Inversion algorithm of vertical visibility based on lidar and its error evaluation
-
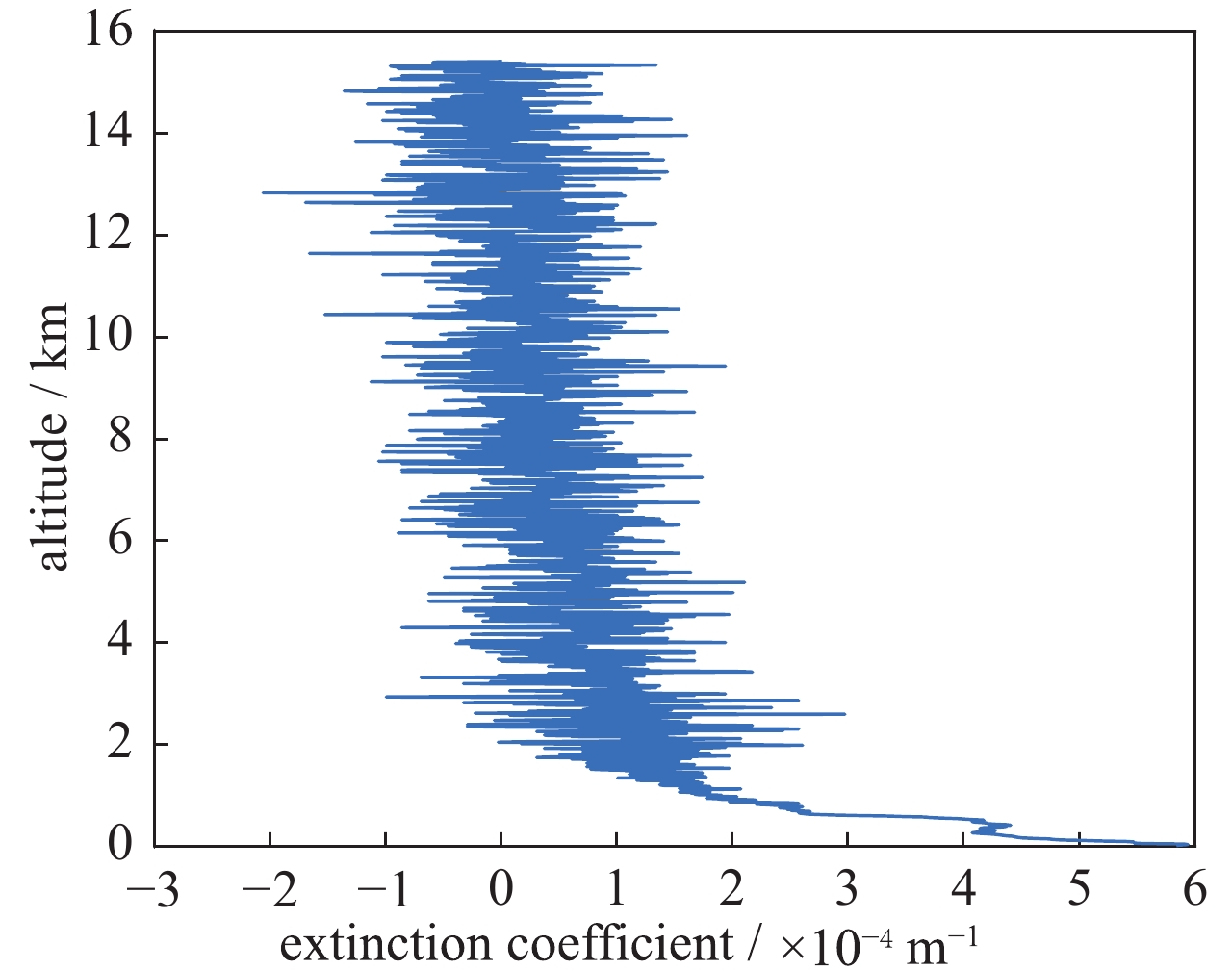
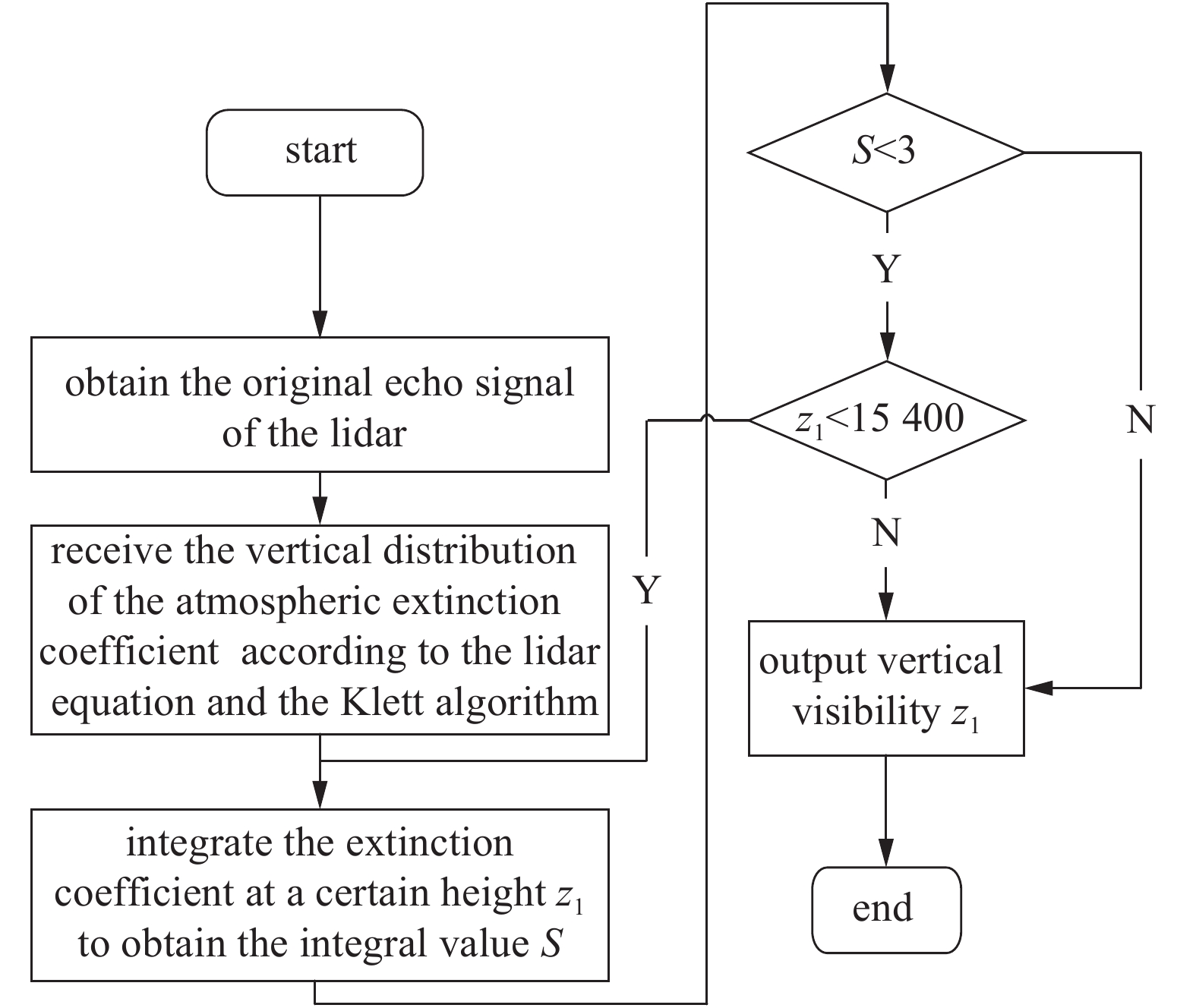
摘要: 针对大气垂直方向上消光系数分布不均匀难以用传统方法直接测量垂直能见度的问题,提出了一种基于激光雷达探测垂直能见度的计算方法。根据大气辐射传输基本原理,借助于辐射传输方程,推导出了垂直能见度的计算公式;然后利用激光雷达原理方程和Klett算法反演出大气垂直方向上的消光系数分布,基于此提出了垂直能见度的迭代算法。最后,利用灰色模型GM(1,1)和批统计算法,对激光雷达反演得到的后向散射系数进行了评估,给出了误差置信区间为(0.760±0.339)×10−4(srad·km)−1。结果表明,该方法是一种特别有效的计算垂直能见度的方法,符合探测的基本需求,且误差小精度高。Abstract: To solve the problem that the non-uniform distribution of extinction coefficients in the vertical direction of the atmosphere makes it difficult to directly measure the vertical visibility by traditional methods, this paper presents a method for calculating the vertical visibility based on lidar detection. Firstly, according to the basic principle of atmospheric radiation transmission and radiation transfer equation, it deduces the calculation formula of vertical visibility, which solves the problem that there is no specific formula for calculating vertical visibility. Secondly, it inverts the extinction coefficient distribution in the vertical direction of the atmosphere by using the lidar equation and Klett algorithm. On this basis, it proposes an iterative algorithm for vertical visibility. Finally, it uses the gray model GM(1,1) and batch statistics algorithm to evaluate the backscattering coefficient obtained by laser radar inversion, and gives the error confidence interval (0.760±0.339)×10−4(srad·km)−1. The results show that the method is a particularly effective one for calculating vertical visibility, which meets the basic requirements of detection, with small error and high precision.
-
Key words:
- lidar /
- vertical visibility /
- extinction coefficient /
- radiative transfer equation /
- GM(1,1) model /
- batch statistics
-
表 1 CL51型激光雷达主要技术指标
Table 1. The main technical indicators of CL51 lidar
laser wavelength/nm operating mode pulse energy/μWs repetition rate/kHz optics focus/mm effective lens diameter/mm measurement range/km range resolution/m measurement interval/s field-of-view divergence/mrad 910 pulsed 3.0 6.5 450 148 0~15.4 10 6 0.56 表 2 后向散射系数的批统计结果分析表
Table 2. Backscattering coefficient deviation result analysis by batch statistics
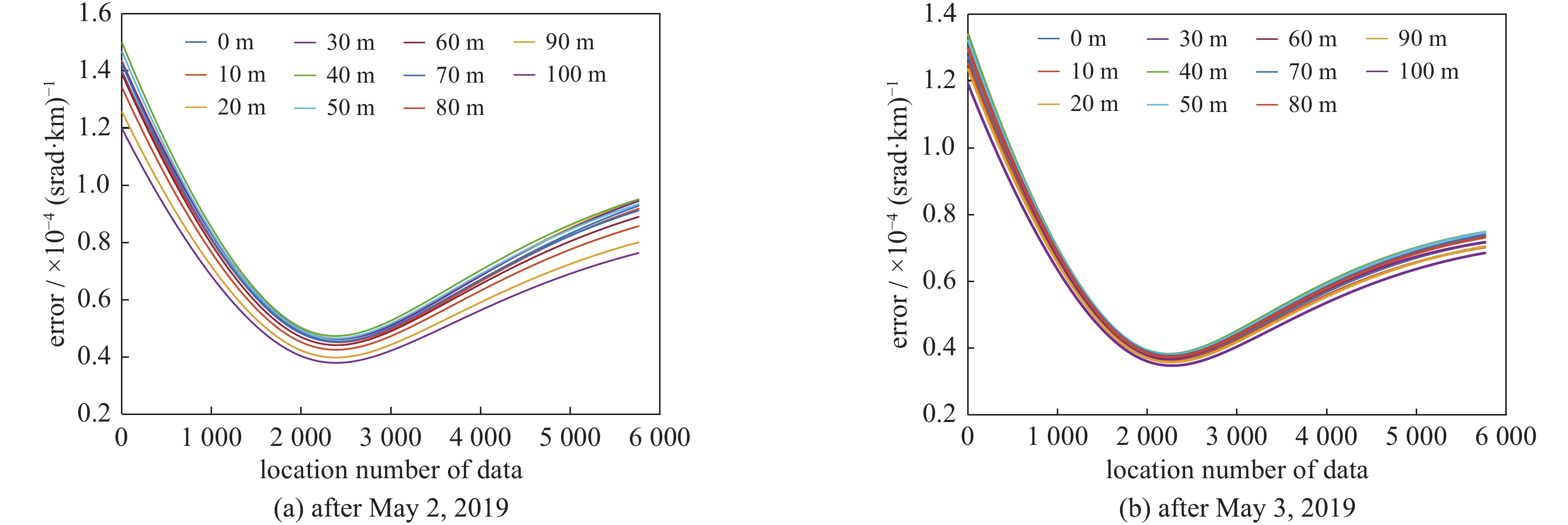
date altitude/m mean of error/10−4(srad·km)−1 standard deviation of error/10−4(srad·km)−1 confidence interval/10−4(srad·km)−1 2019-05-02 0 0.726 0.225 0.726±0.318 10 0.721 0.223 0.721±0.316 20 0.743 0.231 0.743±0.327 30 0.741 0.230 0.741±0.326 40 0.760 0.240 0.760±0.339 50 0.746 0.235 0.746±0.332 60 0.708 0.223 0.708±0.223 70 0.726 0.228 0.726±0.322 80 0.683 0.215 0.683±0.304 90 0.639 0.201 0.639±0.284 100 0.609 0.192 0.609±0.192 2019-05-03 0 0.604 0.203 0.604±0.287 10 0.593 0.200 0.593±0.282 20 0.608 0.206 0.608±0.292 30 0.608 0.207 0.608±0.292 40 0.632 0.213 0.632±0.302 50 0.628 0.211 0.628±0.298 60 0.619 0.207 0.619±0.293 70 0.618 0.207 0.617±0.292 80 0.615 0.207 0.615±0.292 90 0.590 0.197 0.590±0.279 100 0.571 0.190 0.571±0.269 -
[1] 中国气象局. 地面气象观测规范[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2003.China Meteorological Administration. Ground weather observation criterion. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2003 [2] 冯帅, 蒋立辉, 熊兴隆, 等. 含有突变信号的激光雷达能见度反演[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2017, 46(3):222-228. (Feng Shuai, Jiang Lihui, Xiong Xinglong, et al. Lidar visibility inversion with breakpoint signal[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(3): 222-228 [3] 熊兴隆, 闫朴, 蒋立辉, 等. 测风激光雷达应用于机场能见度及云底高探测[J]. 激光与红外, 2010, 40(8):817-820. (Xiong Xinglong, Yan Pu, Jiang Lihui, et al. Application of wind lidar in detection of the airport’s visibility and cloud base height[J]. Laser and Infrared, 2010, 40(8): 817-820 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2010.08.004 [4] 吕炜煜, 苑克娥, 魏旭, 等. 对流层气溶胶和水汽的车载激光雷达系统的探测[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2016, 45(3):200-206. (Lü Weiyu, Yuan Ke’e, Wei Xu, et a1. A mobile lidar system for aerosol and water vapor detection in troposphere with mobile lidar[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(3): 200-206 [5] 熊兴隆, 蒋立辉, 冯帅. Mie散射激光雷达回波信号处理方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2012, 41(1):89-95. (Xiong Xinglong, Jiang Lihui, Feng Shuai. Return signals processing method of Mie scattering lidar[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2012, 41(1): 89-95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.01.018 [6] Kyung W K. The comparison of visibility measurement between image-based visual range, human eye-based visual range, and meteorological optical range[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2018, 190: 74-86. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.07.020 [7] 李浩, 孙学金, 单陈华, 等. 关于气象能见度理论与观测的讨论[J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 14(3):297-302. (Li Hao, Sun Xuejin, Shan Chenhua, et al. Basis theory and observation of meteorological visibility[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2013, 14(3): 297-302 [8] 孙学金, 王晓蕾, 李浩, 等. 大气探测学[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2009: 362-367.Sun Xuejin, Wang Xiaolei, Li Hao, et al. Atmospheric detection theory. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2009: 362-367 [9] Cai Y, Korotkova O, Eyyuboğlu H T, et al. Active laser radar systems with stochastic electromagnetic beams in turbulent atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(20): 15834-15846. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.015834 [10] Ji Hongzhu, Chen Siying, Zhang Yinchao, et al. Calibration method for the reference parameter in Fernald and Klett inversion combining Raman and Elastic return[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2017, 188: 71-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2016.06.041 [11] 田鹏飞, 张镭, 曹贤洁, 等. 基于Fernald和Klett方法确定气溶胶消光系数边界值[J]. 量子电子学报, 2013, 30(1):57-65. (Tian Pengfei, Zhang Lei, Cao Xianjie, et al. A novel approach based on Fernald’s and Klett’s method to determine the atmospheric extinction coefficient boundary value[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2013, 30(1): 57-65 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2013.01.011 [12] 林洪桦. 测量误差与不确定度评估[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2009: 384-397.Lin Honghua. Measurement error and uncertainty assessment. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2009: 384-397 [13] Hessling J P. Propagation of dynamic measurement uncertainty[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2011, 22(10): 105-117. [14] Engel R, Baade H. Quantifying impacts on the measurement uncertainty in flow calibration arising from dynamic flow effects[J]. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 2014, 44(8): 51-60. [15] Xia X, Meng Y, Shi B J, et al. Bootstrap forecasting method of uncertainty for rolling bearing vibration performance based on GM(1,1)[J]. Journal of Grey System, 2015, 27(2): 78-92. [16] Tang D, Peng J. Evaluation about measurement uncertainty of vertical metal oil tank based on grey system theory[C]//IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Informatics and Cognitive Computing. 2011: 235-239. [17] Reese S E, Archer K J, Therneau T M, et al. A new statistic for identifying batch effects in high-throughput genomic data that uses guided principal component analysis[J]. Bioinformatic, 2013, 29(22): 2877-2883. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt480 [18] 汪启跃, 王中宇, 王岩庆, 等. 乏信息空间机械臂随机振动信号的灰自助评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(4):858-864. (Wang Qiyue, Wang Zhongyu, Wang Yanqing, et al. Estimation of space manipulator random vibration signals with poor information based on grey bootstrap method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(4): 858-864 [19] Wang Y, Wang Z, Sun J, et al. Dynamic uncertainty analysis for random vibration signals in flight test[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2014, 51(6): 1966-1972. doi: 10.2514/1.C032710 [20] Zhang H, Tian X, Deng X, et al. Multiphase batch process with transitions monitoring based on global preserving statistics slow feature analysis[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 293: 64-86. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.02.091 [21] 王丰效. 基于合作对策的非等距灰色组合预测模型[J]. 沈阳理工大学学报, 2006, 25(6):35-38. (Wang Fengxiao. Unequal interval gray combination forecasting model based on cooperative game[J]. Transactions of Shenyang Ligong University, 2006, 25(6): 35-38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1251.2006.06.011 -




 下载:
下载: