Development of miniaturized inductor-isolated Marx generator
-
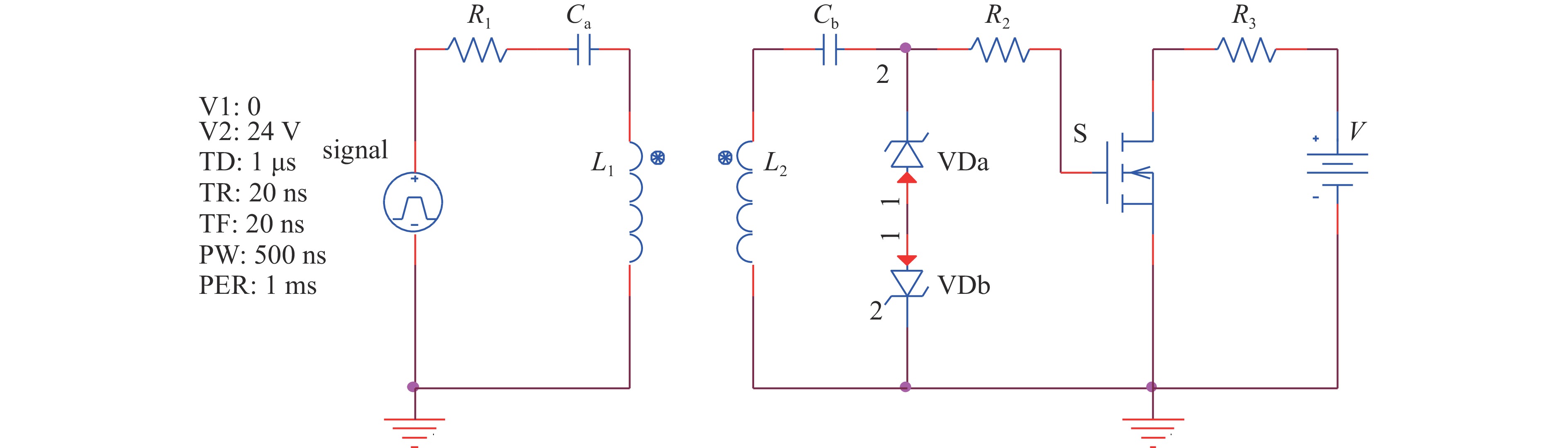
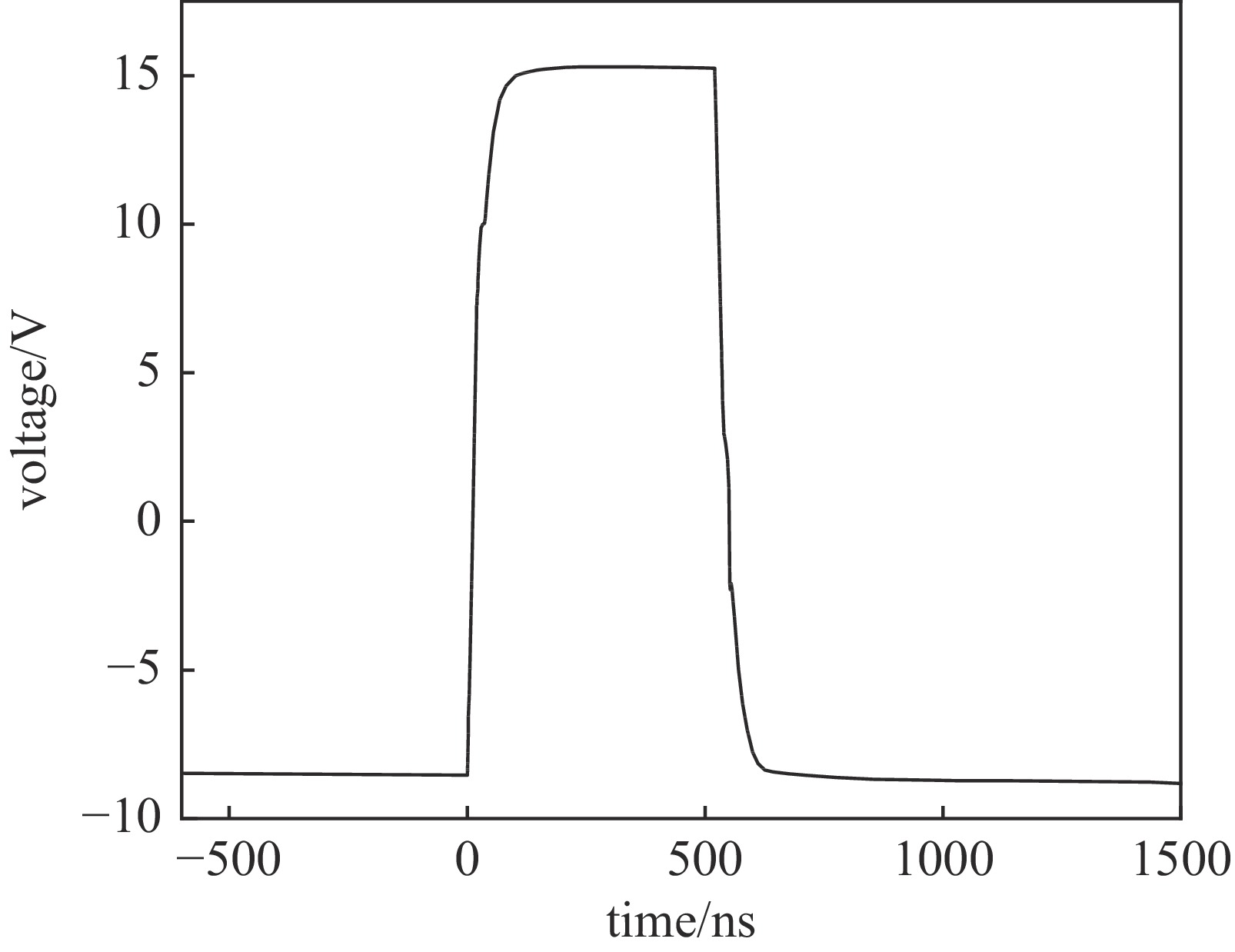
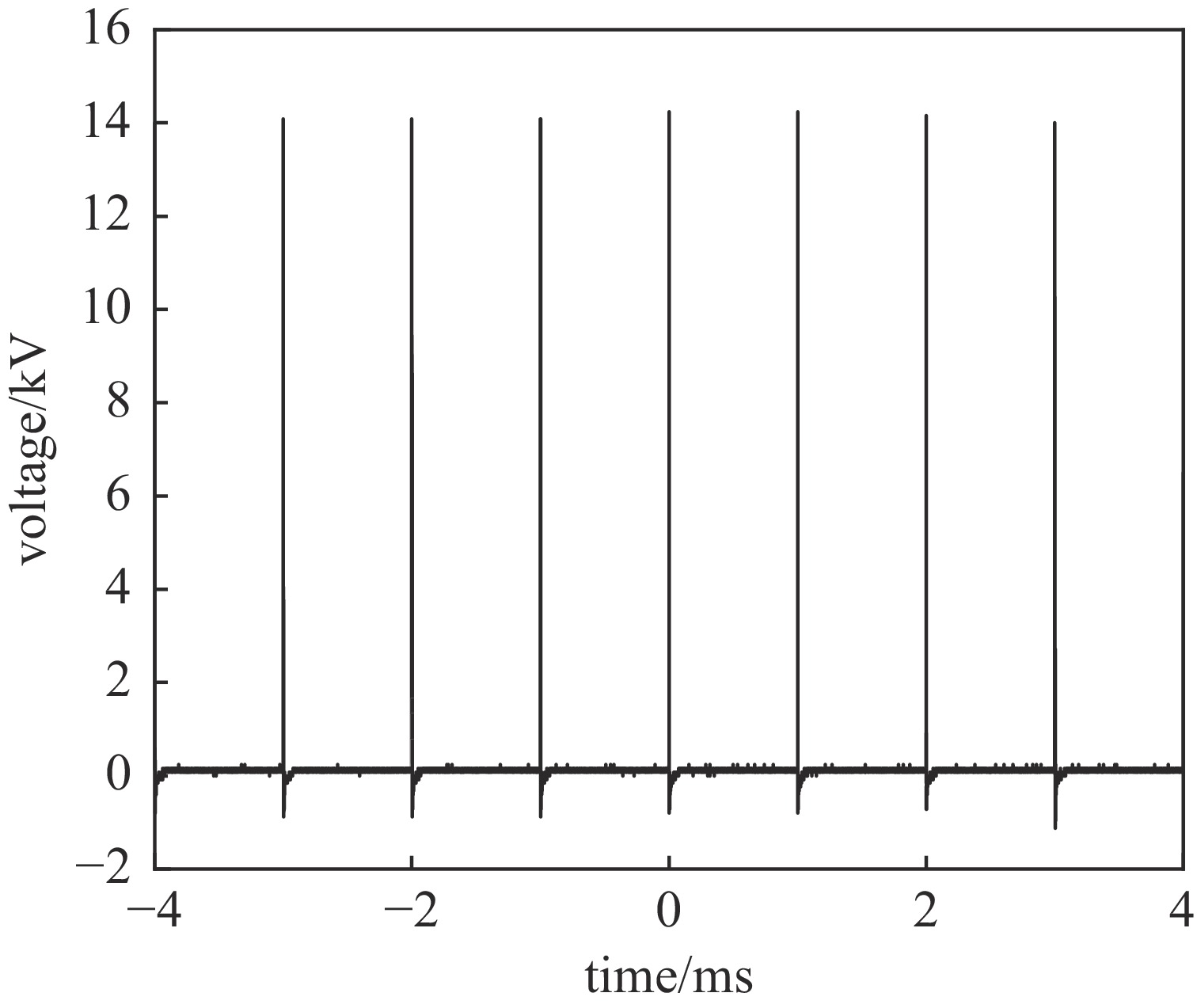
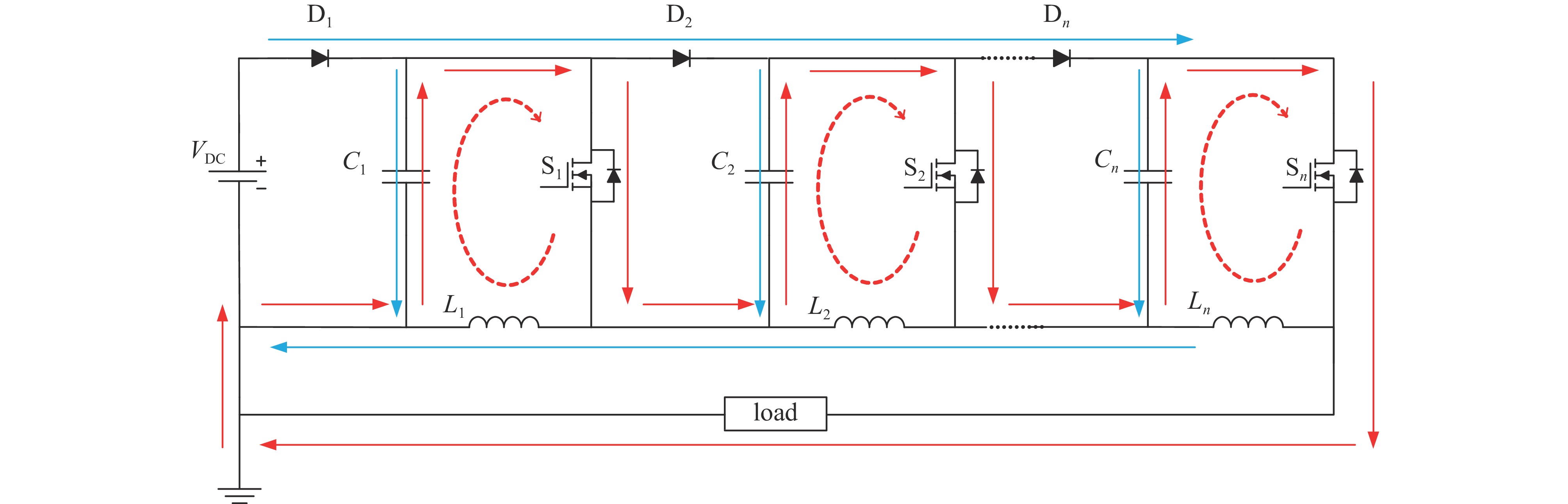
摘要: 随着脉冲功率技术的发展,纳秒脉冲电场被逐渐应用到等离子体水处理、不可逆电穿孔肿瘤消融等技术中。为了满足纳秒脉冲的应用需求,电源需要输出十几kV高压,拥有纳秒窄脉宽和快速的上升沿,同时尽量减小电源体积,降低成本。该纳秒脉冲电源采用电感隔离型Marx发生器结构,电路可以实现模块化叠加,电感隔离可以减少开关数量,抬升充电电压,以获得更高的电压输出。所设计的驱动电路仅需一路控制信号和一个直流供电模块,经功率放大和磁隔离后可同时控制所有放电管,该驱动电路结构简单、成本低、体积小,耐压水平高。所设计的24级电源样机,在50 kΩ阻性负载上,可输出0~14 kV电压,频率0.5~1 kHz,脉宽500 ns。该电源主电路的长宽高尺寸仅为23 cm×10 cm×12 cm。Abstract: With the development of pulsed power technology, nanosecond pulsed electric field has been gradually applied to plasma water treatment, irreversible electroporation for tumor ablation and other technologies. To meet the application requirements of nanosecond pulses, the power supply is required to output high voltage exceeding 10 kV, with narrow nanosecond pulse width and fast rising edge. At the same time, it is required to reduce the size and the cost. The nanosecond pulse power supply is an inductor-isolated Marx generator, whose circuit can realize modular superposition. Inductive isolation can reduce the number of switches and raise the charging voltage to obtain a higher voltage output. The driving circuit has only one control signal and one DC power supply module, which can control all discharge tubes at the same time after power amplification and magnetic isolation. The driving circuit has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, small volume and high voltage resistance. The power supply has 24 stages. Under the condition of 50 kΩ resistive load, high voltage pulses with 500 ns pulse width, amplitude of 0−14 kV and adjustable frequency of 0.5−1 kHz are generated. The size of the main circuit is only 23 cm×10 cm×12 cm.
-
Key words:
- Marx generator /
- pulsed power supply /
- pulsed power /
- inductive isolation
-
表 1 不同频率下的输出电压
Table 1. Simulated output voltage at different frequencies
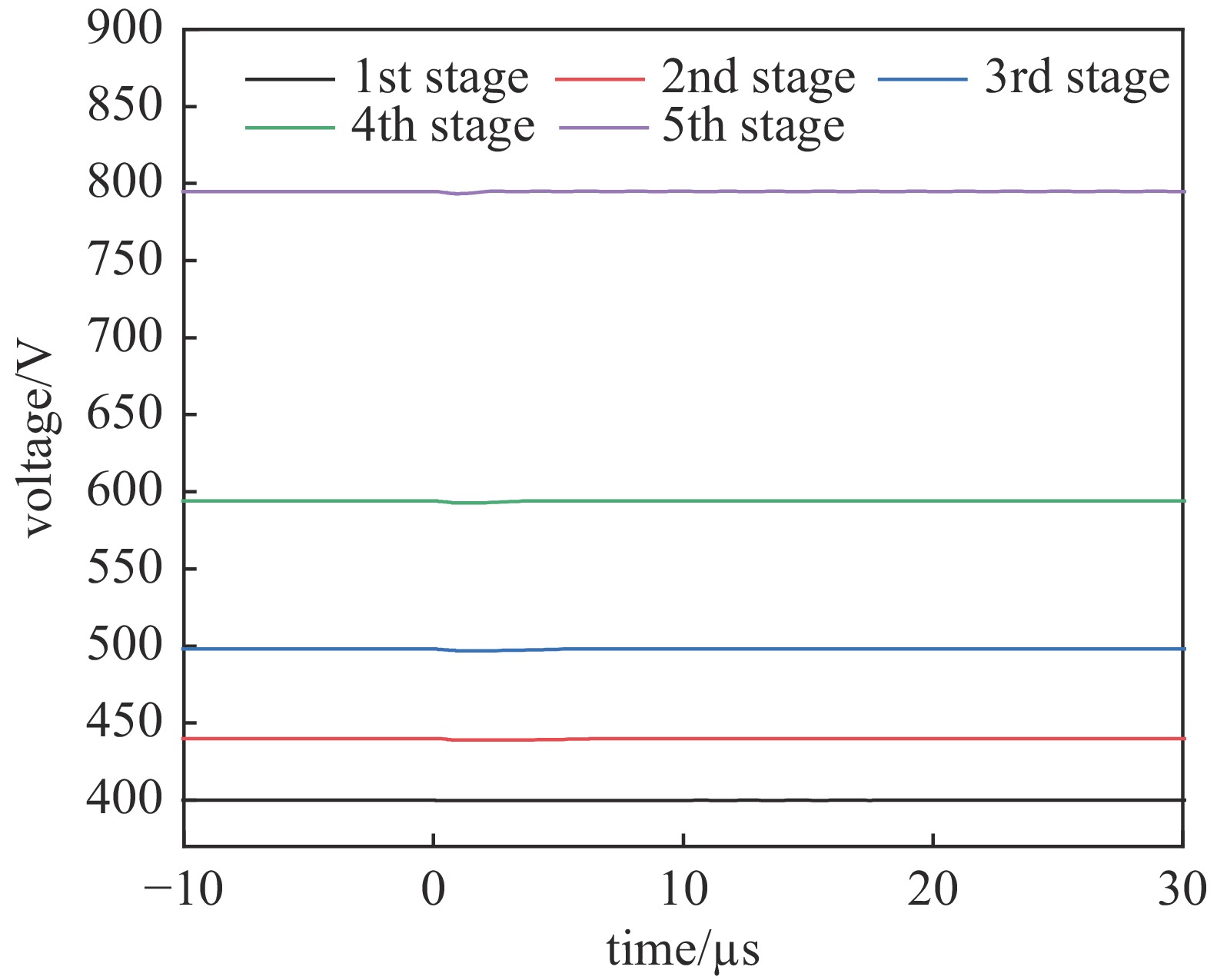
No. frequency/kHz output voltage/kV 1 0.1 2.0 2 0.5 2.2 3 1 2.3 4 5 2.6 5 10 2.7 表 2 电压输出结果
Table 2. Experimental results of voltage output
No. input voltage/V output voltage/kV 1 120 4 2 250 8 3 320 10 4 400 12 5 515 14 -
[1] 江伟华. 高重复频率脉冲功率技术及其应用: (6)代表性的应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:030201 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142603.30201Jiang Weihua. Repetition rate pulsed power technology and its applications: (VI) Typical applications[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 030201 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142603.30201 [2] 江伟华. 高重复频率脉冲功率技术及其应用: (7)主要技术问题和未来发展趋势[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:010201 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.010201Jiang Weihua. Repetition rate pulsed power technology and its applications: (VII) Major challenges and future trends[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 010201 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.010201 [3] 姚陈果, 米彦, 李成祥, 等. 纳秒级陡脉冲电场诱导癌细胞凋亡的实验及作用机理研究[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2008, 27(5):739-744 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2008.05.020Yao Chenguo, Mi Yan, Li Chengxiang, et al. The effects of nanosecond pulsed electric field on apoptosis of human ovarian carcinoma cell line SKOV3 and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2008, 27(5): 739-744 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2008.05.020 [4] 何天帅, 谭焜, 孙倩倩, 等. 不可逆电穿孔肿瘤消融器械发展现状[J]. 中国医疗器械杂志, 2021, 45(6):655-661 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7104.2021.06.014He Tianshuai, Tan Kun, Sun Qianqian, et al. Development status of irreversible electric perforated tumor ablation device[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Instrumentation, 2021, 45(6): 655-661 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7104.2021.06.014 [5] Beebe S J, Schoenbach K H. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields: a new stimulus to activate intracellular signaling[J]. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 2005, 4(2005): 297-300. [6] Yao Chenguo, Hu Xiaoqian, Mi Yan, et al. Window effect of pulsed electric field on biological cells[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2009, 16(5): 1259-1266. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2009.5293936 [7] Tang Tao, Wang Fei, Kuthi A, et al. Diode opening switch based nanosecond high voltage pulse generators for biological and medical applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2007, 14(4): 878-883. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2007.4286519 [8] Akiyama M, Sakugawa T, Hosseini S H R, et al. High-performance pulsed-power generator controlled by FPGA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2010, 38(10): 2588-2592. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2042463 [9] Yao Chenguo, Zhang Ximing, Guo Fei, et al. FPGA-controlled all-solid-state nanosecond pulse generator for biological applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2012, 40(10): 2366-2372. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2012.2188908 [10] 嵇保健, 王若冰, 洪峰, 等. 基于Marx电路的纳秒级高压脉冲电源设计[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(12):3758-3762Ji Baojian, Wang Ruobing, Hong Feng, et al. Design of nanosecond high-voltage pulsed power source based on Marx generator[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(12): 3758-3762 [11] Baek J W, Ryu M H, Yoo D W. High voltage pulse generator using boost converter array[C]//IEEE 2002 28th Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society. IECON 02. 2002: 395-399. [12] dos Santos K P, Neto T R F, Cruz C M T. Voltage impulse generator using boost converter array applied in electrical grounding systems[C]//2015 IEEE 13th Brazilian Power Electronics Conference and 1st Southern Power Electronics Conference (COBEP/SPEC). 2015: 1-5. [13] Baek J W, Yoo D W, Rim G H, et al. Solid state Marx generator using series-connected IGBTs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2005, 33(4): 1198-1204. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2005.852409 [14] 李盈. 软磁材料高频磁化特性和损耗特性分析[J]. 机电信息, 2019(8):60-61Li Ying. Analysis of high frequency magnetization and loss characteristics of soft magnetic materials[J]. Mechanical and Electrical Information, 2019(8): 60-61 [15] 饶俊峰, 宋子鸣, 王永刚, 等. 基于磁隔离驱动的亚微秒高压脉冲电源[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:115002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210332Rao Junfeng, Song Ziming, Wang Yonggang, et al. Sub-microsecond high voltage pulse power supply based on magnetic isolated driving[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 115002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210332 [16] 刘金涛. 便携式脉冲发生器可靠性技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2010: 9-18Liu Jintao. Research on reliability technology of portable pulse generator[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2010: 9-18 -




 下载:
下载: