| [1] |
MacGill R A, Dickinson M R, Brown I G. Vacuum arc ion sources—Micro to macro[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1996, 67(3): 1210-1212. doi: 10.1063/1.1146734
|
| [2] |
Ying Jianjian, Xiao Xiangheng, Dai Zhigao, et al. Synthesis of graphene by MEVVA source ion implantation[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2013, 305: 29-32. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2013.04.044
|
| [3] |
Hollinger R, Galonska M. Status of vacuum arc ion source development for injection of high current uranium ion beams into the GSI accelerator facility[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2005, 239(3): 227-244. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2005.04.062
|
| [4] |
Wang J L, Zhang G L, Wang Y N, et al. Grid-shadow effect in grid-enhanced plasma source ion implantation[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2005, 192(1): 101-105. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2004.04.069
|
| [5] |
米夏兹 Г А. 真空放电物理和高功率脉冲技术[M]. 李国政, 译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2007: 149-151.Месяц Г А. Vacuum discharge physics and high power pulse technology[M]. Li Guozheng, trans. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2007: 149-151
|
| [6] |
Beilis I I. Vacuum arc cathode spot theory: history and evolution of the mechanisms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2019, 47(8): 3412-3433. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2019.2904324
|
| [7] |
Anders A. Cathodic arcs: from fractal spots to energetic condensation[M]. New York: Springer, 2008: 183-186.
|
| [8] |
拉弗蒂J M. 真空电弧理论和应用[M]. 程积高, 译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1985: 148-149.Lafferty J M. Vacuum arcs theory and application[M]. Cheng Jigao, trans. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1985: 148-149
|
| [9] |
唐建, 卢彪, 伍春雷, 等. 条纹相机在真空弧离子源等离子体诊断中的应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:084001. (Tang Jian, Lu Biao, Wu Chunlei, et al. Application of a streak camera to diagnosis of plasma in vacuum arc ion source[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 084001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.084001
|
| [10] |
Aleksandrov V D, Bogolubov E P, Bochkarev O V, et al. Application of neutron generators for high explosives, toxic agents and fissile material detection[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2005, 63(5/6): 537-543.
|
| [11] |
郑世平, 秦爱玲, 赵舒平. 测井中子发生器[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2009, 24(4):1521-1526. (Zheng Shiping, Qin Ailing, Zhao Shuping. Well logging neutron generator[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2009, 24(4): 1521-1526 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.04.047
|
| [12] |
Walko R J, Rochau G E. A high output neutron tube using an occluded gas ion source[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1981, 28(2): 1531-1534. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1981.4331459
|
| [13] |
Shkol’nik S M. Arc discharges with gas-impregnated cathodes in vacuum[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2001, 29(5): 675-683. doi: 10.1109/27.964453
|
| [14] |
Barengolts S A, Karnaukhov D Y, Nikolaev A G, et al. Generation of hydrogen isotope ions in a vacuum arc discharge with a composite zirconium deuteride cathode[J]. Technical Physics, 2015, 60(7): 989-999. doi: 10.1134/S1063784215070051
|
| [15] |
陈磊, 金大志, 程亮, 等. 含氢电极脉冲放电等离子体特性诊断[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(5):1361-1364. (Chen Lei, Jin Dazhi, Cheng Liang, et al. Diagnosis of plasmas generated by pulsed vacuum arc discharge at hydrogen impregnated electrodes[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(5): 1361-1364 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112305.1361
|
| [16] |
董攀, 李杰, 郑乐, 等. 真空弧放电TiH合金阴极表面形貌分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30:014001. (Dong Pan, Li Jie, Zheng Le, et al. Surface morphology analysis of TiH cathode in vacuum arc discharge[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 014001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.170356
|
| [17] |
Kaufmann H T C, Cunha M D, Benilov M S, et al. Detailed numerical simulation of cathode spots in vacuum arcs: Interplay of different mechanisms and ejection of droplets[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 122: 163303. doi: 10.1063/1.4995368
|




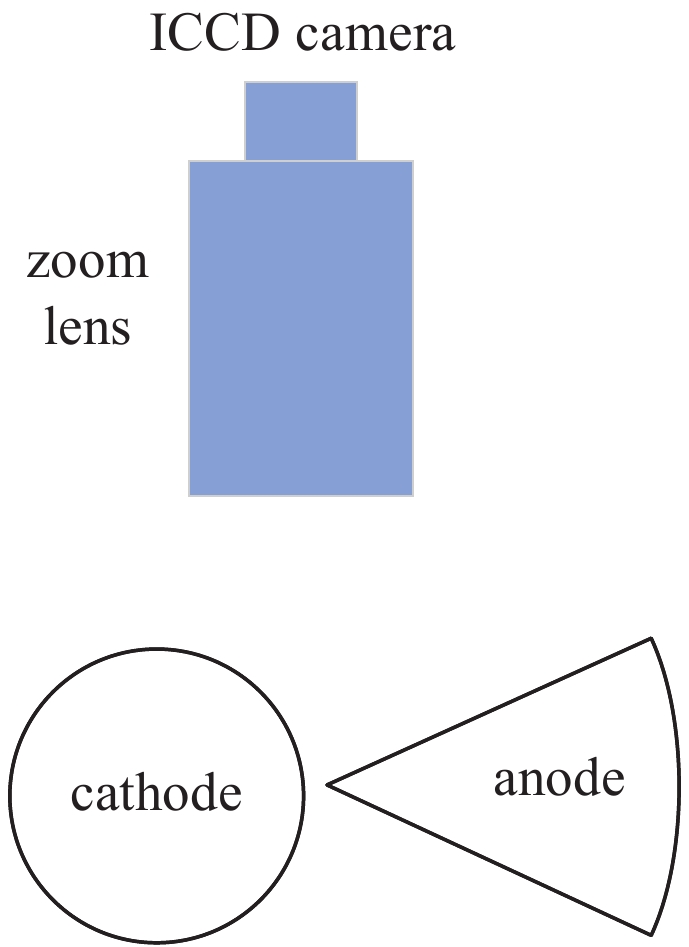
 下载:
下载: