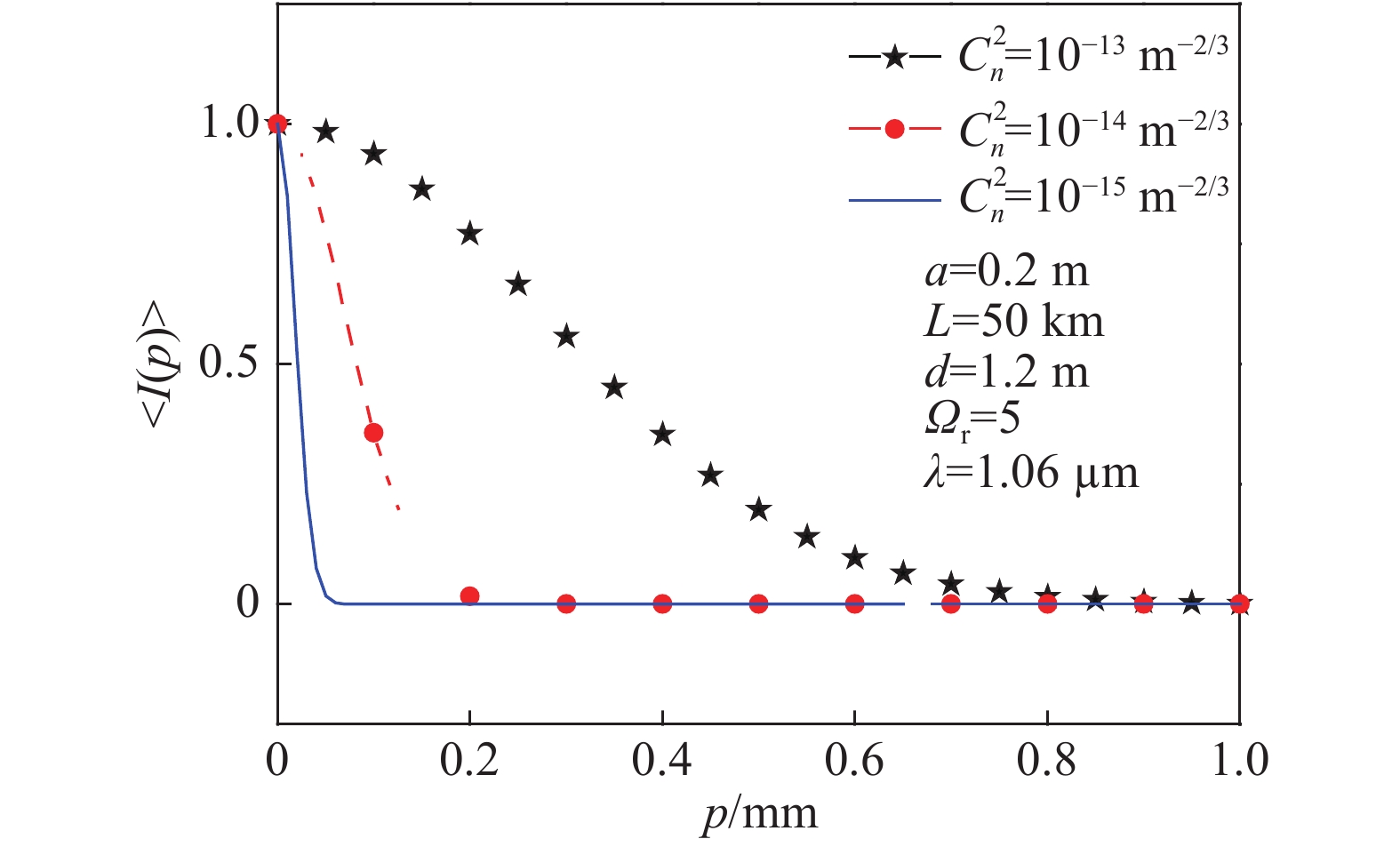
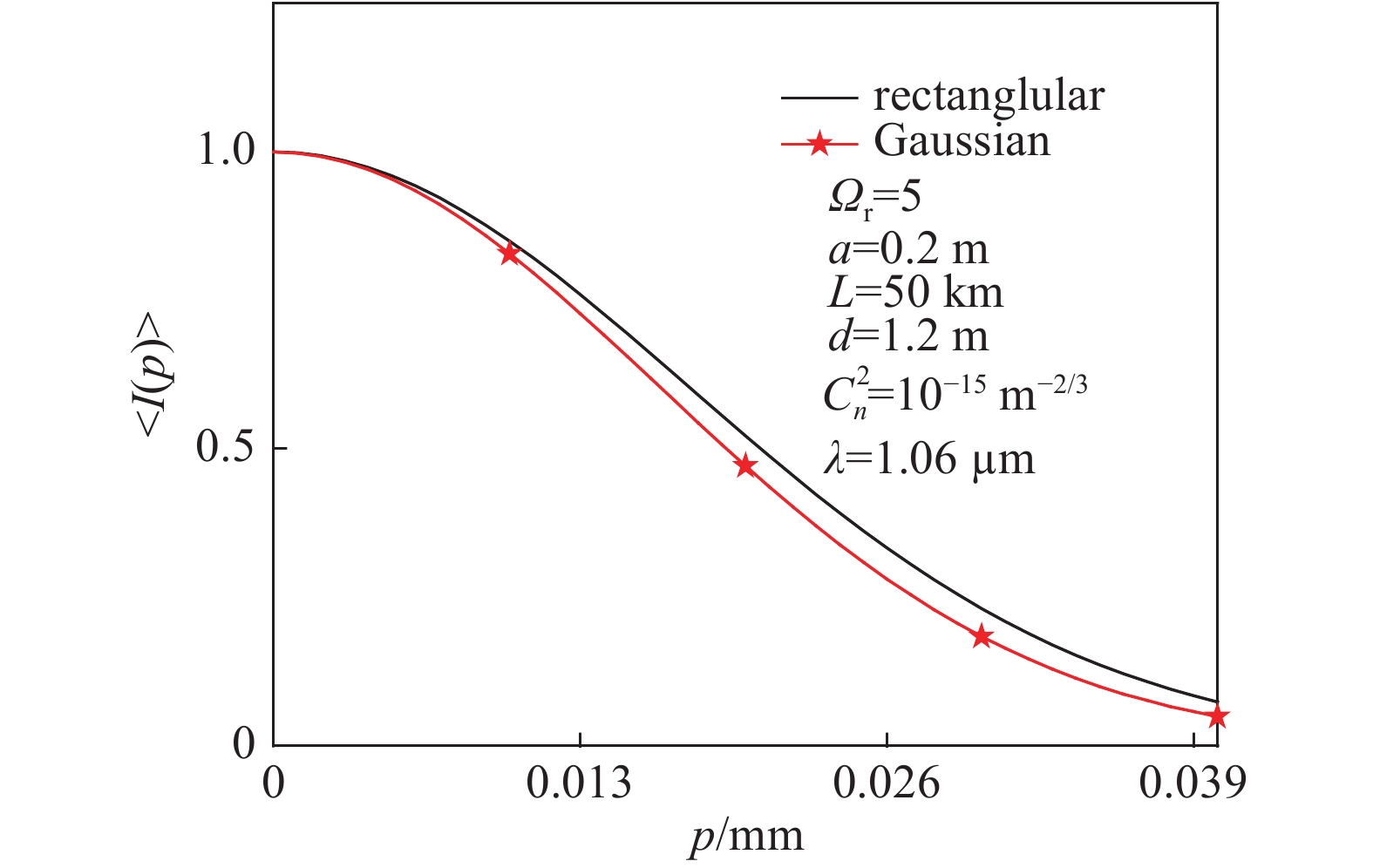
| [1] |
Fried D L. Optical resolution through a randomly inhomogeneous medium for very long and very short exposures[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1966, 56: 1372-1379. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.56.001372
|
| [2] |
Ishimaru A. Limitation on image resolution imposed by a random medium[J]. Applied Optics, 1978, 17: 348-352. doi: 10.1364/AO.17.000348
|
| [3] |
Mahajan V N, Lum B K. Imaging through atmospheric turbulence with annular pupils[J]. Applied optics, 1981, 20: 3233-3237. doi: 10.1364/AO.20.003233
|
| [4] |
Yura H T. Signal-to-noise ratio of heterodyne lidar systems in the presence of atmospheric turbulence[J]. Optica Acta International Journal of Optics, 1979, 26: 627-644.
|
| [5] |
Shapiro J H, Capron B A, Harney R C. Imaging and target detection with a heterodyne-reception optical radar[J]. Applied optics, 1981, 20: 3292-3313. doi: 10.1364/AO.20.003292
|
| [6] |
Wang S J, Plonus M A. Imaging through turbulence: Degradation of signal-to-noise ratio[J]. Optics Communications, 1984, 50: 73-78. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(84)90139-1
|
| [7] |
Elsebelgy B, Plonus M, Yang C C. Double-passage imaging of an object behind a random medium[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1995, 12: 307-313. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.12.000307
|
| [8] |
Loktev L, Svyatoslav S, Gleb V. Speckle imaging through turbulent atmosphere based on adaptable pupil segmentation[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36: 2656-2658. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002656
|
| [9] |
Gal R, Kiryati N. Progress in the restoration of image sequences degraded by atmospheric turbulence[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2014, 48: 8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2014.04.007
|
| [10] |
Douglas A, Jefferies M, Stuart M, et al. High-resolution speckle imaging through strong atmospheric turbulence[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(11): 12116-12129. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.012116
|
| [11] |
Plemmons R J, Prasad S, Zhang Qiang. Deblurring compressive spectro-polarimetric images taken trough atmospheric turbulence[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 6(86): 13-17.
|
| [12] |
Cui L Y, Cao X G, Zhou F G. Influence of moderate-to-strong non-Kolmogorov turbulence on the imaging system by atmospheric turbulence MTF[J]. Optik, 2015, 126: 191-198. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.08.147
|
| [13] |
Plonus M A, Ouyang C F, Wang S H. Intensity properties of partially coherent beam waves[J]. Applied Optics, 1980, 19: 3082-3085. doi: 10.1364/AO.19.003082
|
| [14] |
Plonus M A, Wang S J. Quadratic structure functions and scintillation[J]. Applied Optics, 1985, 24: 570-571. doi: 10.1364/AO.24.000570
|




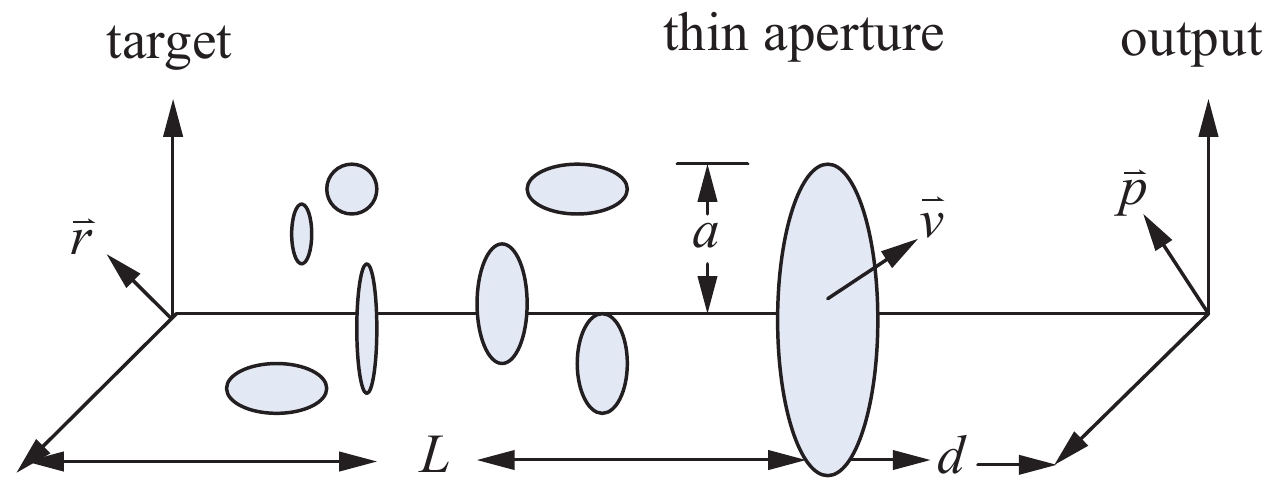
 下载:
下载: