Simulation of imaging ability of 11 MeV proton radiography with energy-loss imaging lens
-
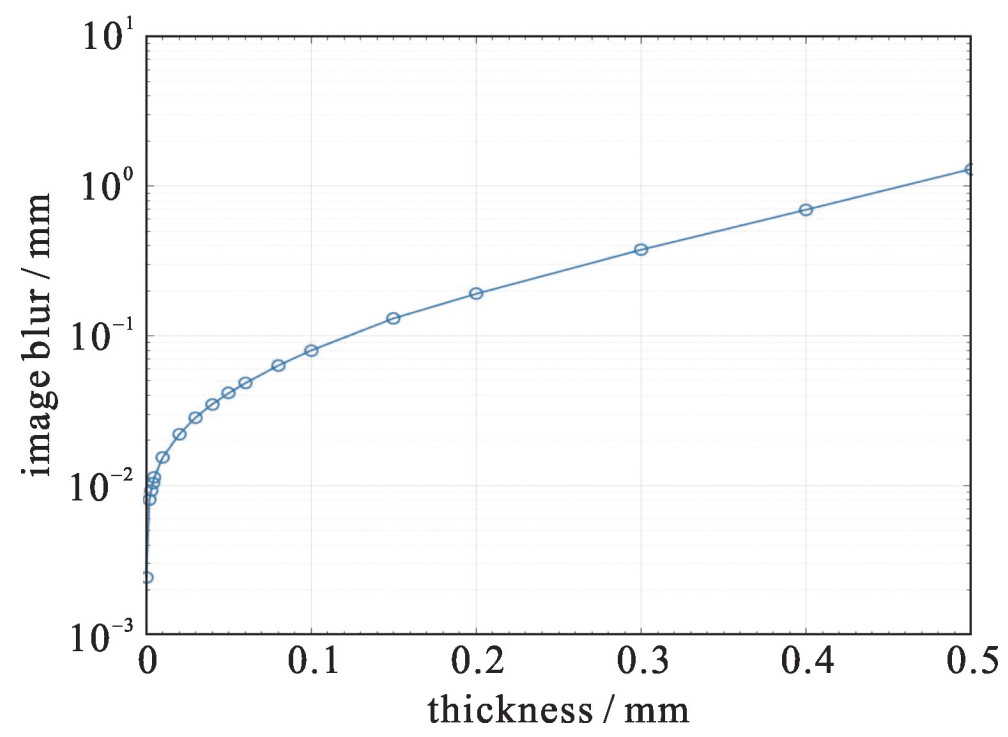
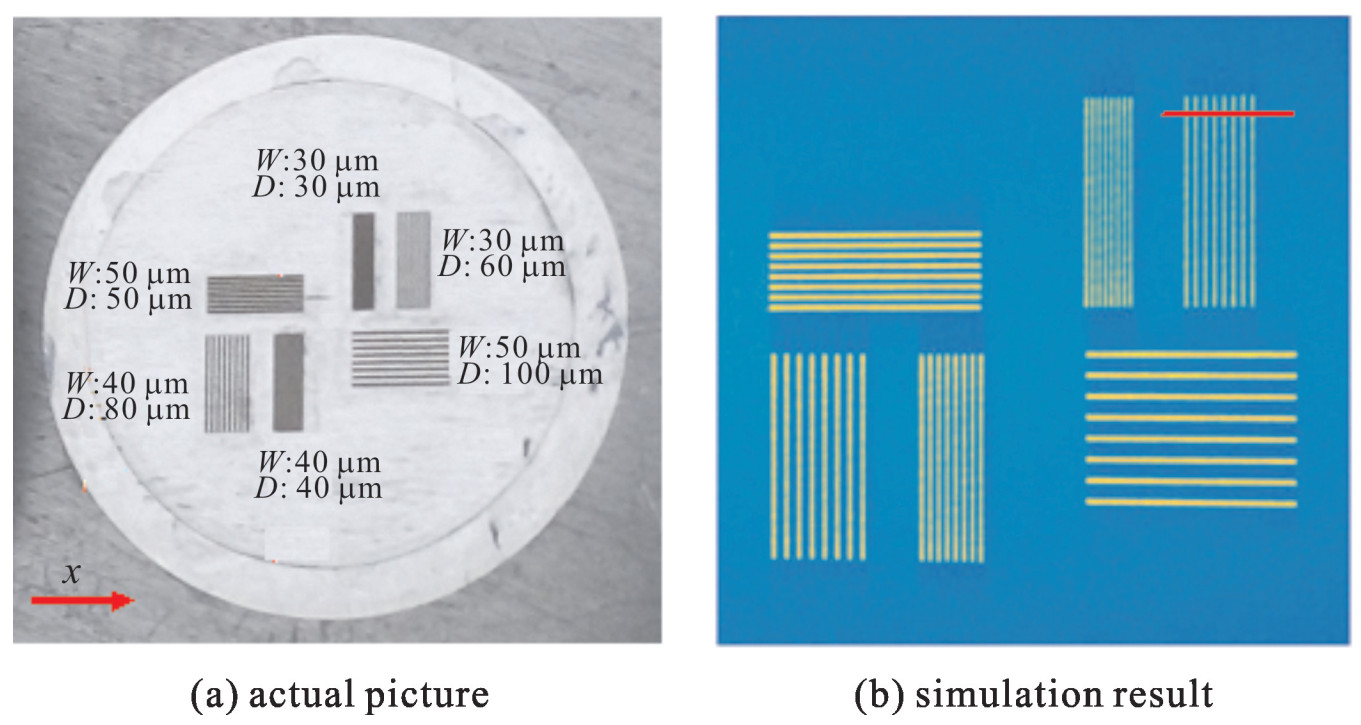
摘要: 透射质子的能损和散射角是质子照相成像模糊的主要来源。基于Zumbro聚焦成像磁透镜的质子照相技术,可基本消除散射角引起的成像模糊,实现几十μm的空间分辨,但无法对能损信息进行优化是其空间分辨能力难以进一步提升的主要原因。为利用透射质子的能损信息,进一步提高质子照相的空间分辨能力,提出了一种新型的成像磁透镜,称之为能损型聚焦成像磁透镜。基于11 MeV低能能损型质子照相的实验束线和Geant4模拟软件,建立全过程照相模型,研究11 MeV能损型成像束线的空间分辨能力。模拟研究表明:对于10 μm厚的Al箔,考虑点扩散函数等测量系统成像模糊的影响,11 MeV能损型成像束线可实现约30 μm的空间分辨。与等大型Zumbro磁透镜相比,空间分辨能力得到显著提升。Abstract: Energy loss and scattering angle of penetrating protons are main sources of image blur for proton radiography (PRAD). PRAD relying on Zumbro lens can basically eliminate the image blur caused by scattering angle and achieve spatial resolution of several tens microns. However, the chromatic blur resulted from energy loss cannot be optimized, and it is the major cause for limiting spatial resolution. To eliminate the influence of energy loss and make a further improvement of spatial resolution, a new type of magnetic lens is proposed, called energy-loss focused imaging lens. A 11 MeV low-energy energy-loss imaging beamline is designed and a numerical model is built for energy-loss PRAD by using GEANT4 to study its image ability in simulation. The simulation results show that the 11 MeV low-energy energy-loss PRAD can achieve about 30 μm spatial resolution for 10 μm Al target. Compared with Zumbro lens of the same size, the spatial resolution is improved obviously.
-
Key words:
- Zumbro lens /
- energy-loss imaging lens /
- Fourier plane /
- spatial resolution
-
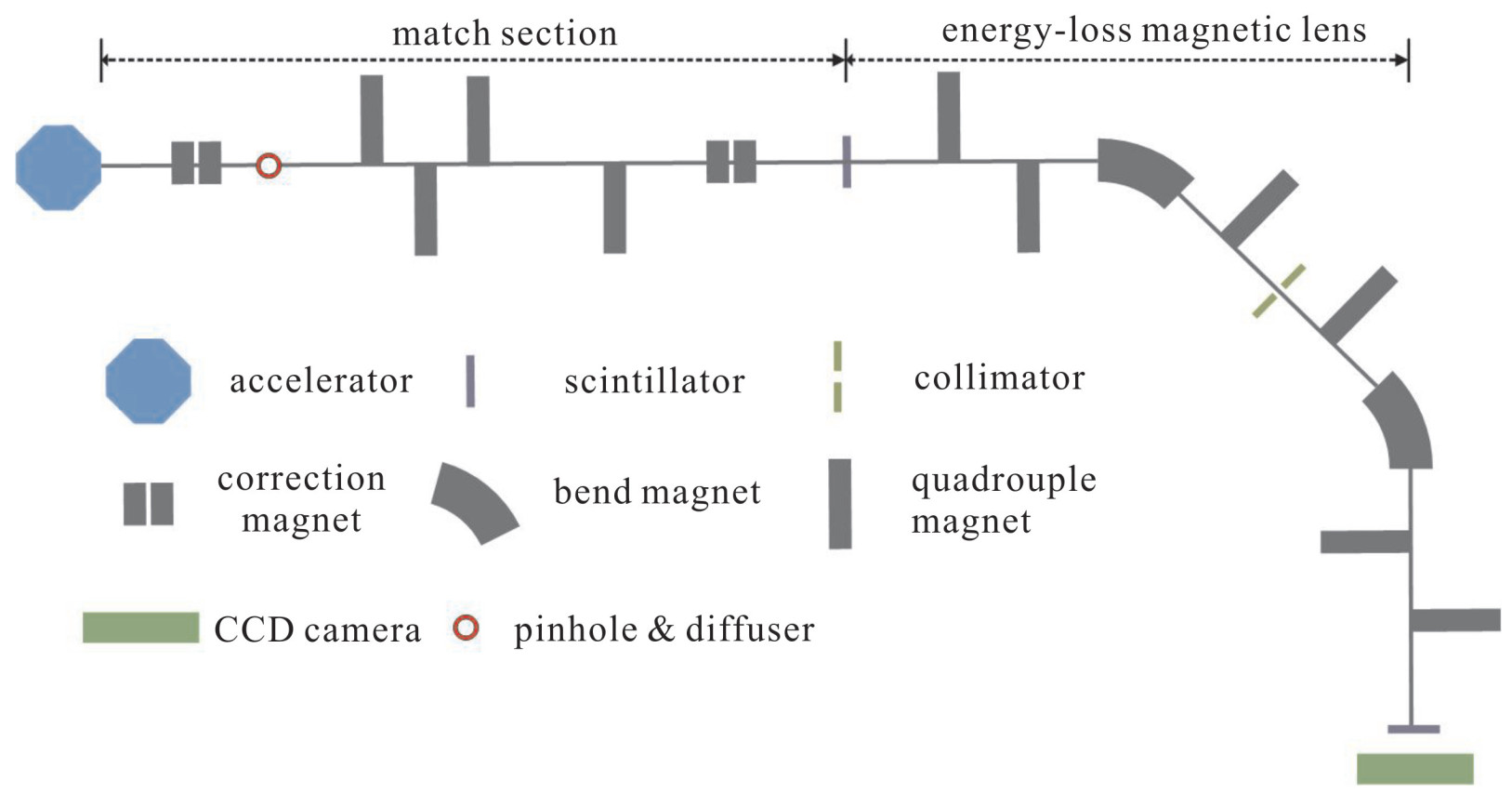
表 1 11 MeV能损型聚焦成像磁透镜参数
Table 1. Detailed parameter of 11 MeV energy-loss magnetic lens
parameter value parameter value M12(at the energy Fourier plane(EFP)) -0.299 mm/mrad M16(at the EFP) 611.44 m R126 (at the image plane) 2.912 m R166 (at the image plane) -385.3 m bending radius of dipoles 1 m bending angle of dipoles 45° drift space(first five) 0.8, 0.5, 0.5, 0.4, 0.4 m quadrupole length(first three) 0.15, 0.1, 0.1 m bending gradients 4.806 kg quadrupole gradients (first three) 72.234, -73.343, 56.692 kg·m-1 total length 7.4705 m beam pipeline radius 25 mm -
[1] Koehler A M. Proton radiography[J]. Science, 1968, 160: 303-304. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.303 [2] Mottershead C T, Zumbro J D. Magnetic optics for proton radiography[C]//Proceedings of Particle Accelerator Conference. 1997: 1397-1399. [3] Morris C L, King N S P, Kwiatkowski K, et al. Charged particle radiography[J]. Rep Prog Phys, 2013, 76: 046301. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/76/4/046301 [4] 何小中, 杨国君, 刘承俊. 质子照相磁透镜优化设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2008, 20(2): 297-300. http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/3041He Xiaozhong, Yang Guojun, Liu Chengjun. Optimization research on image lens of proton radiography. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2008, 20(2): 297-300 http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/3041 [5] King N S P, Ables E, Adams K, et al. An 800 MeV proton radiography facility for dynamic experiments[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1999, 424: 84-91 doi: 10.1016/S0168-9002(98)01241-8 [6] Morris C L, Ables E, Alrick K R, et al. Flash radiography with 24 GeV/c protons[J]. J Appl Phys, 2011, 109: 104905. doi: 10.1063/1.3580262 [7] Wei Tao, Yang Guojun, Li Yiding, et al. First experimental research of low energy proton radiography[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2014, 38: 087003. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/38/8/087003 [8] Zhang Xiaoding, Li Yiding, Yang Guojun, et al. Measurement of spatial resolution of 11 MeV proton radiography[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2014, 25: 060204. [9] Li Yiding, Zhang Xiaoding, Wei Tao, et al. Imaging principle and experiment results of an 11 MeV low-energy proton radiography system[J]. Nuclear Science and Technique, 2014, 25: 060203. [10] Li Yiding, Yang Guojun, Zhang Xiaoding, et al. 11 MeV low-energy magnifying PRAD at CAEP[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 2016, 814: 104-109. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2016.01.011 [11] Yang Guojun, Wei Tao, Zhang Zhuo, et al. Concept and design of charged particle optics using energy Fourier plane collimation[J]. Physical Review Special Topics——Accelerators and Beams, 2014, 17: 094701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.17.094701 -




 下载:
下载: