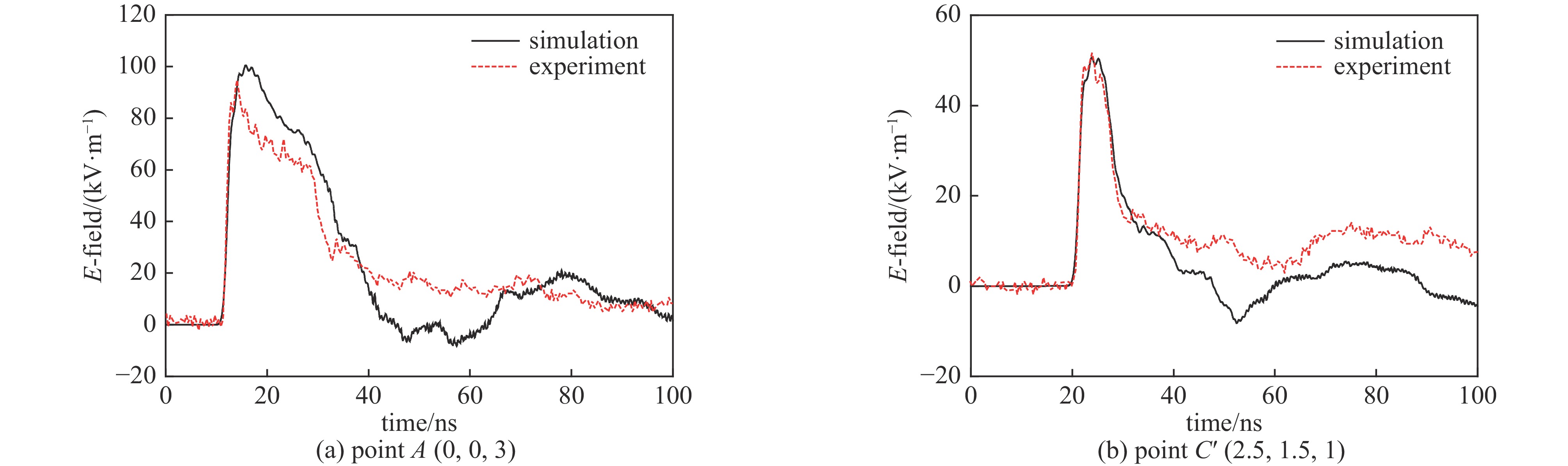
表 1 5 m×3 m×2 m工作空间内不同测点的峰值场强
Table 1. Peak E-field in the working volume of 5 m×3 m×2 m
point location / m peak E-field/(kV·m−1) experiment simulation A (0, 0, 3) 94.8 100.4 B (2.5, 0, 3) 70.5 71.9 C (2.5, 1.5, 3) 65 65.7 D (0, 1.5, 3) 89.9 92 A′ (0, 0, 1) 64.2 63.8 B′ (2.5, 0, 1) 55.8 52.3 C′ (2.5, 1.5, 1) 51.8 50.6 D′ (0, 1.5, 1) 54.1 61.3 表 2 6 m×5m×2 m工作空间内不同测点的峰值场强
Table 2. Peak E-field in the working volume of 6 m×5 m×2 m
point location / m peak E-field/(kV·m−1) experiment simulation A (0, 0, 3.5) 74.3 79.1 B (3, 0, 3.5) 62.5 67.1 C (3, 2.5, 3.5) 55.9 60.4 D (0, 2.5, 3.5) 63.5 68.9 A′ (0, 0, 1.5) 55.1 54.2 B′ (3, 0, 1.5) 48.9 49.5 C′ (3, 2.5, 1.5) 42.9 46.4 D′ (0, 2.5, 1.5) 45.1 50.4 -
[1] Martin A R, Bond A. Nuclear pulse propulsion: a historical review of an advanced propulsion concept[J]. Journal of the British Interplanetary Society, 1979, 32: 283-310. [2] Giri D V, Tesche F M. Classification of intentional electromagnetic environments (IEME)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2004, 46(3): 322-328. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2004.831819 [3] 寇科男, 金晗冰, 吴海燕, 等. 指挥通信车强电磁脉冲效应仿真分析[J]. 无线电工程, 2020, 50(6):479-483Kou Kenan, Jin Hanbing, Wu Haiyan, et al. Simulation of electromagnetic pulse effects on command vehicle[J]. Radio Engineering, 2020, 50(6): 479-483 [4] 周璧华, 石立华, 王建宝, 等. 电磁脉冲及其工程防护[M]. 2版. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2019Zhou Bihua, Shi Lihua, Wang Jianbao, et al. Electromagnetic pulse and its engineering protection[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2019 [5] Baum C E. EMP simulators for various types of nuclear EMP environments: an interim categorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1978, 26(1): 35-53. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1978.1141794 [6] Baum C E. Review of hybrid and equivalent-electric-dipole EMP simulators[R]. Sensor and Simulation Notes 277, 1982. [7] 李云伟, 王泽忠, 卢斌先, 等. 电磁脉冲模拟器仿真与实验研究[J]. 高电压技术, 2007, 33(1):128-131Li Yunwei, Wang Zezhong, Lu Binxian, et al. Simulation and experimental study of electromagnetic pulse simulator[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2007, 33(1): 128-131 [8] 周开明, 李铮迪, 邓建红. 大动态高精度有界波电磁脉冲模拟器设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:063004Zhou Kaiming, Li Zhengdi, Deng Jianhong. Design of a high-precision and widely tunable bounded-wave electromagnetic pulse simulator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 063004 [9] 孟粉霞, 夏洪富, 王建国. 电磁脉冲辐射波模拟器笼形天线的理论和数值研究[J]. 微波学报, 2001, 23(s1):6-10Meng Fenxia, Xia Hongfu, Wang Jianguo. Theoretical and numerical studies on cage antenna of EMP radiating-wave simulator[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2001, 23(s1): 6-10 [10] Blackburn R F, Taylor C D. On the electromagnetic fields from a hybrid type of EMP simulator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 1978, 20(1): 240-247. [11] Bailey V, Carboni V, Eichenberger C, et al. A 6-MV pulser to drive horizontally polarized EMP simulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2010, 38(10): 2554-2558. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2065245 [12] 朱湘琴, 吴伟, 王海洋. 大型水平极化电磁脉冲有界波模拟器的辐射场分布特性分析[J]. 现代应用物理, 2020, 11:040502Zhu Xiangqin, Wu Wei, Wang Haiyang. Characteristics of radiation electric field distribution in large EMP bounded wave simulator with horizontal polarization[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2020, 11: 040502 [13] 肖晶, 吴刚, 王海洋, 等. 两种不同线栅结构的水平极化辐射波模拟器[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:033004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200281Xiao Jing, Wu Gang, Wang Haiyang, et al. Horizontally polarized radiation-wave simulator with two different wire grating structures[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 033004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200281 [14] 肖晶, 吴刚, 谢霖燊, 等. 线栅参数对双锥-平面线栅水平极化辐射波模拟器的影响[J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(8):1708-1715Xiao Jing, Wu Gang, Xie Linshen, et al. Influence of wire grating on horizontally polarized radiated-wave simulator with biconical-wire grating structure[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(8): 1708-1715 [15] 吴伟, 王海洋, 吴刚, 等. 9.5 m高水平极化有界波电磁脉冲模拟器内场分布特性的初步实验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:043005 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200303Wu Wei, Wang Haiyang, Wu Gang, et al. Preliminary experimental investigation of field distribution characteristics in horizontally polarized bounded-wave EMP simulator with 9.5 m in height[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 043005 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200303 [16] IEC 61000-2-9, Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)—part 2: environment—section 9: description of HEMP environment-radiated disturbance[S]. [17] 刘锡三. 高功率脉冲技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005Liu Xisan. High pulsed power technology[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2005 [18] Nagasawa K, Matsuzuka I. Radiation field consideration of biconical horn antenna with different flare angles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1988, 36(9): 1306-1310. doi: 10.1109/8.8608 [19] 杜雷鸣, 谢彦召, 王绍飞. 平行板传输线特性阻抗仿真计算及解析修正[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:083201 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.083201Du Leiming, Xie Yanzhao, Wang Shaofei. Simulation computation and analytic modification of characteristic impedance of parallel-plate transmission line[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 083201 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.083201 -





 下载:
下载: