Multi-scale simulation and analysis of gas evacuation processes in a microcavity
-
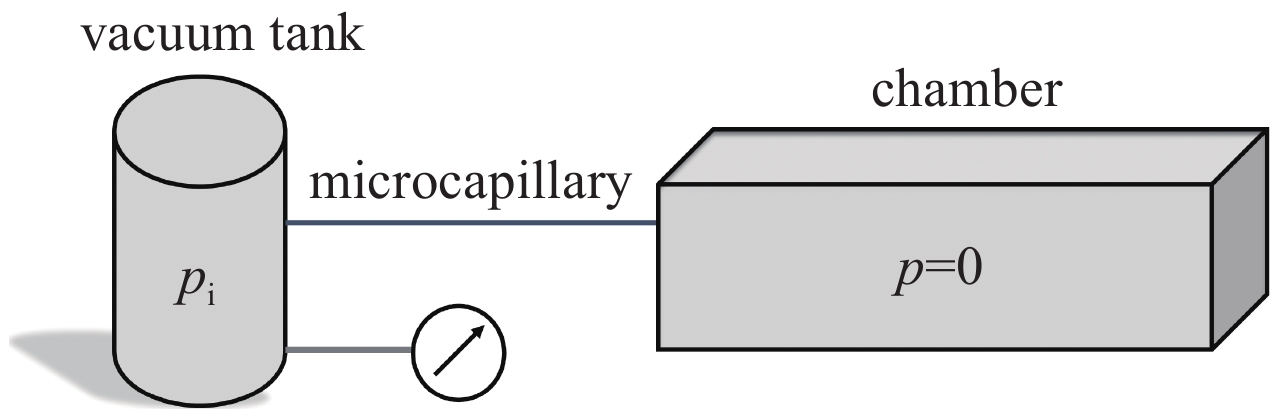
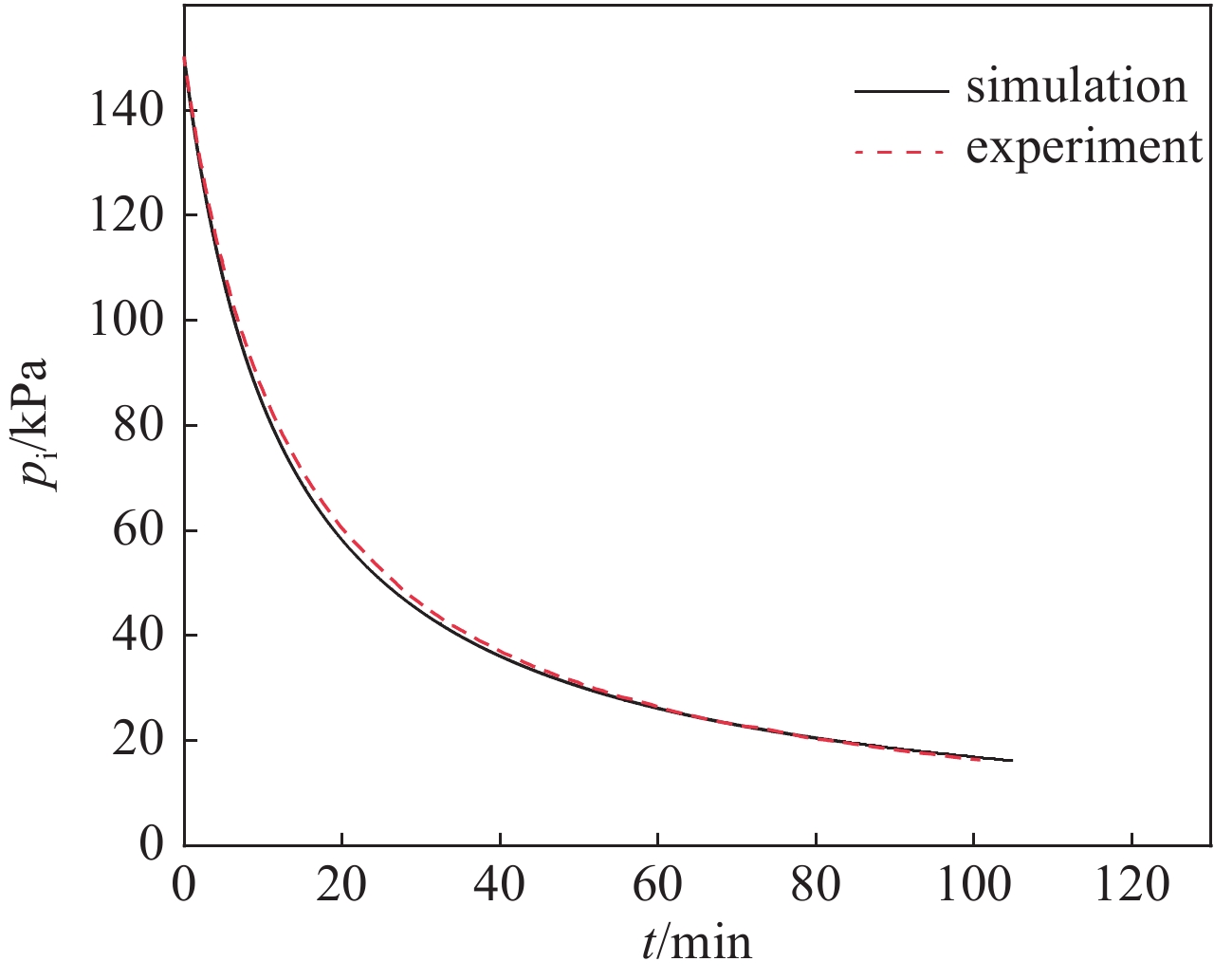
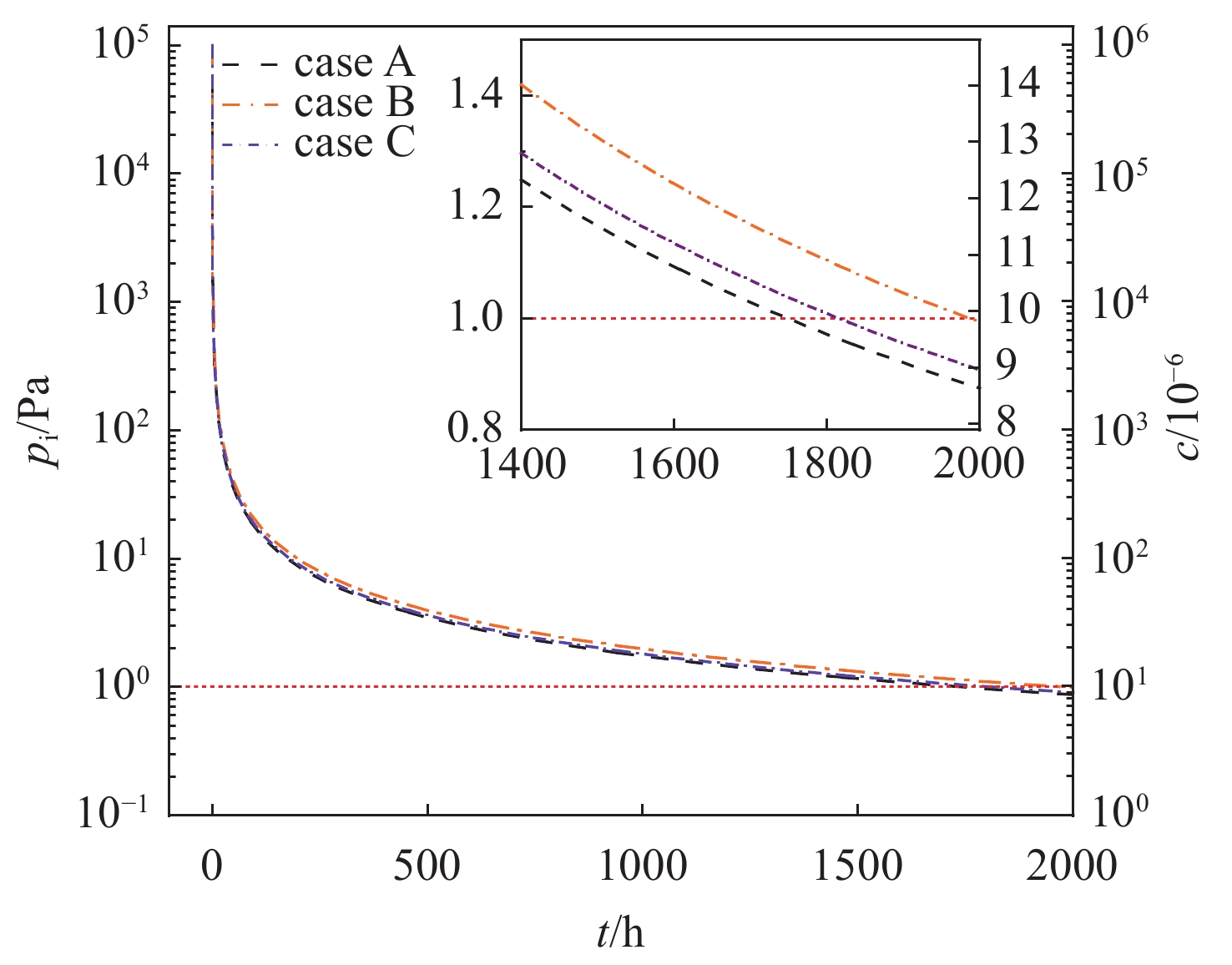
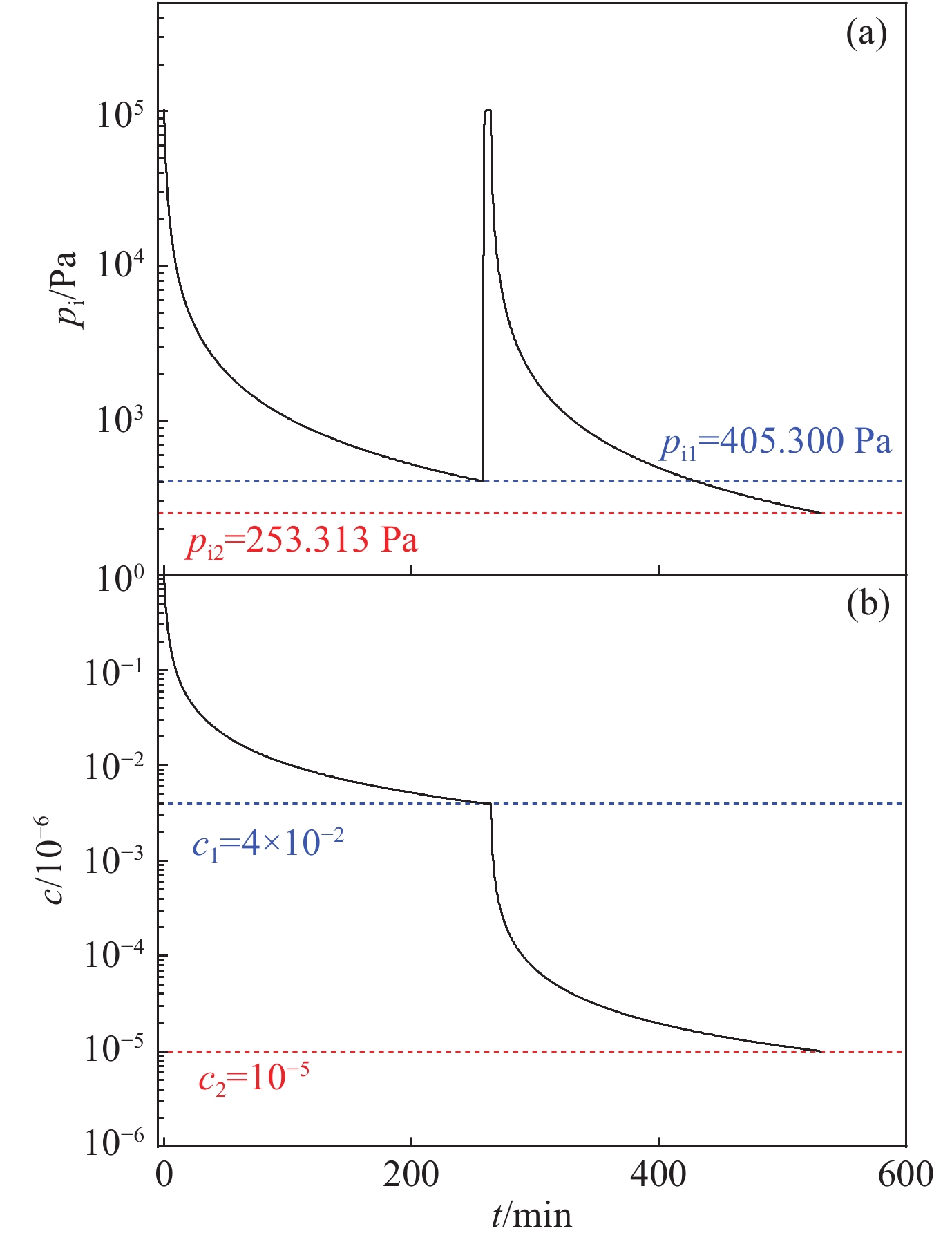
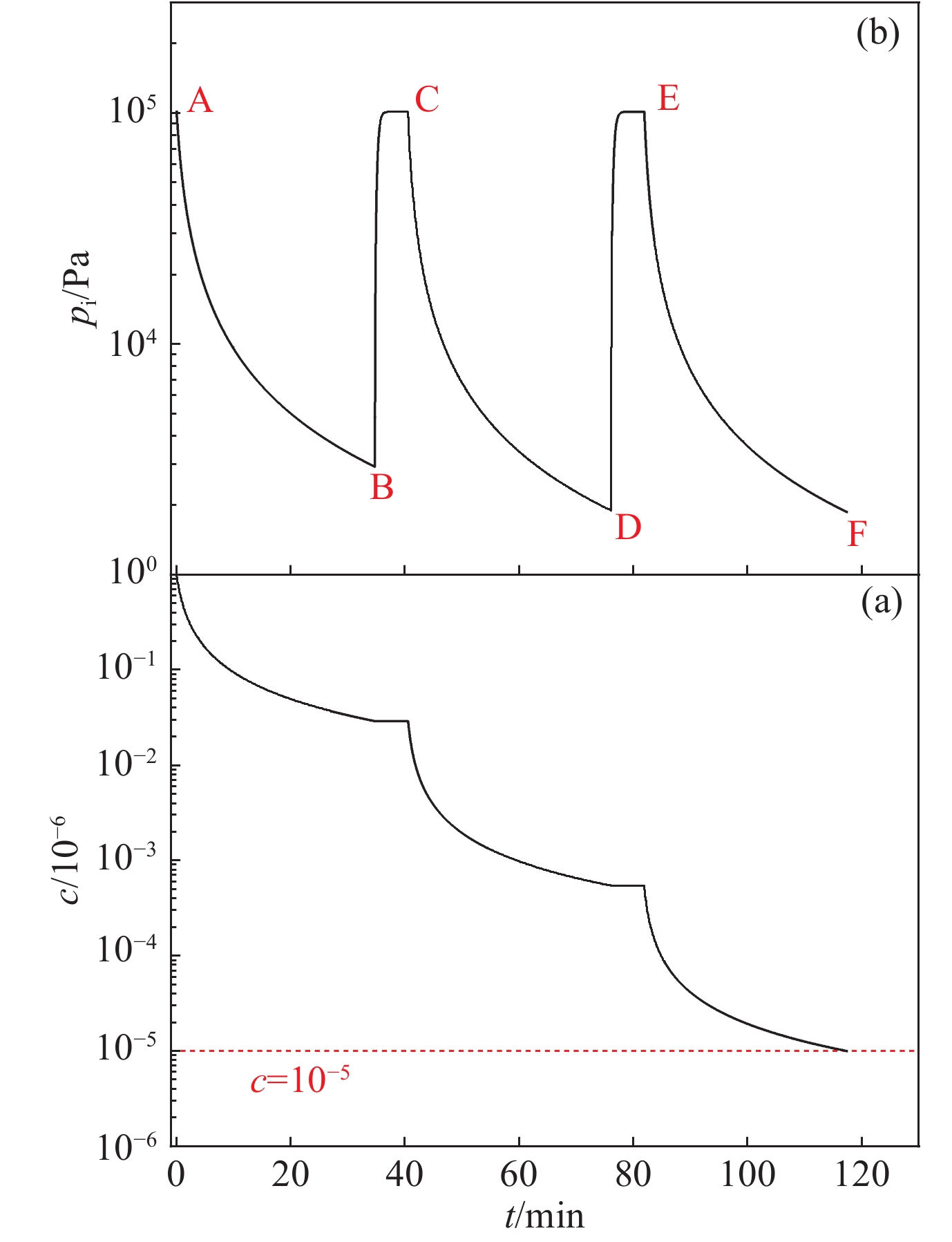
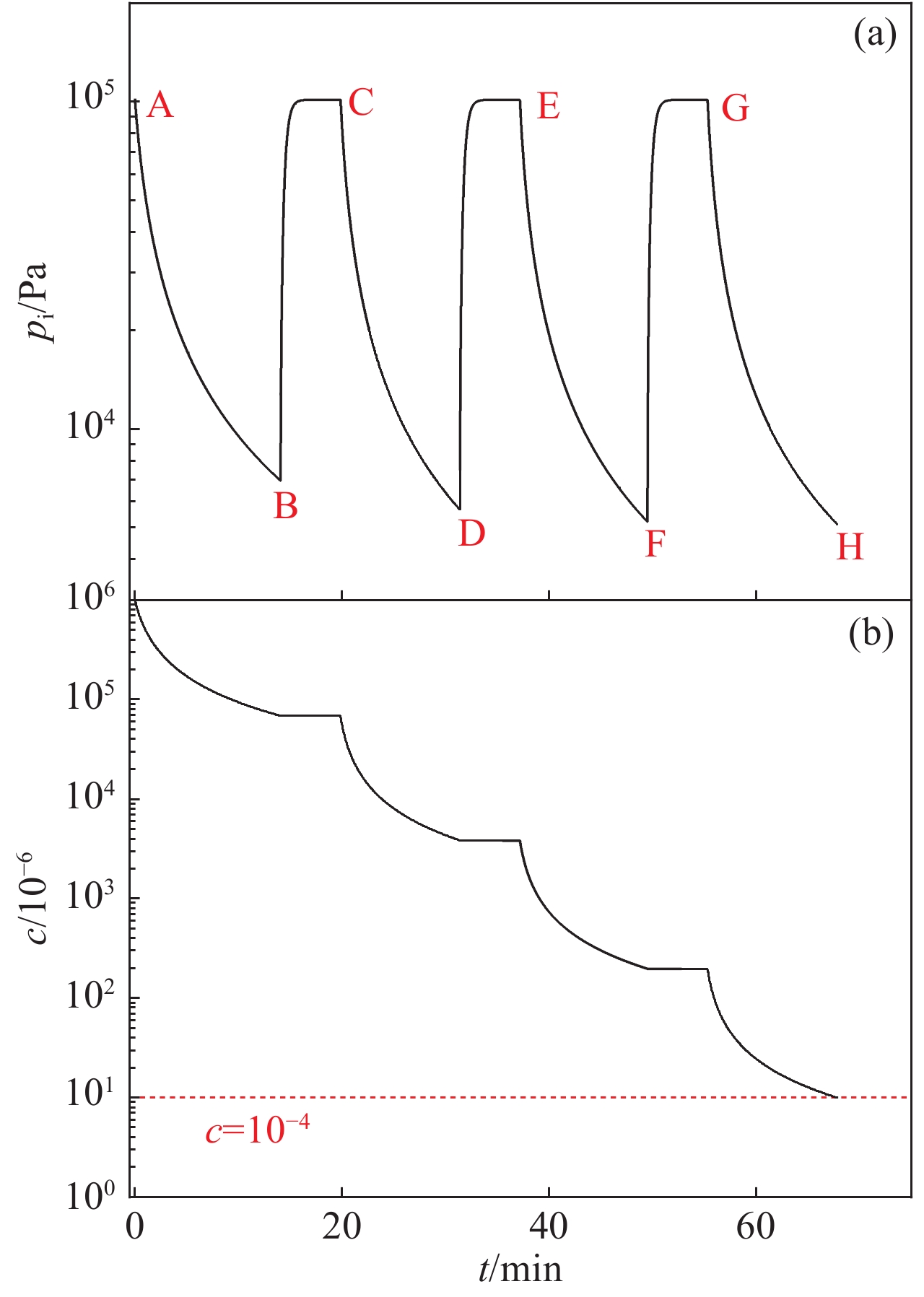
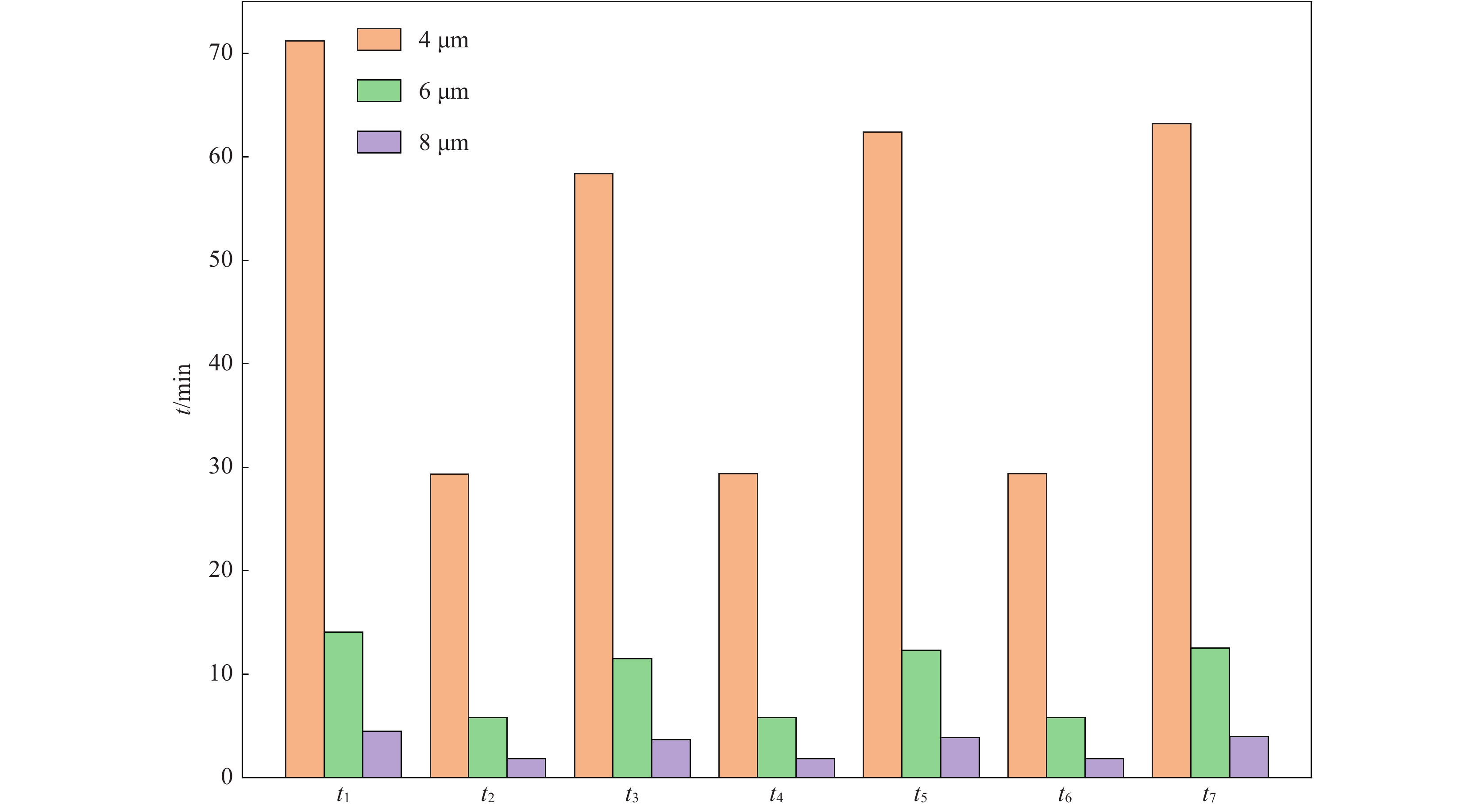
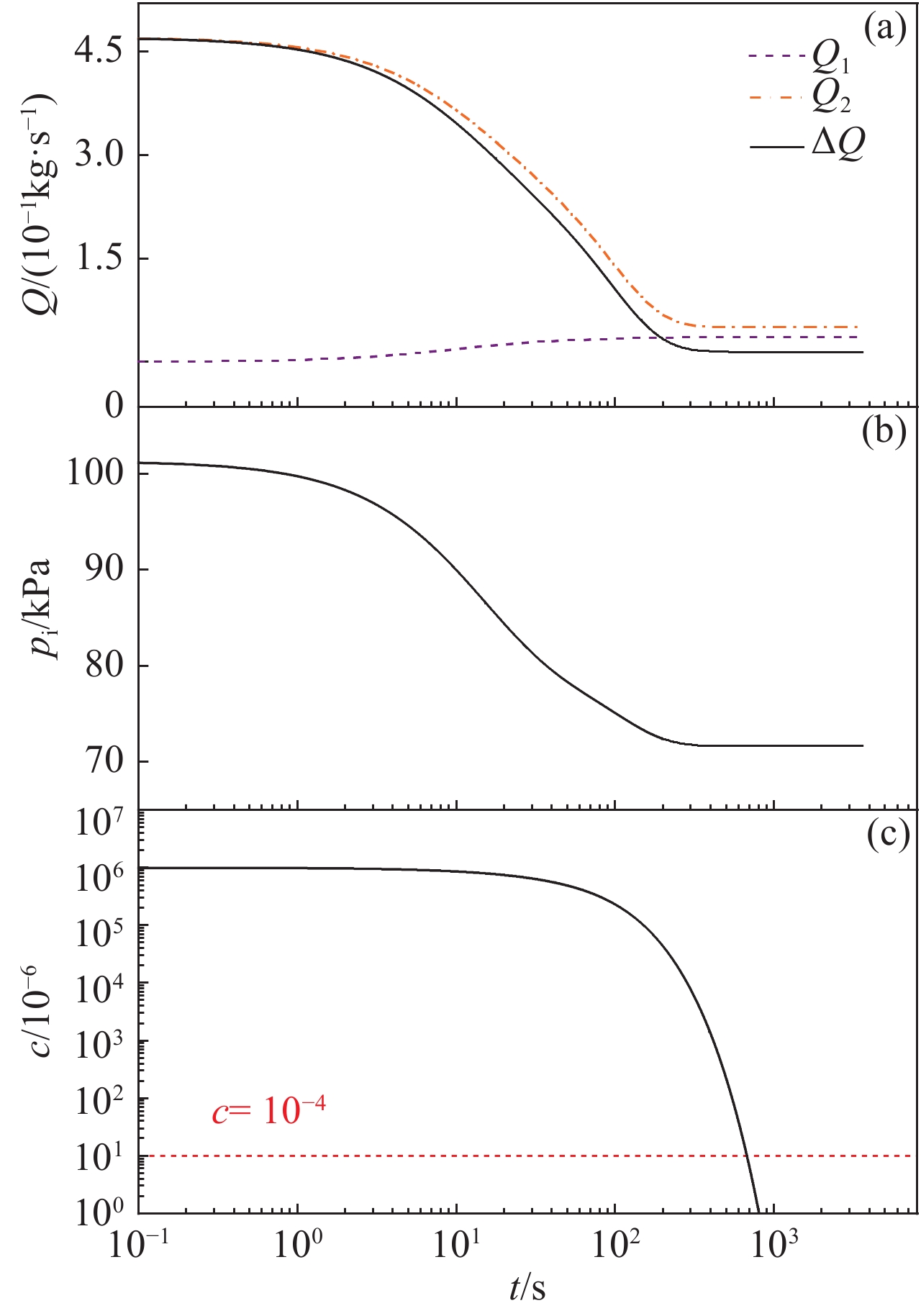
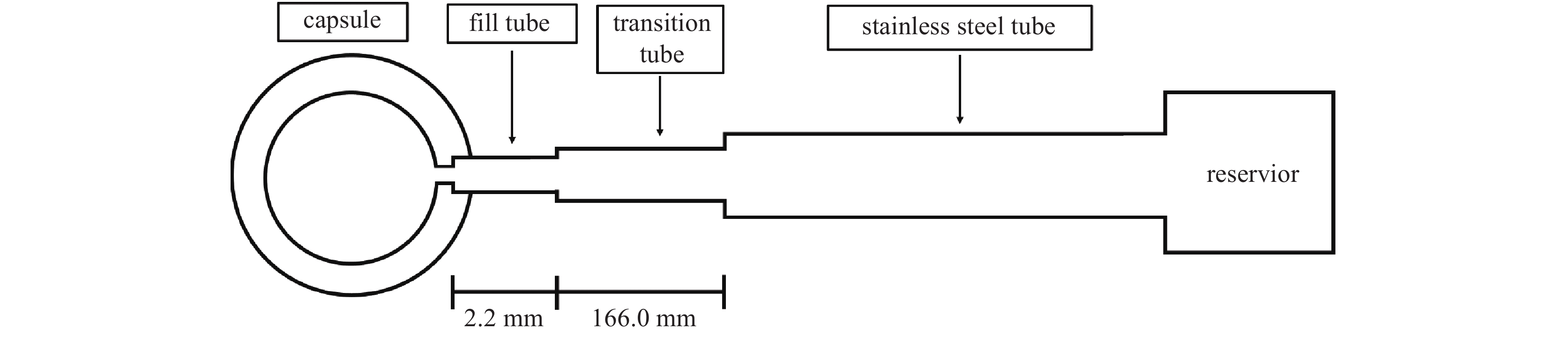
摘要: 基于适用于整个克努森数范围的流动理论,建立了去除惯性约束聚变实验中靶丸内空气的理论模型,并设计实验验证了此模型的可靠性。物理实验要求靶丸内空气浓度低于10×10−6,数值模拟了去除靶丸内空气的过程,重点分析了靶丸内空气浓度、压力与除气时间的关系。计算并比较了单管路一次抽气法、单管路循环抽气法与双管路流洗法三种去除靶丸内空气方法的时间成本。数值计算结果表明:单管路一次抽气法中,靶丸上的微通道的存在对去除靶丸内空气所需时间的影响不可忽略,在考虑靶丸上微通道与充气管的情况下,需要1961.77 h才能使靶丸内的空气浓度达到标准。单管路循环抽气法中,抽气次数与单次抽气程度会影响去除靶丸内空气所需总时间,在单次抽气程度值取最优的情况下,采用充三次,抽四次的方案可使达标总时间减少至1 h左右,此方案下单次充气和抽气时间分别为6 min和10 min。而采用双管路流洗法则仅需11 min便可使靶丸内空气浓度达标。Abstract: Based on the flow theory applicable to the whole Knudsen number range, a theoretical model for removing air from the target shot in inertial confinement fusion was established, and the reliability of the model was verified by designed experiments. The physical experiment requires the air concentration in the target shot to be lower than 10×10−6, the process of removing air in the target shot was simulated numerically, and the relationship between the air concentration in the target shot, the pressure in the target shot and time was emphatically analyzed. The time cost of three methods for removing the air in the target shot, namely the single-pipe one-time gas evacuation method, the single-pipe circulation gas evacuation method and the double-pipe flow washing method, were calculated and compared. Numerical calculation results show that: in the single-pipe one-time gas evacuation method, the existence of the micro-channel on the target shot has a non-negligible effect on the time required to remove the air in the target shot, and it takes 1961.77 h to make the air concentration in the target shot reach the standard when the micro-channel on the target shot and the gas-filling pipe is considered. In the single-pipe cycle gas evacuation method, the number of evacuation times and the degree of single gas evacuation will affect the total time required to remove the air in the target shot. When the single gas evacuation degree is at the optimal value, the plan that filling three times and evacuation four times can reduce the total time to reach the standard to about 1 h, while the single gas filling and gas evacuation times under this plan are 6 min and 10 min, respectively. However, it only takes 11 minutes to make the air concentration in the target shot reach the standard by using the double-pipe flow washing method.
-
Key words:
- filling /
- evacuation /
- microcapillary tube /
- free molecular flow /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 情况B不同阶段的抽气时间
Table 1. Evacuation time at different stages of Case B
stage the initial pressure/Pa the final pressure/Pa extraction time/h the proportion/% I 101325 10132.5 0.17 0.01 II 10132.5 1013.25 1.77 0.09 III 1013.25 101.325 17.66 0.90 IV 101.325 10.1325 176.56 9.00 V 10.1325 1.01325 1765.61 90.00 -
[1] Campbell E M, Goncharov V N, Sangster T C, et al. Laser-direct-drive program: promise, challenge, and path forward[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2017, 2(2): 37-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mre.2017.03.001 [2] Craxton R S, Anderson K S, Boehly T R, et al. Direct-drive inertial confinement fusion: a review[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2015, 22: 110501. doi: 10.1063/1.4934714 [3] Li Feng, Zhang Zhanwen, Li Jing, et al. Study on the strength of titanium doped hollow glass microspheres[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2017, 459: 18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.12.029 [4] 陈鹏玮, 厉彦忠, 丁岚, 等. 低温冷冻靶微管燃料充注流动冷凝特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2017, 29:122001. (Chen Pengwei, Li Yanzhong, Ding Lan, et al. Flow and condensation characteristics of fuel filling in cryogenic target fill tube[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2017, 29: 122001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201729.170178 [5] Schmitt M L, Shelby J E, Hall M M. Preparation of hollow glass microspheres from sol–gel derived glass for application in hydrogen gas storage[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2006, 352(6/7): 626-631. [6] Hoppe M L, Steinman D A. New developments in glass shells from SiGDP-residual gases, gas filling and tailored half-lives[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2007, 51(4): 606-610. doi: 10.13182/FST07-A1452 [7] Parham T, Kozioziemski B, Atkinson D, et al. Cryogenic target system for hydrogen layering[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 407-419. doi: 10.13182/FST15-162 [8] 张占文, 李波, 唐永建, 等. 准动态柱腔充气靶制备工艺研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2005, 17(2):209-212. (Zhang Zhanwen, Li Bo, Tang Yongjian, et al. Fabrication of the hohlraum gas-filled target connected with gas source[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2005, 17(2): 209-212 [9] Kline J L, Hager J D. Aluminum X-ray mass-ablation rate measurements[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2017, 2(1): 16-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mre.2016.09.003 [10] Chen Yongping, Deng Zilong. Hydrodynamics of a droplet passing through a microfluidic T-junction[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2017, 819: 401-434. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2017.181 [11] Chen Yongping, Wu Liangyu, Zhang Chengbin. Emulsion droplet formation in coflowing liquid streams[J]. Physical Review E Statistical Nonlinear & Soft Matter Physics, 2013, 87: 013002. [12] Zhang Chengbin, Deng Zilong, Chen Yongping. Temperature jump at rough gas–solid interface in Couette flow with a rough surface described by Cantor fractal[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 70: 322-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.10.080 [13] Deng Zilong, Liu Xiangdong, Zhang Chengbin, et al. Melting behaviors of PCM in porous metal foam characterized by fractal geometry[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 113: 1031-1042. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.05.126 [14] 林伟, 王凯, 毕鹏, 等. ICF冷冻靶微管充气过程中气体压力测量[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(10):2343-2346. (Lin Wei, Wang Kai, Bi Peng, et al. Gas pressure measurement in ICF cryogenic target micro-tube gas-filling process[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(10): 2343-2346 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122410.2343 [15] Wu Liangyu, Zhou Hua, Yu Cheng, et al. Simulation of the gas filling and evacuation processes in an Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF) hohlraum[J]. Processes, 2019, 7: 269. doi: 10.3390/pr7050269 [16] Yu Cheng, Wu Suchen, Yang Weibo. Theoretical investigation of Gas filling and leaking in inertial confinement fusion hohlraum[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10: 3763. doi: 10.3390/su10103763 [17] Bhandarkar S D, Parham T, Fair J. Modeling and experiments of compressible gas flow through microcapillary fill tubes on NIF targets[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2021, 59(1): 51-57. [18] Takagi M, Saito K, Frederick C, et al. Fabrication and attachment of polyimide fill tubes to plastic NIF capsules[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2007, 51(4): 638-642. doi: 10.13182/FST51-638 [19] Johal Z Z, Crippen J W, Forsman A C, et al. Robust capsule and fill tube assemblies for the national ignition campaign[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2009, 55(3): 331-336. doi: 10.13182/FST08-3503 [20] Dongari N, Sharma A, Durst F. Pressure-driven diffusive gas flows in micro-channels: from the Knudsen to the continuum regimes[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2009, 6(5): 679-692. doi: 10.1007/s10404-008-0344-y [21] Present R D, Debethune A J. Separation of a gas mixture flowing through a long tube at low pressure[J]. Physical Review Journals Archive, 1949, 75(7): 1050-1057. -




 下载:
下载: