Progress of intense heavy ion beam driven high energy density physics
-
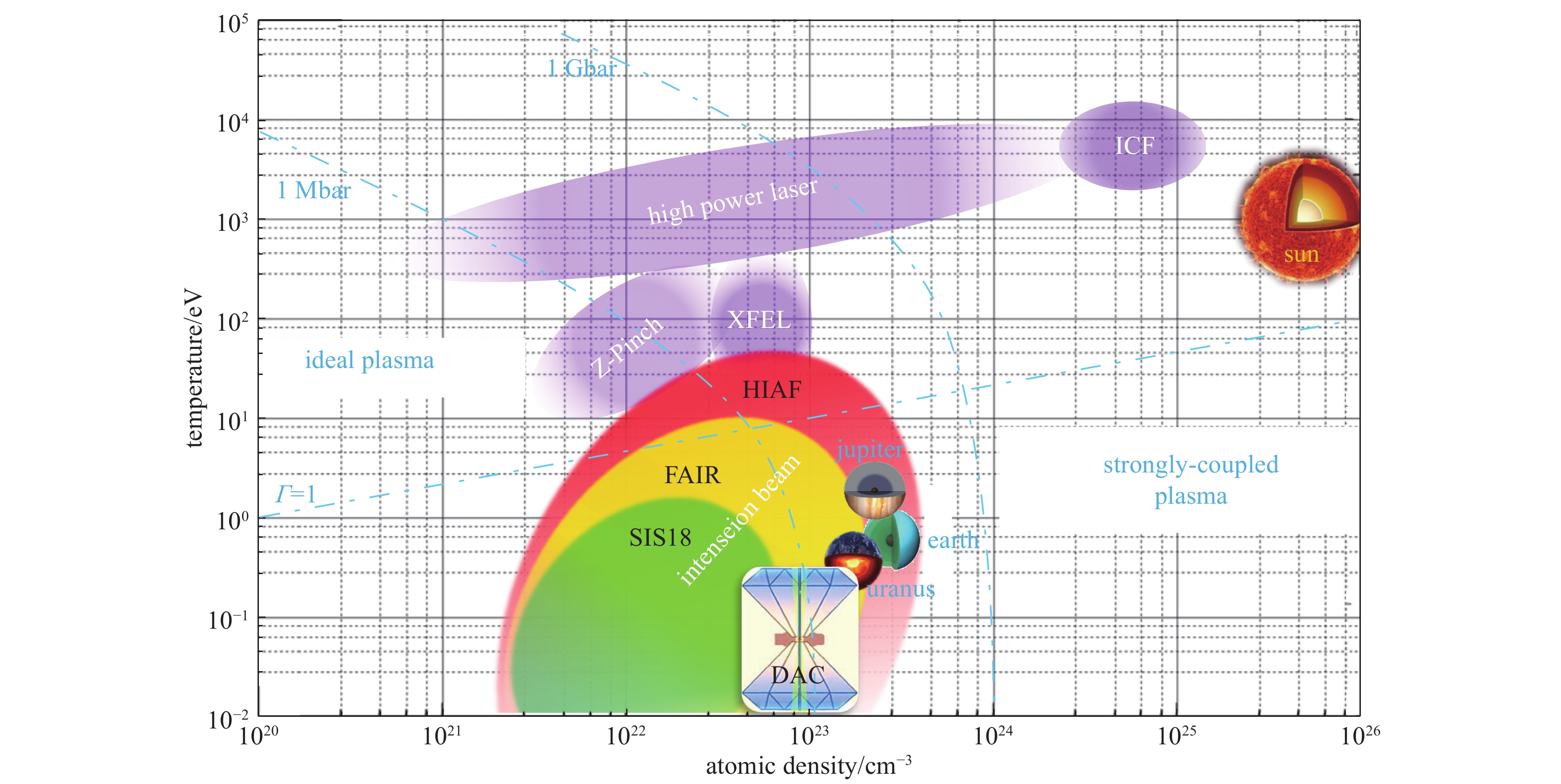
摘要: 强流高能离子束可以准等容加热任何高密度样品,制备出尺度大、状态均匀、内部无冲击波的高能量密度物质,为实验室研究高能量密度物理提供了一种独特的新手段。介绍了国内外典型的强流重离子加速器装置及其与高能量密度物理相关的关键参数设计和研究规划;展示了基于粒子和流体模拟的离子束驱动高能量密度物质产生和状态演化规律进展;介绍了一套兼具高时空分辨和高穿透力的高能电子成像诊断技术;分析了中低能区离子束与等离子体相互作用过程中的碰撞和电荷交换微观机制,以及激光加速超短超强离子束在等离子体中的非线性输运和欧姆能损机制。Abstract: Intense ion beams can quasi-isometrically heat any high-density sample and generate warm dense matter (WDM) with large scale, uniform state distribution without any shock wave inside. This kind of driver provides a new opportunity for the laboratory high energy density physics (HEDP) research. The typical intense ion beam accelerators around the world, as well as their critical parameters and research plans of HEDP study are introduced.The progress of ion driven WDM generation and evolution using PIC and hydrodynamic simulations is shown. The high energy electron beam radiography technique with high spatial resolution, high temporal evolution, and high penetrating ability is also introduced. The collisional and charge transfer processes of the interaction between low-to-medium energy ion and plasma are analyzed. The nonlinear effect during the intense ion beam stopping and transportation process are presented.
-
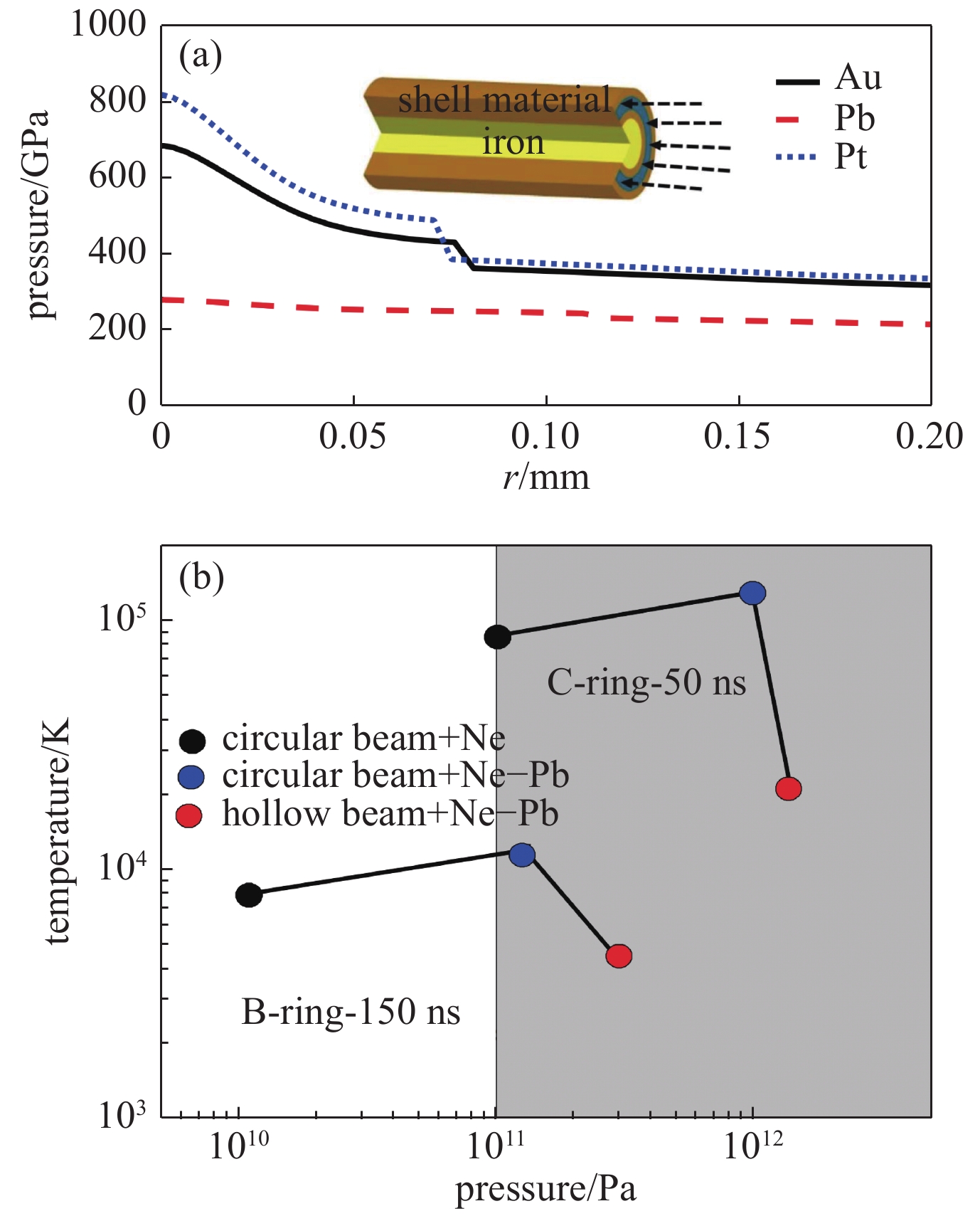
图 4 (a)HIAF B-Ring离子束轰击LAPLAS靶外层材料(金、铅、铂)驱动冲击波压缩内层铁样品制备的低温高密温稠密物质压强分布[33];(b)HIAF离子束与不同构型的靶耦合可制备的氖物质状态[[34]
Figure 4. (a) Pressure of inner-shell iron sample within LAPLAS target (outer shell materials: Au, Pb, Pt) heated by HIAF B-Ring beams[33]; (b) The state of neon with different HIAF beam-target schemes[34]
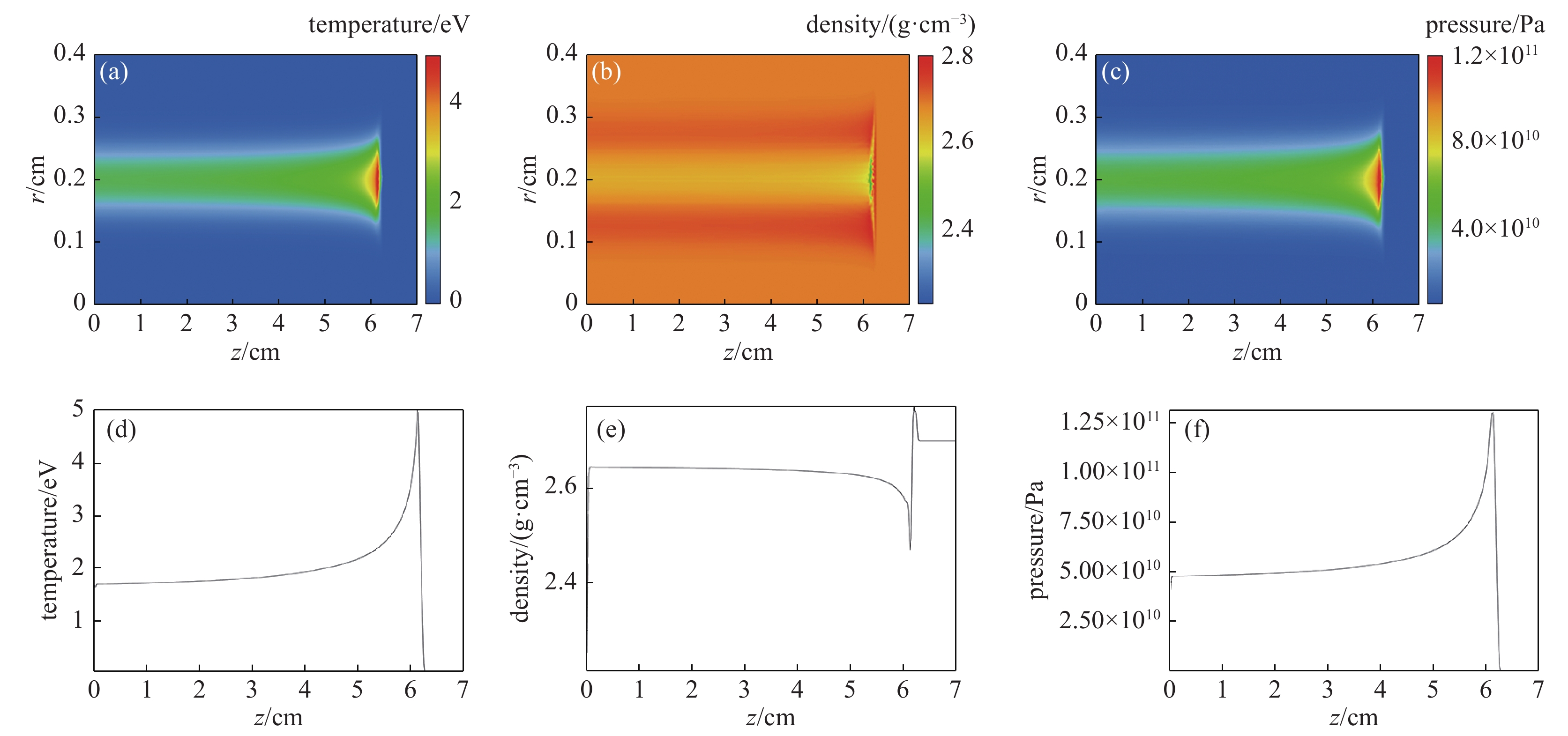
图 5 HIAF强流离子束直接驱动下铝的(a)温度、(b)密度及(c)压强二维分布图及中心(r=0.2 cm)处的(d)温度、(e)密度及(f)压强
Figure 5. Two-dimension distribution of (a) temperature, (b) density and (c) pressure of aluminum target heated by the HIAF-provided uranium beams, and intensity of (d) temperature, (e) density and (f) pressure at center of r=0.2 cm.
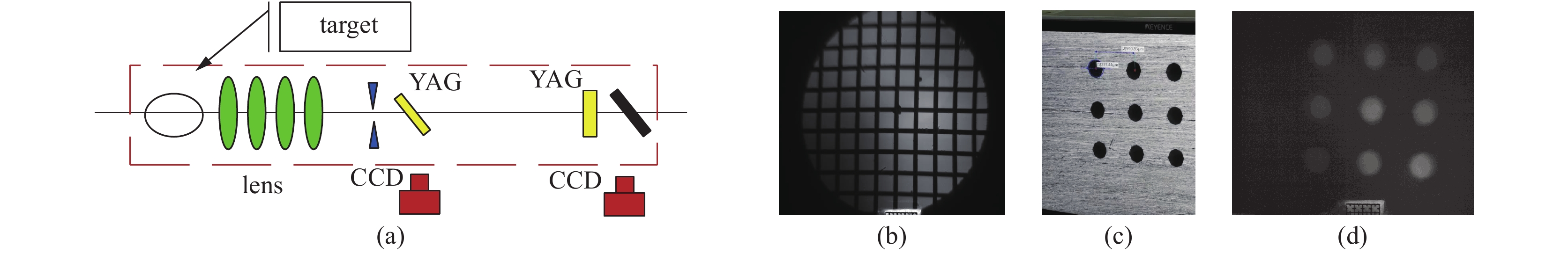
图 7 (a)高能电子透射成像实验装置图;(b)100目TEM网格成像结果,空间分辨约4 µm;(c)样品:通孔九宫格厚板后贴不同厚度的铁片;(d)对(c)中样品成像结果,对不同厚度的样品可分辨
Figure 7. (a) Experimental setup for electron beam radiography; (b) Radiography image of 100 TEM meshes with spatial resolution of 4 µm; (c) sample: holed thick plane with various-density iron foil on the holes; (d) Radiography image of the sample shown in (c). The thickness difference can be distinguished
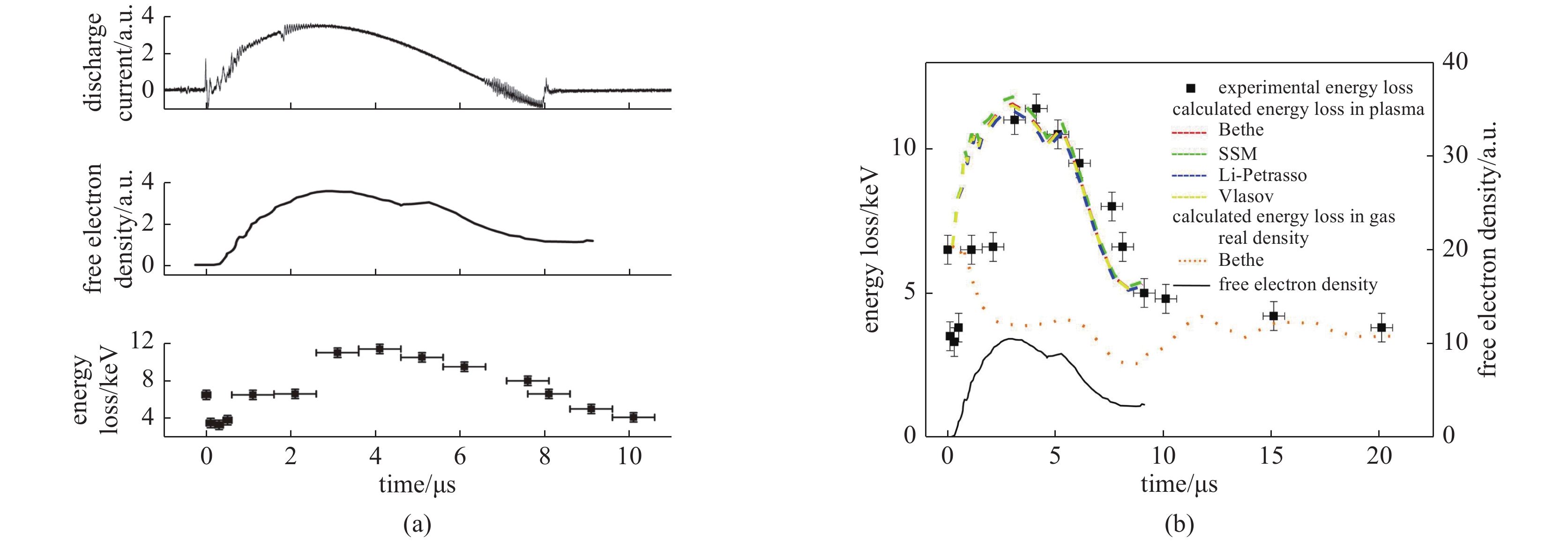
图 8 (a)气体放电等离子体装置放电电流(上)、等离子体自由电子密度(中)及质子穿过等离子体后的能量沉积(下)随着放电时间的变化关系;(b)质子的能量沉积与不同理论对比图
Figure 8. (a) Temporal evolution of discharging current of the device (top), free electron density of the plasma (central) as well as the energy loss of protons after passing through the plasma (bottom); (b) Energy loss comparison between the experimental energy loss with various theories of helium ions in gas-discharge plasmas versus discharging time
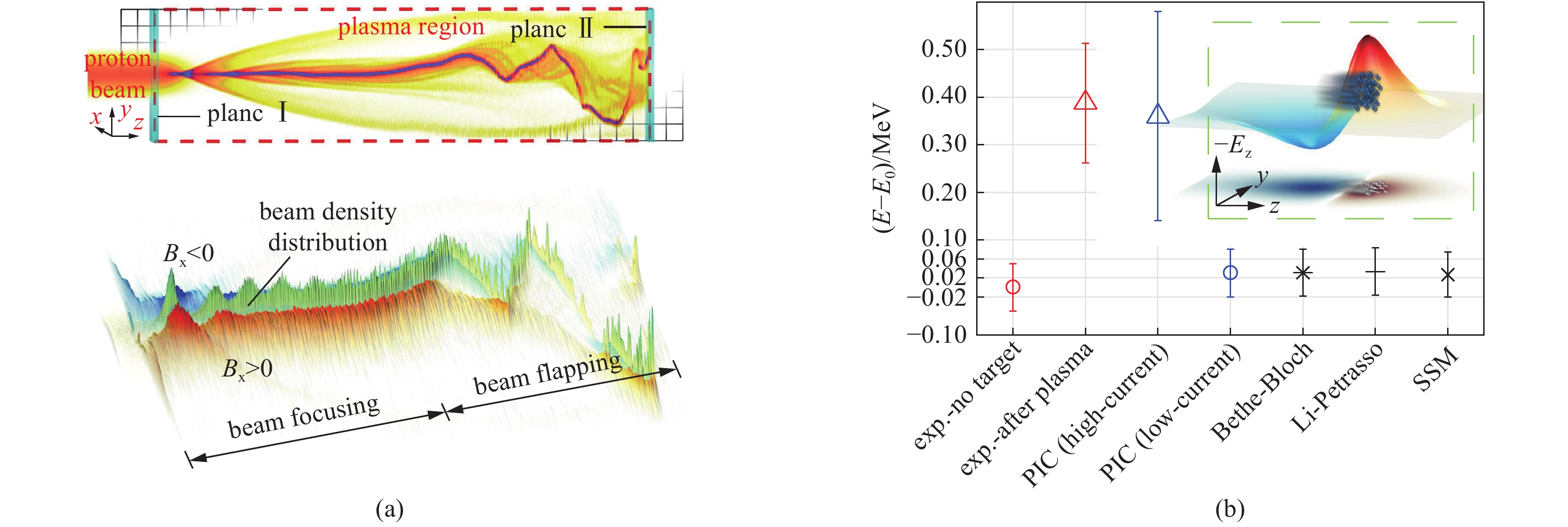
图 10 (a)强流质子束在等离子体中传输时的聚焦和扭曲现象[60];(b)激光加速的强流质子束在稠密等离子体中的能量沉积实验测量值与理论对比图,插图表示强流离子束在稠密等离子体中激发的纵向电场图像[61]
Figure 10. (a) The focusing and twisting phenomenon of intense proton beam transportation in large-scale plasma[65]; (b) Comparison between the measured energy loss of laser-accelerated ions in dense plasma with different theories. The inset shows the longitudinal electric field induced by the intense protons in the plasma[66]
表 1 不同装置的典型参数
Table 1. Typical parameters of various facilities
facility typical ion species kinetic energy pulse duration/ns particle per pulse focal spot/mm energy deposition power under
direct heating/(J·m−3)GSI-SIS18[10] uranium 0.4 GeV/u 300 4×1010 1.00 2×1011 (in gold) FAIR-SIS100[10] uranium 1.0 GeV/u 100 4×1011 1.00 2×1012 (in gold) HIAF[10] uranium 1.3 GeV/u 100 5×1011 0.70 5×1012 (in gold) HIAF-U[10] uranium 4.4 GeV/u 30 2×1012 0.70 2×1013 (in gold) NDCX-II[20] helium 1.1 MeV 1~600 1×1011 1.00 4×108 (in tin) Laser acceleration[25] proton 1.1 MeV (kT) 0.001 8×1011 0.05 6×1012 (in copper) -
[1] Hurricane O A, Callahan D A, Casey D T, et al. Inertially confined fusion plasmas dominated by alpha-particle self-heating[J]. Nature Physics, 2016, 12: 800. doi: 10.1038/nphys3720 [2] Zhang F, Cai H B, Zhou W M, et al. Enhanced energy coupling for indirect-drive fast-ignition fusion targets[J]. Nature Physics, 2020, 16: 810. doi: 10.1038/s41567-020-0878-9 [3] Tateno S, Hirose K, Ohishi Y, et al. The structure of iron in Earth’s inner core[J]. Science, 2010, 330: 359-361. doi: 10.1126/science.1194662 [4] Dubrovinsky L, Dubrovinskaia N, Prakapenka V B, et al. Implementation of micro-ball nanodiamond anvils for high-pressure studies above 6 Mbar[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 1163. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2160 [5] Kritcher A, Doppner T, Swift D, et al. Probing matter at Gbar pressures at the NIF[J]. High Energy Density Physics, 2014, 10: 27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.hedp.2013.11.002 [6] Hall C A. Isentropic compression experiments on the Sandia Z accelerator[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2000, 7: 2069-2075. doi: 10.1063/1.874029 [7] Hall C, Asay J, Knudson M, et al. Experimental configuration for isentropic compression of solids using pulsed magnetic loading[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2001, 72: 3587-3595. doi: 10.1063/1.1394178 [8] Branitsky A V, Fedulov M V, Grabovsky E V, et al. Z-pinch implosion for ICF physics study on Angara-5-1[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1997, 40: 125. [9] 张思群, 王昆仑, 李晶, 等. 聚龙一号丝阵负载Z箍缩硬X射线能谱测量[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30:105004. (Zhang Siqun, Wang Kunlun, Li Jing, et al. Measurement of hard X-ray spectrum during wire array implosion on PTS[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 105004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.180183 [10] 赵永涛, 肖国青, 李福利. 基于现代加速器的惯性约束聚变物理研究现状及发展[J]. 物理, 2016, 45:98-107. (Zhao Yongtao, Xiao Guoqing, Li Fuli. The physics of inertial confinement fusion based on modern accelerators: status and perspectives[J]. Physics, 2016, 45: 98-107 doi: 10.7693/wl20160204 [11] Schoenberg K, Bagnoud V, Blazevic A, et al. High-energy-density-science capabilities at the Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2020, 27: 043103. doi: 10.1063/1.5134846 [12] Ni P, Hoffmann D, Kulish M, et al. Pyrometric system for temperature measurements of HED matter generated by intense heavy ion beams[J]. Journal de Physique IV, 2006, 133: 977-980. [13] Mintsev V, Kim V, Lomonosov I, et al. Non-ideal plasma and early experiments at FAIR: HIHEX-heavy ion heating and expansion[J]. Plasma of Physics, 2016, 56: 281-285. doi: 10.1002/ctpp.201500105 [14] The GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung. FAIR — The Universe in the Lab[EB/OL]. https://www.gsi.de/en/researchaccelerators/fair.htm. [15] Institute of Modern Physics, CAS. The High Intensity Heavy-ion Accelerator Facility[EB/OL]. http://hiaf.impcas.ac.cn/. [16] Tahir N, Deutsch C, Fortov V, et al. Proposal for the study of thermophysical properties of high-energy-density matter using current and future heavy-ion accelerator facilities at GSI Darmstadt[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 95: 035001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.035001 [17] Tahir N A, Shutov A, Piriz A R, et al. Application of intense ion beams to planetary physics research at the Facility for Antiprotons and Ion Research facility[J]. Plasma of Physics, 2019, 59: e201800135. doi: 10.1002/ctpp.201800135 [18] Cheng R, Zhou X, Wang Y, R, et al. Energy loss of protons in hydrogen plasma[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 36(1): 98-104. doi: 10.1017/S0263034618000010 [19] 赵永涛, 张子民, 程锐, 等. 基于HIAF装置的高能量密度物理研究[J]. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2020, 50:112004. (Zhao Yongtao, Zhang Zimin, Cheng Rui, et al. High-energy-density physics based on HIAF[J]. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 2020, 50: 112004 doi: 10.1360/SSPMA-2020-0275 [20] Seidl P A, Barnard J J, Feinberg E, et al. Irradiation of materials with short, intense ion pulses at NDCX-II[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2017, 35(2): 373-378. doi: 10.1017/S0263034617000295 [21] Stepanov A D, Barnard J J, Friedman A et al. , Optimizing beam transport in rapidly compressing beams on the neutralized drift compression experiment-II[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2018, 3: 78. doi: 10.1016/j.mre.2018.01.001 [22] Kawata S, Karino T, Ogoyski A I. Review of heavy-ion inertial fusion physics[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2016, 1, 89. [23] Sharkov B, Hoffmann D, Golubev A A, et al. High energy density physics with intense ion beams[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2016, 1: 28-47. doi: 10.1016/j.mre.2016.01.002 [24] Ingo Hofmann. Review of accelerator driven heavy ion nuclear fusion[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2018, 3: 1. doi: 10.1016/j.mre.2017.12.001 [25] Patel P K, Mackinnon A J, Key M H, et al. Isochoric heating of solid-density matter with an ultrafast proton beam[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91: 125004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.125004 [26] Yuan Ping, Heather D, Whitley, et al. Heat-release equation of state and thermal conductivity of warm dense carbon by proton differential heating[J]. Physical Review E, 2019, 100: 043204. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.100.043204 [27] Burkart F, Schmidt R, Raginel V, et al. Analysis of 440 GeV proton beam–matter interaction experiments at the High Radiation Materials test facility at CERN[J]. Journal of applied physics, 2015, 118: 055902. doi: 10.1063/1.4927721 [28] Kim J, Qiao B, McGuffey C, et al. Self-consistent simulation of transport and energy deposition of intense laser-accelerated proton beams in solid-density matter[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 115: 054801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.054801 [29] Wu D, He X T, Yu W, et al. Monte Carlo approach to calculate ionization dynamics of hot solid density plasmas within particle-in-cell simulations[J]. Physical Review E, 2017, 95: 023208. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.95.023208 [30] Wu D, He X T, Yu W, et al. Monte Carlo approach to calculate proton stopping in warm dense matter within particle-in-cell simulations[J]. Physical Review E, 2017, 95: 023207. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.95.023207 [31] Wu D, Yu W, Fritzsche S, et al. High-order implicit particle-in-cell method for plasma simulations at solid densities[J]. Physical Review E, 2019, 100: 013207. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.100.013207 [32] Wu D, Yu W, Zhao Y, et al. Particle-in-cell simulation of transport and energy deposition of intense proton beams in solid-state materials[J]. Physical Review E, 2019, 100: 013208. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.100.013208 [33] Zhang Lin, Zhao Yongtao, Ren Jieru, et al. Warm-dense-matter state of iron generated by intense heavy-ion beams[J]. IEEE Trans Plasma Science, 2019, 47(1): 853-857. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2018.2857798 [34] Ren Jieru, Zhao Yongtao, Cheng Rui, et al. Hydrodynamic response of solid target heated by heavy ion beams from future facility HIAF[J]. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms, 2017, 406: 703-707. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2017.03.018 [35] Zhang Lin, Zhao Yongtap, Ren Jieru, et al. Two dimensional hydrodynamic simulations of metal targets under irradiation of intense proton beams: Effects of target materials[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2018, 25: 113108. doi: 10.1063/1.5045585 [36] Zhang Ya, Wei Jiang. Enhancement of valley polarization in graphene with an irradiating charged particle[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 26: 012102. doi: 10.1063/1.5070085 [37] Merrill F, Harmon F, Hunt A, et al. Electron radiography[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 2007, 261: 382-386. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2007.04.127 [38] Merrill F E, Goett J, Gibbs J W, et al. Demonstration of transmission high energy electron microscopy[J]. Applied Physical Letters, 2018, 112: 144103. doi: 10.1063/1.5011198 [39] Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Gai W, et al. High energy electron radiography scheme with high spatial and temporal resolution in three dimension based on a e-LINAC[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 34(2): 338-342. doi: 10.1017/S0263034616000124 [40] Zhou Zheng, Du Yingchao, Cao Shuchun, et al. Experiments on bright-field and darkfield high-energy electron imaging with thick target material[J]. Physical Review Accelerations and Beams, 2018, 21: 074701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.21.074701 [41] Zhou Zheng, Fang Yu, Chen Han, et al. Visualizing the melting processes in ultrashort intense laser triggered gold mesh with high energy electron radiography[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2019, 4: 065402. doi: 10.1063/1.5109855 [42] Li Chikang, Petrasso R D. Fokker-Planck equation for moderately coupled plasmas[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 70(20): 3063. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.3063 [43] Maynard G and Deutsch C. Born random phase approximation for ion stopping in an arbitrarily degenerate electron fluid[J]. Journal de Physique, 1985, 46(7): 1113-1122. doi: 10.1051/jphys:019850046070111300 [44] Bethe H. Zur theorie des Durchgangs schneller Korpuskularstrahlen durch Materie[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1930, 397(3): 325-400. doi: 10.1002/andp.19303970303 [45] Bloch F. Zur Bremsung rasch beweg Terteilchen beim Durchgang durch Materie[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1933, 408(3): 285-320. doi: 10.1002/andp.19334080303 [46] Ding Y H, White A J, Hu S X, et al. Ab initio studies on the stopping power of warm dense matter with time-dependent orbital-free density functional theory[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 121: 145001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.145001 [47] Peter T, Meyer-ter-Vehn J. Energy loss of heavy ions in dense plasma. I. Linear and nonlinear Vlasov theory for the stopping power[J]. Physical Review A, 1991, 43: 1998-2014. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.43.1998 [48] Deutsch C, Maynard G, Chabot M, et al. Ion stopping in dense plasma target for high energy density physics[J]. The Open Plasma Physics Journal, 2010, 3(1). [49] Xu Ge, Barriga-Carrasco M D, Blazevic A, et al. Determination of hydrogen density by swift heavy ions[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2017, 119: 204801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.204801 [50] Cayzac W, Bagnoud W, Basko M M, et al. Predictions for the energy loss of light ions in laser-generated plasmas at low and medium velocities[J]. Physical Review E, 2015, 92: 053109. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.053109 [51] Morales R, Barriga-Carrasco M D, Casas D. Instantaneous charge state of uranium projectiles in fully ionized plasmas from energy loss experiments[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2017, 24: 042703. doi: 10.1063/1.4979132 [52] Loisch G, Xu G, Blazevic A, et al. Hydrogen plasma dynamics in the spherical theta pinch plasma target for heavy ion stripping[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2015, 22: 053502. doi: 10.1063/1.4919851 [53] Rosmej O N, Blazevic A, Korostiy S, et al. Charge state and stopping dynamics of fast heavy ions in dense matter[J]. Physical Review A, 2015, 72: 052901. [54] Braenzel J, Barriga-Carrasco M D, Morales R, et al. Charge-transfer processes in warm dense matter: Selective spectral filtering for laser-accelerated ion beams[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120: 184801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.184801 [55] Chen S N, Atzeni S, Gangolf T, et al. Experimental evidence for the enhanced and reduced stopping regimes for protons propagating through hot plasmas[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 14586. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32726-2 [56] Chou Shaowei, Xu Jia, Khrennikov K, et al. Collective deceleration of laser-driven electron bunches[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 117: 144801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.144801 [57] Honda M, Meyer-ter-Vehn J, Pukhov A. Collective stopping and ion heating in relativistic-electron-beam transport for fast ignition[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 85(10): 2128. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.2128 [58] Tatarakis M, Beg F N, Clark E L, et al. Propagation instabilities of high-intensity laser-produced electron beams[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 90: 175001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.175001 [59] Vauzour B, Debayle A, Vaisseau X, et al. Unraveling resistive versus collisional contributions to relativistic electron beam stopping power in cold-solid and in warm-dense plasmas[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2014, 21: 033101. doi: 10.1063/1.4867187 [60] Cayzac W, Frank A, Ortner A, et al. Experimental discrimination of ion stopping models near the Bragg peak in highly ionized matter[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15693. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15693 [61] Zylstra A B, Frenje J A, Grabowski P E, et al. Measurement of charged-particle stopping in warm dense plasma[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 114: 215002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.215002 [62] Frenje J A, Florido R, Mancini R, et al. Experimental validation of low-Z ion-stopping formalisms around the Bragg peak in high-energy-density plasmas[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 122: 015002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.015002 [63] Chen Yanhong, Cheng Rui, Zhang Min, et al. Experimental investigation on diagnosing effective atomic density in gas-type target by using proton energy loss[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018(4):83-89. [64] Zhao Y T, Zhang Y N, Cheng R, et al. Significant contribution of projectile excited states to the stopping of slow helium ions in hydrogen plasma[DB/OL]. 2020, arXiv: 2006.01380. [65] Chen B Z, Wu D, Ren J R, et al. Transport of intense particle beams in large-scale plasmas[J]. Physical Review E, 2020, 101: 051203. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.101.051203 [66] Ren Jieru, Deng Zhigang, Qi Wei, et al. Observation of a high degree of stopping for laser-accelerated intense proton beams in dense ionized matter[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5157. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18986-5 [67] Ren Jieru, Zhao Yongtao, Wei Wenqing, et al. Experimental scheme for investigation of stopping and fusion reactions initiated by laser-accelerated proton beams in a dense boron plasma[R]. GSI Annual Scientific Reports, 2020. -




 下载:
下载: