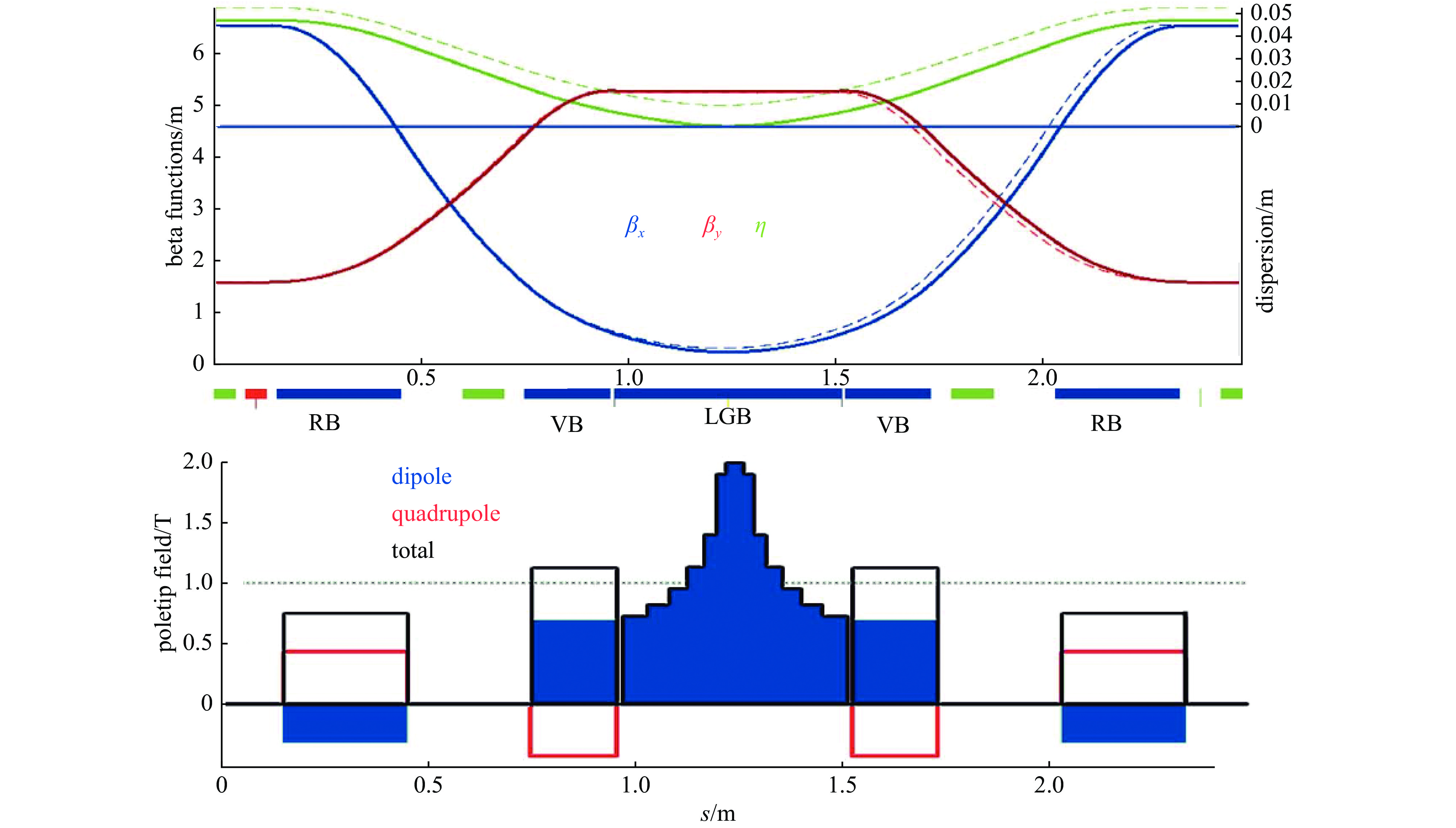
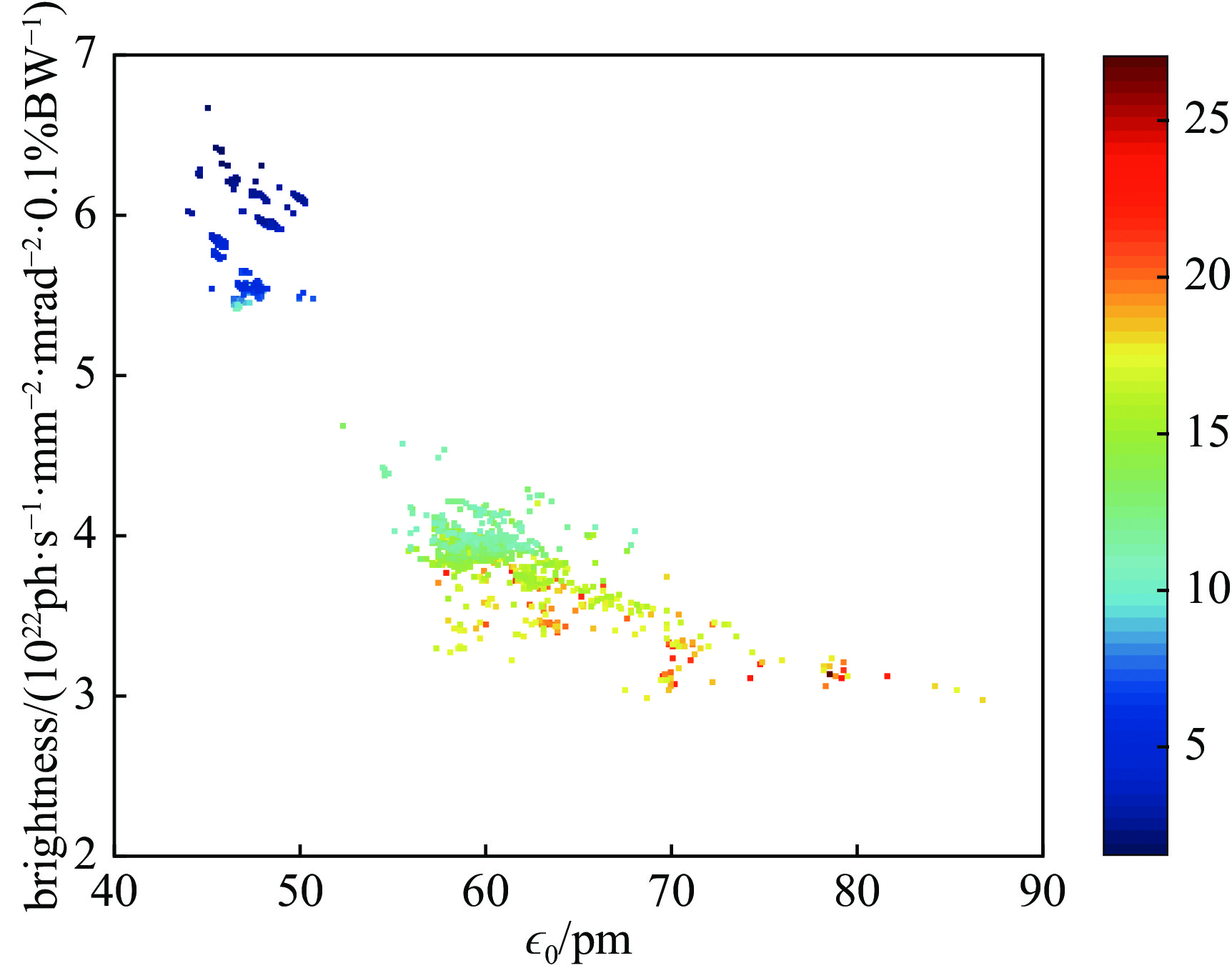
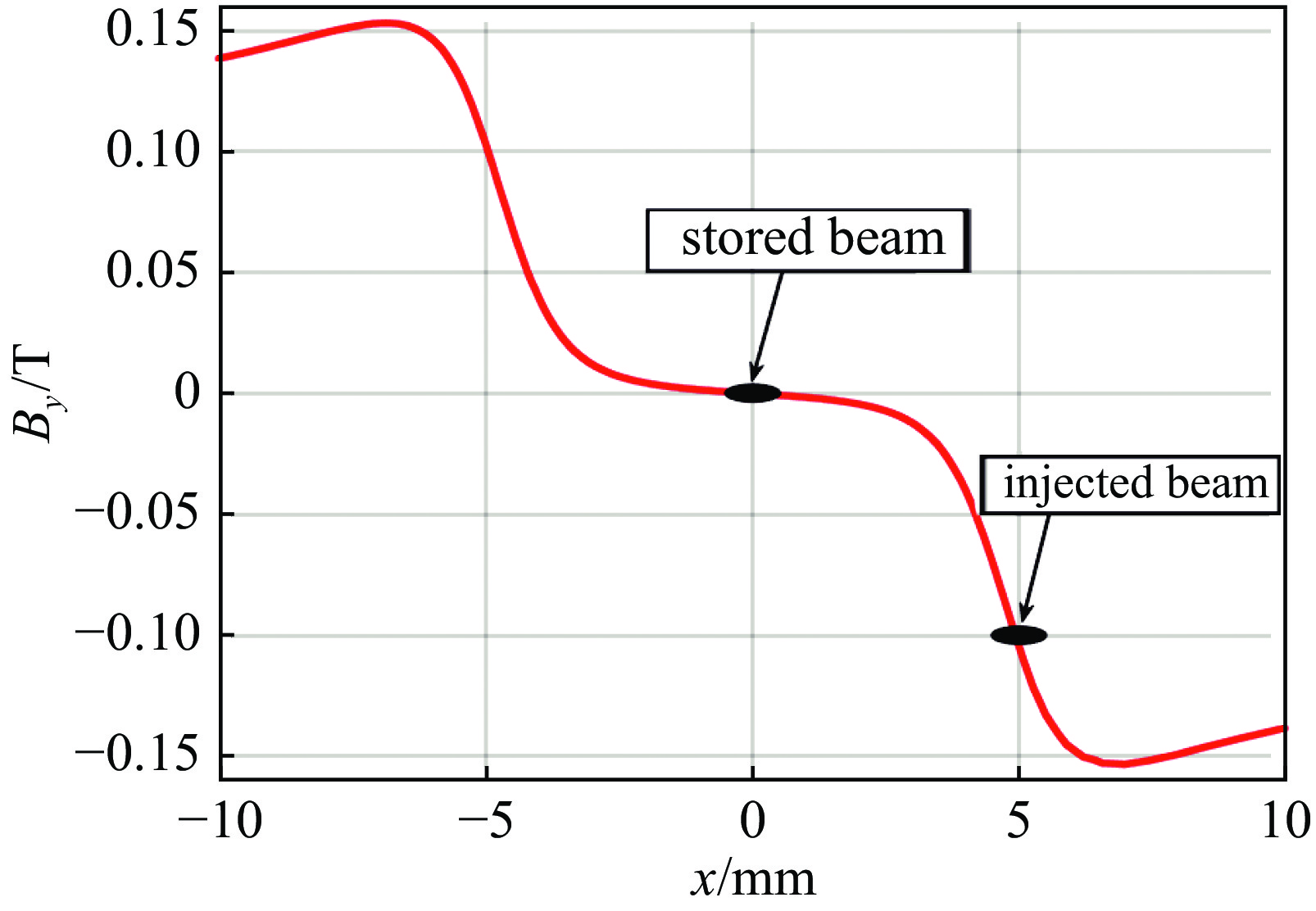
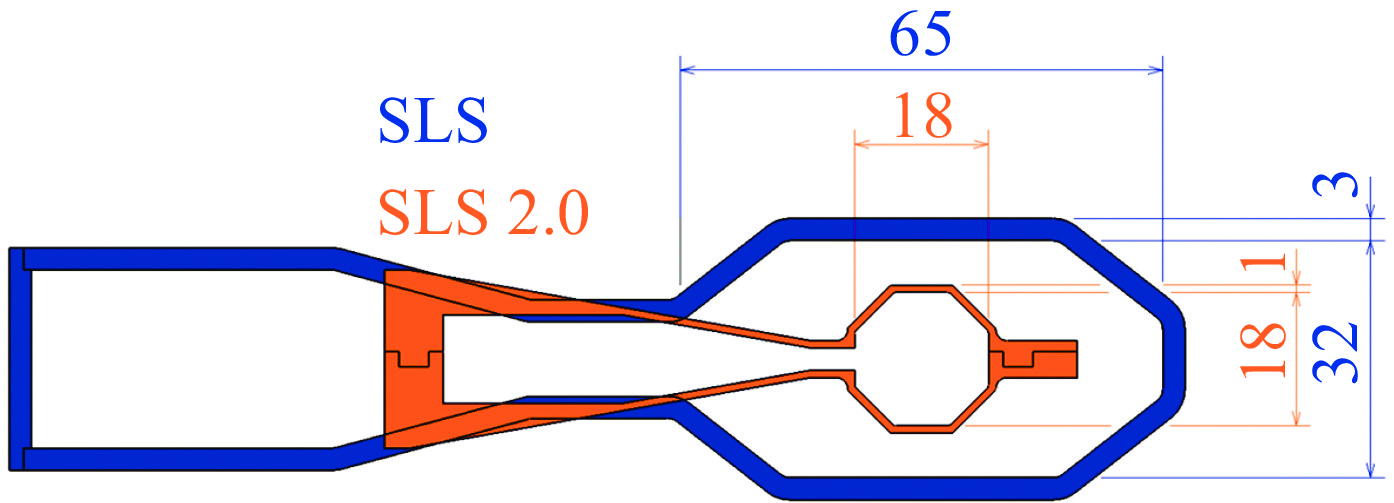
Physics design and optimization of the fourth-generation synchrotron light sources
-
摘要: 近十年来,世界上开始大力发展第四代同步辐射光源——衍射极限储存环光源。目前我国正在建设或立项建设两台第四代同步辐射光源:高能同步辐射光源和合肥先进光源。从储存环磁聚焦结构设计与优化、束流注入与集体效应等方面,对第四代同步辐射光源的物理设计与优化进行了介绍;对国际范围内第四代储存环光源装置的研制情况进行了介绍。Abstract: Over the past decade, the fourth-generation synchrotron light sources based on diffraction-limited storage rings (DLSRs) have been extensively designed and developed around the world. In China, two fourth-generation synchrotron light sources, the High Energy Photon Source and the Hefei Advanced Light Facility, are being or will be constructed. This paper will report the main issues and progresses in physics design and optimization of DLSRs, including lattice design and optimization, beam injection and collective effects, and will also introduce the current design and construction status of DLSR facilities around the world.
-
表 1 目前世界上在建及运行的高能区第四代储存环光源的主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of high-energy fourth-generation synchrotron light sources being in operation or under construction
light
sourceenergy/
GeVcircumference/m natural emittance/
(pm·rad)momentum
compaction/10−5energy loss per
turn/MeVnumber of straight
sectionsH/V β @
long straight/mESRF-EBS 6.0 844 133 8.7 2.56 32 6.9/2.7 APS-U 6.0 1103.6 41.7 4.0 2.74 40 5.19/2.4 HEPS 6.0 1360.4 34.8 1.8 2.64 48 8.18/5.0(2.56/2.31) 表 2 目前世界上主要的中低能区第四代储存环光源的设计参数(Elettra 2.0,Diamond-II和HALF的直线节数目包括长、中直线节)
Table 2. Main parameters of medium- and low-energy fourth-generation synchrotron light source designs (Elettra 2.0, Diamond-II and HALF have long and short straight sections in each lattice period)
light
sourceenergy/GeV circumference/m lattice natural emittance/
(pm·rad)number of straight
sectionsmomentum
compaction/10−5natural damping
time (H/V/L)/msALS-U 2.0 196.5 9BA 109 12 20 7.7/14.4/12.7 HALF 2.2 479.86 6BA 86 20+20 9 27.2/37.7/23.4 Elettra 2.0 2.4 259.2 6BA 214 12+12 12 5.5/9.1/6.8 SLS-2 2.7 288 7BA 158 12 10.5 4.1/7.5/6.4 SOLEIL-U 2.75 353.74 7BA-4BA 81 20 9.1 7.1/13.2/11.7 MAX IV 3.0 528 7BA 328 20 30.6 15.8/29.4/25.8 Sirius 3.0 518.4 5BA 250 20 16.4 16.9/22.0/12.9 SKIF 3.0 476.14 7BA 72 16 7.6 9.2/17.9/17.0 ILSF 3.0 528 5BA 270 20 18.2 18.9/26.0/16.0 Diamond-II 3.5 560.56 6BA 159 24+24 11 9.5/18.1/16.4 -
[1] Zhao Zhentang. Storage ring light sources[J]. Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology, 2010, 3(1): 57-76. doi: 10.1142/S1793626810000361 [2] Pellegrini C, Marinelli A, Reiche S. The physics of X-ray free-electron lasers[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2016, 88: 015006. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.88.015006 [3] Bilderback D H, Brock J D, Dale D S, et al. Energy recovery linac (ERL) coherent hard X-ray sources[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2020, 12: 035011. [4] Hettel R. DLSR design and plans: an international overview[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2014, 21(5): 843-855. doi: 10.1107/S1600577514011515 [5] Einfeld D, Schaper J, Plesko M. Design of a diffraction limited light source (DIFL)[C]//Proceedings Particle Accelerator Conference. Dallas, USA, 1995: 177-179. [6] Tavares P F, Leemann S C, Sjöström M, et al. The MAX IV storage ring project[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2014, 21(Pt 5): 862-877. [7] Martensson N, Eriksson M. The saga of MAX IV, the first multi-bend achromat synchrotron light source[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 907: 97-104. [8] Liu L, Milas N, Mukai A H C, et al. The Sirius project[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2014, 21(Pt 5): 904-911. [9] Farvacque L, Carmignani N, Chavanne J, et al. A low-emittance lattice for the ESRF[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Shanghai, China, 2013: 79-81. [10] Borland M, Sun Y, Sajaev V, et al. Lower emittance lattice for the advanced photon source upgrade using reverse bending magnets[C]//Proceedings of NAPAC2016. Chicago, USA, 2016: 877-880. [11] Jiao Yi, Xu Gang, Cui Xiaohao, et al. The HEPS project[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2018, 25(Pt 6): 1611-1618. [12] Bai Zhenghe, Liu Gangwen, He Tianlong, et al. A modified hybrid 6BA lattice for the HALF storage ring[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Campinas, Brazil, 2021: 407-409. [13] 焦毅, 徐刚, 陈森玉, 等. 衍射极限储存环物理设计研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:045108 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.045108Jiao Yi, Xu Gang, Chen Senyu, et al. Advances in physical design of diffraction-limited storage ring[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 045108 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.045108 [14] Sands M. Physics of electron storage rings: an introduction[R]. SLAC-121, 1970. [15] Teng L C. Minimizing the emittance in designing the lattice of an electron storage ring[R]. Fermilab Report TM-1269, 1984. [16] Jiao Yi, Cai Yunhai, Chao A W. Modified theoretical minimum emittance lattice for an electron storage ring with extreme-low emittance[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2011, 14: 054002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.14.054002 [17] Nagaoka R, Wrulich A F. Emittance minimisation with longitudinal dipole field variation[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2007, 575(3): 292-304. [18] Streun A. The anti-bend cell for ultralow emittance storage ring lattices[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2014, 737: 148-154. [19] Streun A, Garvey T, Rivkin L, et al. SLS-2 – the upgrade of the Swiss light source[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2018, 25(Pt 3): 631-641. [20] Riemann B, Streun A. Low emittance lattice design from first principles: reverse bending and longitudinal gradient bends[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2019, 22: 021601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.22.021601 [21] Jiao Yi, Xu Gang. PEPX-type lattice design and optimization for the High Energy Photon Source[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2015, 39: 067004. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/39/6/067004 [22] Steier C, Robin D, Nadolski L, et al. Measuring and optimizing the momentum aperture in a particle accelerator[J]. Physical Review E, 2002, 65: 056506. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.65.056506 [23] Bengtsson J. The sextupole scheme for the Swiss light source (SLS): an analytic approach[R]. SLS Note 9/97, 1997. [24] Nadolski L, Laskar J. Review of single particle dynamics for third generation light sources through frequency map analysis[J]. Physical Review Special Topics–Accelerators and Beams, 2003, 6: 114801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.6.114801 [25] Bengtsson J, Streun A, Singh B, et al. Control of the nonlinear dynamics for medium energy synchrotron light sources[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 4037-4041. [26] Bengtsson J, Streun A. Robust design strategy for SLS-2[R]. Technical Report SLS2-BJ84-001, 2017. [27] Borland M, Decker G, Emery L, et al. Lattice design challenges for fourth-generation storage-ring light sources[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2014, 21(Pt 5): 912-936. [28] Bai Zhenghe, Wang Lin. Study of multi-bend achromat lattices for the HALS diffraction-limited storage ring[C]//Proceedings of the 60th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on Future Light Sources. Shanghai, China, 2018: 25-27. [29] Yang Lingyun, Li Yongjun, Guo Weiming, et al. Multiobjective optimization of dynamic aperture[J]. Physical Review Special Topics–Accelerators and Beams, 2011, 14: 054001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.14.054001 [30] Borland M, Emery L, Sajaev V, et al. Multi-objective optimization of a lattice for potential upgrade of the advanced photon source[R]. Technical Report LS-319, 2010. [31] Bai Zhenghe, Wang Lin, Li Weimin, et al. Enlarging dynamic and momentum aperture by particle swarm optimization[C]//Proceedings of IPAC2011. San Sebastián, Spain, 2011: 948-950. [32] Huang Xiaobiao, Safranek J. Nonlinear dynamics optimization with particle swarm and genetic algorithms for SPEAR3 emittance upgrade[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2014, 757: 48-53. [33] Jiao Yi. Improving nonlinear performance of the HEPS baseline design with a genetic algorithm[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2016, 40: 077002. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/40/7/077002 [34] Jiao Yi, Xu Gang. Optimizing the lattice design of a diffraction-limited storage ring with a rational combination of particle swarm and genetic algorithms[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2017, 41: 027001. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/41/2/027001 [35] 万金宇, 孙正, 张相, 等. 机器学习在大型粒子加速器中的应用回顾与展望[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:094001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210199Wan Jinyu, Sun Zheng, Zhang Xiang, et al. Machine learning applications in large particle accelerator facilities: review and prospects[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 094001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210199 [36] 赵瑀, 李志平, 刘伟航, 等. 衍射极限储存环光源相关物理问题[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(24):2587-2600 doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0165Zhao Yu, Li Zhiping, Liu Weihang, et al. Physics issues of the diffraction-limited storage ring light source[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(24): 2587-2600 doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0165 [37] Edelen A, Neveu N, Frey M, et al. Machine learning for orders of magnitude speedup in multiobjective optimization of particle accelerator systems[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2020, 23: 044601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.23.044601 [38] Li Yongjun, Cheng Weixing, Yu Lihua, et al. Genetic algorithm enhanced by machine learning in dynamic aperture optimization[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2018, 21: 054601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.21.054601 [39] Wan Jinyu, Chu P, Jiao Yi, et al. Improvement of machine learning enhanced genetic algorithm for nonlinear beam dynamics optimization[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2019, 946: 162683. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2019.162683 [40] Wan Jinyu, Chu P, Jiao Yi. Neural network-based multiobjective optimization algorithm for nonlinear beam dynamics[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2020, 23: 081601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.23.081601 [41] Takaki H, Nakamura N, Kobayashi Y, et al. Beam injection with a pulsed sextupole magnet in an electron storage ring[J]. Physical Review Special Topics–Accelerators and Beams, 2010, 13: 020705. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.13.020705 [42] Emery L, Borland M. Possible long-term improvements to the Advanced Photon Source[C]//Proceedings of the 2003 Particle Accelerator Conference. Portland, USA, 2003: 256-258. [43] Aiba M, Böge M, Marcellini F, et al. Longitudinal injection scheme using short pulse kicker for small aperture electron storage rings[J]. Physical Review Special Topics–Accelerators and Beams, 2015, 18: 020701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.18.020701 [44] Gough C, Aiba M. Top-up injection with “anti-septum”[C]//Proceedings of the IPAC2017. Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017: 774-776. [45] Braun H, Garvey T, Jorg M, et al. SLS 2.0 storage ring technical design report[R]. PSI Bericht Nr. 21-02, 2021. [46] Chen Jinhui, Shi Hua, Wang Lei, et al. Strip-line kicker and fast pulser R&D for the HEPS on-axis injection system[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2019, 920: 1-6. [47] Jiang Bocheng, Zhao Zhentang, Tian Shuangqi, et al. Using a double-frequency RF system to facilitate on-axis beam accumulation in a storage ring[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 814: 1-5. [48] Xu Gang, Chen Jinhui, Duan Zhe, et al. On-axis beam accumulation enabled by phase adjustment of a double-frequency RF system for diffraction-limited storage rings[C]//Proceedings of the IPAC2016. Busan, Korea, 2016: 2032-2035. [49] Jiang Shichang, Xu Gang. On-axis injection scheme based on a triple-frequency rf system for diffraction-limited storage rings[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2018, 21: 110701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.21.110701 [50] Kim J, Jang G, Yoon M, et al. Injection scheme with deflecting cavity for a fourth-generation storage ring[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2019, 22: 011601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.22.011601 [51] Yang Penghui, Li Wei, Ren Zhiliang, et al. Design of a diffraction-limited storage ring lattice using longitudinal gradient bends and reverse bends[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2021, 990: 164968. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2020.164968 [52] Tarawneh H, Steier C, Falcone R, et al. ALS-II, a potential soft X-ray, diffraction limited upgrade of the advanced light source[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2014, 493: 012020. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/493/1/012020 [53] Nagaoka R, Bane K L F. Collective effects in a diffraction-limited storage ring[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2014, 21(Pt 5): 937-960. [54] Carmignani N, Farvacque L, Liuzzo S M, et al. Linear and nonlinear optimizations for the ESRF upgrade lattice[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Richmond, USA, 2015: 1422-1425. [55] Duarte H O C, Sanfelici L, Marques S R, et al. Design and impedance optimization of the Sirius BPM button[C]//Proceedings of the IBIC2013. Oxford, UK, 2013: 365-368. [56] Wang Na, Tian Saike, Wang Lei, et al. Impedance optimization and measurements of the injection stripline kicker[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2021, 24: 034401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.24.034401 [57] Galayda J N. The advanced photon source[C]//Proceedings of the 1995 Particle Accelerator Conference and International Conference on High Energy Accelerators. Dallas, USA, 1995: 4-8. [58] Science and technology programme 2008-2017 (Purple book)[R]. ESRF, 2007. [59] Tanaka H, Kumagai N, Masaki M, et al. Top-up operation of SPring-8 storage ring with low-emittance optics[C]//Proceedings of the EPAC2006. Edinburgh, Scotland, 2006: 3359-3361. [60] Balewski K, Brefeld W, Decking W, et al. PETRA III: a new high brilliance synchrotron radiation source at DESY[C]//Proceedings of the EPAC 2004. Lucerne, Switzerland, 2004: 2302-2304. [61] Raimondi P, Carmignani N, Carver L R, et al. Commissioning of the hybrid multibend achromat lattice at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2021, 24: 110701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.24.110701 [62] Hettel R. Status of the APS-U project[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Campinas, Brazil, 2021: 7-12. [63] Tanaka H, Ishikawa T, Goto S, et al. SPring-8 upgrade project[C]//Proceedings of the IPAC160. Busan, Korea, 2016: 2867-2870. [64] Schroer C G, Agapov I, Brefeld W, et al. PETRA IV: the ultralow-emittance source project at DESY[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2018, 25(Pt 5): 1277-1290. [65] Jiao Yi. Latest physics design of the HEPS accelerator[J]. Radiation Detection Technology and Methods, 2020, 4: 399. doi: 10.1007/s41605-020-00212-x [66] Jiao Yi, Chen Fusan, He Ping, et al. Modification and optimization of the storage ring lattice of the High Energy Photon Source[J]. Radiation Detection Technology and Methods, 2020, 4(4): 415-424. doi: 10.1007/s41605-020-00189-7 [67] Tao Ye. Groundbreaking ceremony at the High Energy Photon Source in Beijing[J]. Synchrotron Radiation News, 2019, 32: 40. doi: 10.1080/08940886.2019.1654833 [68] Liuzzo S M, Carmignani N, Chavanne J, et al. Optics adaptions for bending magnet beam lines at ESRF: short bend, 2-pole wiggler, 3-pole wiggler[C]//Proceedings of the IPAC’17. Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017: 666-669. [69] Duan Zhe, Chen Jinhui, GuoYuanyuan, et al. The swap-out injection scheme for the high energy photon source[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 4178-4181. [70] Liu L, Alves M B, de Sá F H, et al. Sirius commissioning results and operation status[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Campinas, Brazil, 2021: 13-18. [71] Karantzoulis E, Carniel A, Castronovo D, et al. Elettra and Elettra 2.0[C]//Proceedings of the IPAC2021. Campinas, Brazil, 2021: 1474-1476. [72] Ghasem H, Martin I P S, Singh B, et al. Progress with the diamond-II storage ring lattice[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Campinas, Brazil, 2021: 3973-3976. [73] Loulergue A, Amorin D, Brunelle P, et al. CDR baseline lattice for the upgrade of SOLEIL[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Campinas, Brazil, 2021: 1485-1488. [74] Steier C, Allézy A, Anders A, et al. Status of the conceptual design of ALS-U[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017: 4134-4137. [75] Baranov G, Bogomyagkov A, Morozov I, et al. Lattice optimization of a fourth-generation synchrotron radiation light source in Novosibirsk[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2021, 24: 120704. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.24.120704 [76] Ahmadi E, Jazayeri S M, Rahighi J. Characterizing and studying the nonlinear beam dynamics performance of Iranian Light Source Facility storage ring[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2019, 927: 140-150. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2019.01.078 [77] Tordeux M A, Alexandre P, Ben El Fekih R, et al. Injection schemes for the SOLEIL upgrade[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Particle Accelerator Conference. Campinas, Brazil, 2021: 796-798. -




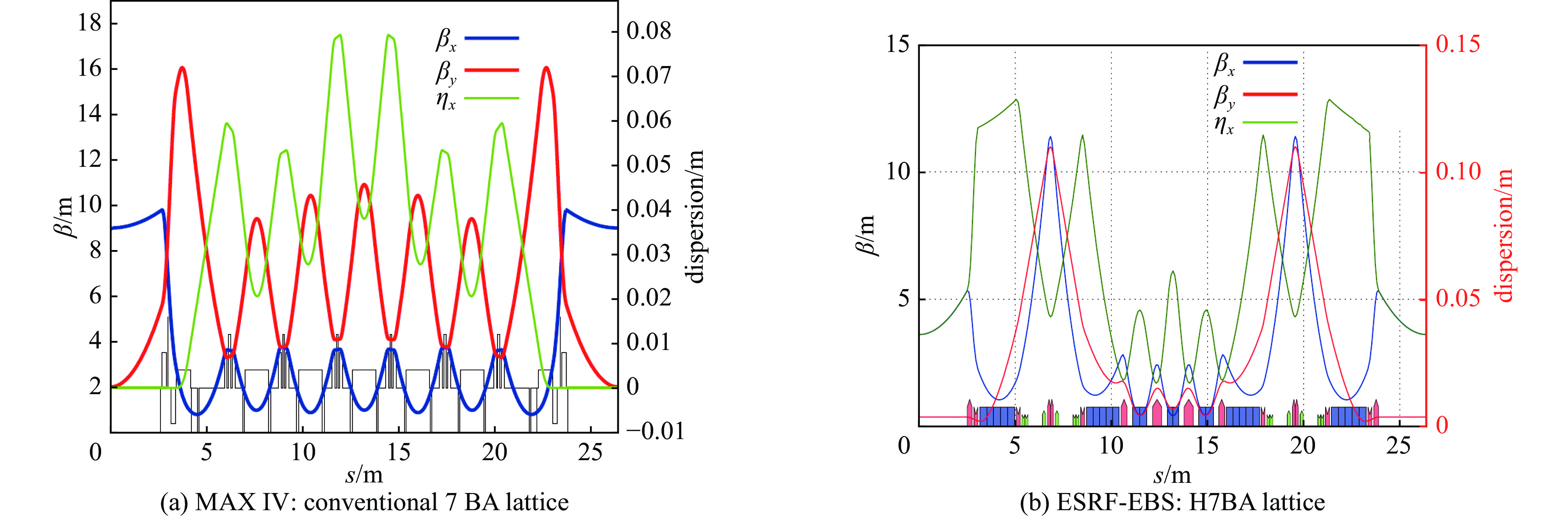
 下载:
下载: