Pre-pulse mechanism and effects of parameters in semiconductor opening switches
-
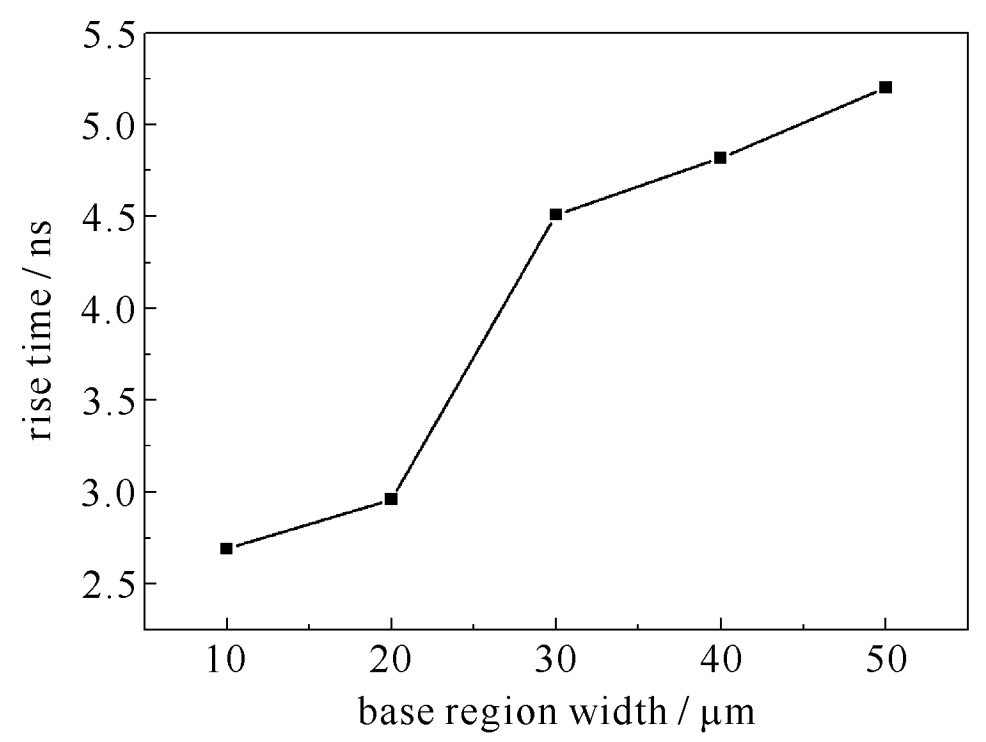
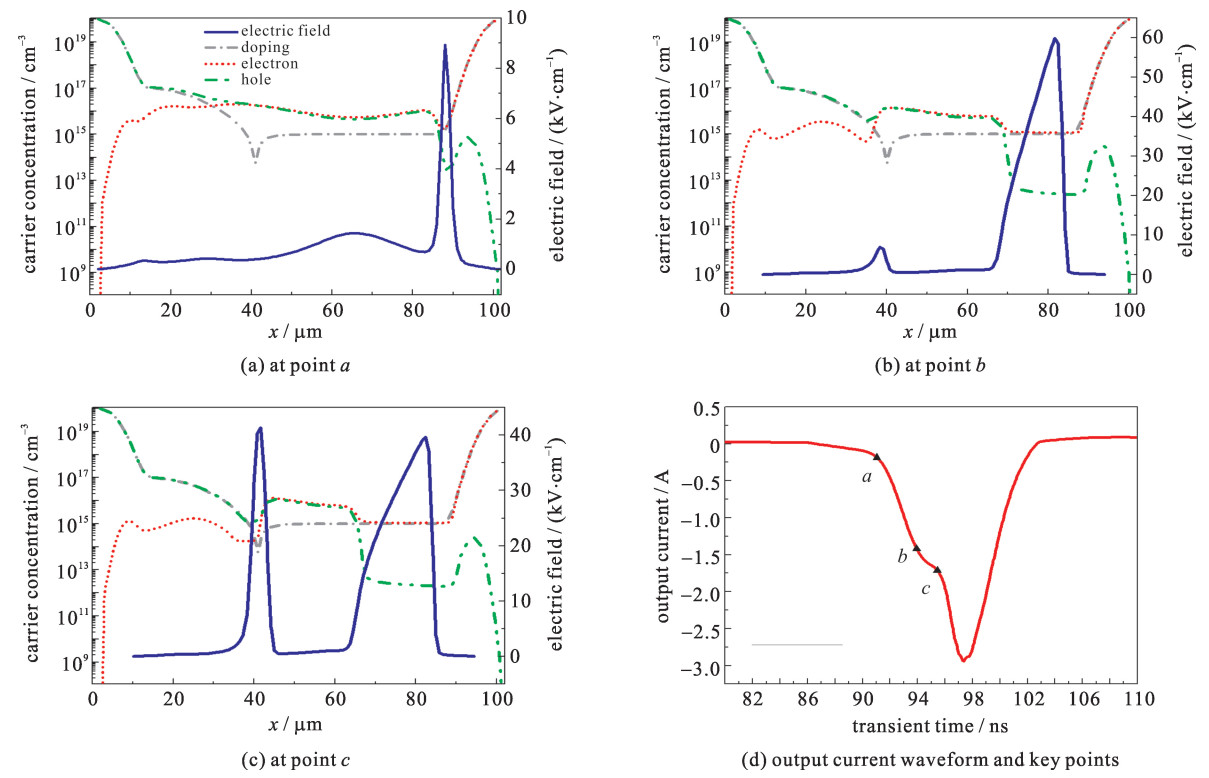
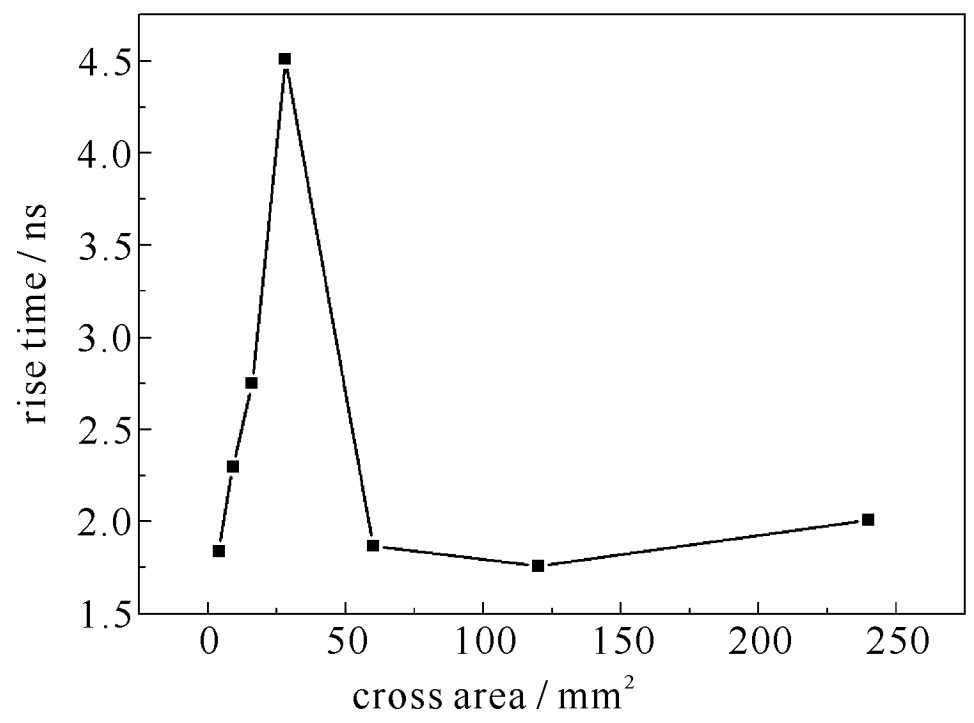
摘要: 半导体断路开关的输出电压中的预脉冲现象,严重影响了整个系统的输出脉冲前沿陡度和重复频率。针对半导体断路开关在反向截断过程中预脉冲产生的过程和机理进行了研究。利用Silvaco Atlas仿真软件对半导体断路开关正反向泵浦过程中载流子的迁移和电场的变化过程进行了详细考察,发现预脉冲的产生是由双边截断过程中N-N+结截断所引起的脉冲前沿变缓现象,其长短主要取决于P型轻掺杂区内的少子电子的迁移率,而脉冲前沿的陡度则取决于双边截断过程中的PN结截断过程。同时,对具有不同基区长度的器件,对其在不同泵浦电流密度下的情况进行了模拟和对比,发现器件基区越窄,脉冲前沿越陡,而预脉冲基本相等;低电流密度条件下只发生N-N+结单边截断,大电流密度条件下则发生双边截断,而双边截断的延迟更长,但脉冲前沿拐点更陡,截断更快。Abstract: As the key components of all solid-state pulse sources, semiconductor opening switches have the advantages of high frequency, long life, fast interruption, and large power capacity. The pre-pulse in output pulse voltage of semiconductor opening switches seriously affects the pulse rise time and the repetition frequency of the system. In this paper, the mechanism of the pre-pulse during the reverse interruption process is studied. The evolution process of the carriers and the electric field during the forward and reverse pumping processes of the semiconductor opening switches are investigated by using the simulation software Silvaco-Atlas. It is found that the pre-pulse is caused by the N-N+ junction interruption in the bilateral interruption process. The length of pre-pulse depends mainly on the mobility of minorities in the P-type region, and the slope of the pulse depends on the PN interruption process. Meanwhile, the devices with different base region lengths and different pumping conditions have been simulated and compared. It is found that the device base region is narrower, the pulse rises faster, and the pre-pulse is almost equal with each other. Under low current density conditions, only N-N+ junction interruption occurs; under high current density, bilateral interruption occurs. The delay of bilateral interruption is longer, but the pulse rises faster.
-
Key words:
- semiconductor opening switch /
- pre-pulse /
- rise time /
- mobility /
- bipolar drift /
- bilateral interruption
-
表 1 SOS数值模拟电路参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of SOS
C1/pF C2/pF L1/μH L2/μH R/Ω series number Vin/kV 400 400 3 0.1 50 100 15 -
[1] Kotov Y A, Mesyats G A, Rukin S N, et al. A novel nanosecond semiconductor opening switch for megavolt repetitive pulsed power technology: experiment and applications[C]//Pulsed Power Conference. 1993, 1: 134. [2] 刘健, 张斌. 半导体断路开关器件研制和实验研究[J]. 电力电子技术, 2006, 40(5): 130-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLDZ200605047.htmLiu Jian, Zhang Bin. Experimental study of semiconductor opening switch device. Power Electronics, 2006, 40(5): 130-132 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLDZ200605047.htm [3] 王古森, 王洪广, 戚玉佳, 等. 半导体断路开关输出脉冲宽度的参数影响规律[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26: 063021. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.063021Wang Gusen, Wang Hongguang, Qi Yujia, et al. Influences of key parameters on width of output pulses by semiconductor opening switch. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 063021 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.063021 [4] 何锋, 苏建仓, 李永东, 等. 半导体断路开关数值模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2005, 17(12): 1893-1896. http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/76He Feng, Su Jiancang, Li Yongdong, et al. Numerical simulation of semiconductor opening switch. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2005, 17(12): 1893-1896 http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/76 [5] 李中杰, 李永东, 王洪广, 等. 半导体断路开关电路-流体耦合数值模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(6): 1411-1414. http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/4667Li Zhongjie, Li Yongdong, Wang Hongguang, et al. Numerical simulation of semiconductor opening switch with circuit-fluid coupled model. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(6): 1411-1414 http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/4667 [6] Lyubutin S K, Mesyats G A, Rukin S N, et al. Repetitive nanosecond all-solid-state pulsers based on SOS diodes[C]//Pulsed Power Conference. 1997, 2: 992-998. [7] Rukin S N, Lyubutin S K, Kostirev V V, et al. Repetitive 200 kV nanosecond all solid state pulser with a semiconductor opening switch[C]//Pulsed Power Conference. 1995, 2: 1211-1214. [8] Rostov V V, Eltchaninov A A, Korovin S D, et al. Generation of high peak and high average power subnanosecond-width 10-GHz microwave pulses[C]//13th International Symposium on High Current Electronic. 2004: 250-253. [9] Ponomarev A V, Lozhkin S V, Rukin S N, et al. SOS-based generator with 100-kHz pulse repetition frequency[C]//14th Symposium on High Current Electronics. 2006: 309-312. [10] 苏建仓, 丁臻捷, 丁永忠, 等. S-5N全固态重复频率脉冲发生器[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2004, 16(10): 1337-1340. http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/522Su Jiancang, Ding Zhenjie, Ding Yongzhong, et al. S-5N all-solid-state repetitive frequency pulsed generator. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2004, 16(10): 1337-1340 http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/522 [11] 苏建仓, 丁永忠, 宋志敏, 等. 半导体断路开关实验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2002, 14(6): 949-953. http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/1544Su Jiancang, Ding Yongzhong, Song Zhimin, et al. Experimental study on the characteristics of semiconductor opening switch. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2002, 14(6): 949-953 http://www.hplpb.com.cn/article/id/1544 [12] Jiang W, Yatsui K, Takayama K, et al. Compact solid-state switched pulsed power and its applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2004, 92(7): 1180-1196. [13] 肖建平. DSRD高功率超宽谱脉冲源及其功率合成初探[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2007, 7(4): 15-18.Xiao Jianping. An available ultrafast switch for high power UWS applications DSRD. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2007, 7(4): 15-18 [14] 林舒, 李永东, 王洪广, 等. 半导体断路开关截断过程模拟的缩比模型[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(9): 2341-2345. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132509.2341Lin Shu, Li Yongdong, Wang Hongguang, et al. Scaled model for simulating opening process of semiconductor opening switches. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(9): 2341-2345 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132509.2341 [15] Benda H, Spenke E. Reverse recovery processes in silicon power rectifiers[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1967, 55(8): 1331-1354. [16] 余岳辉, 梁琳. 脉冲功率器件及其应用[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2010.Yu Yuehui, Liang lin. Pulsed power devices and applications. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2010 -





 下载:
下载: