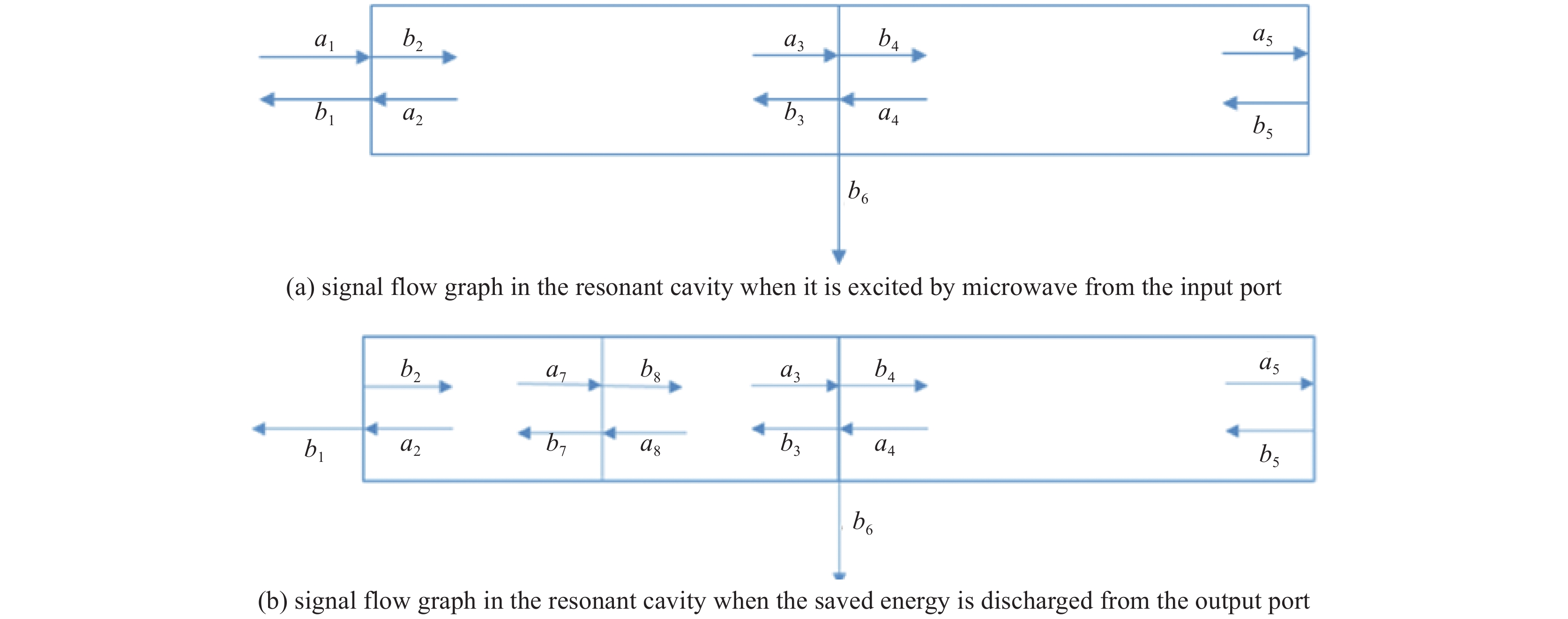
Storing and dumping processes of energy in high quality factor resonant cavity
-
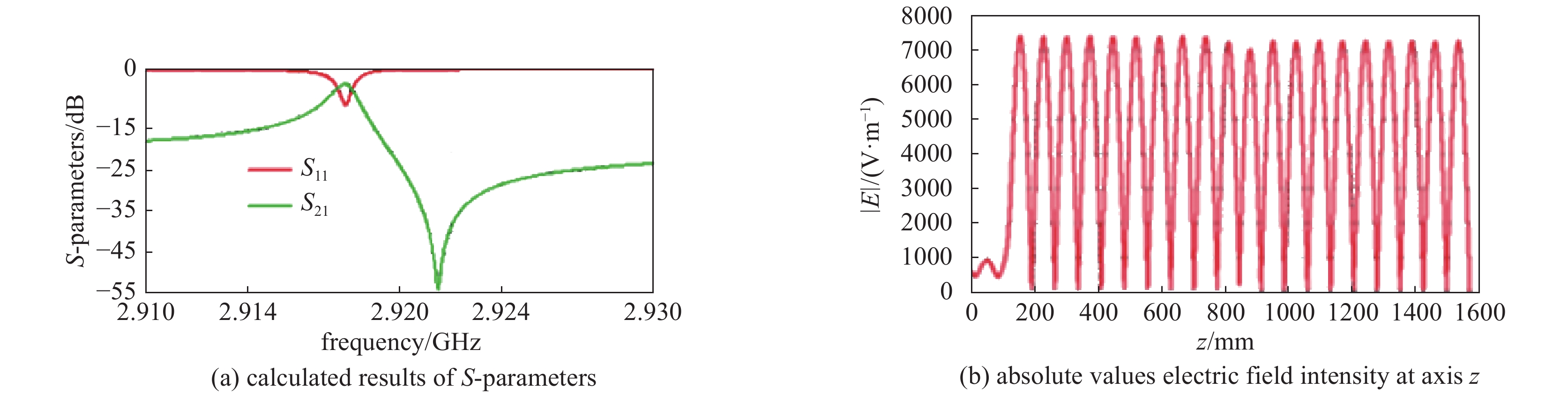
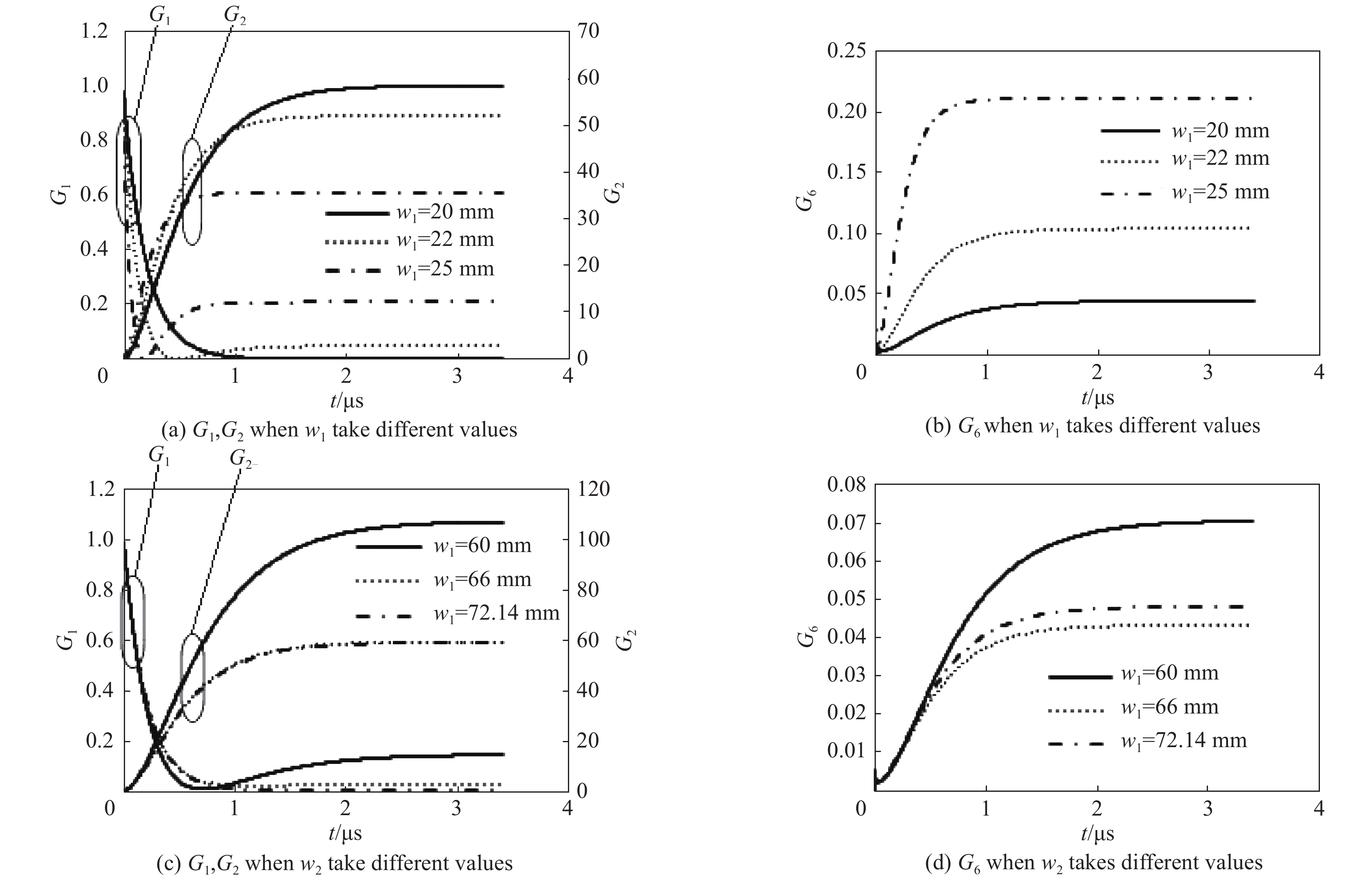
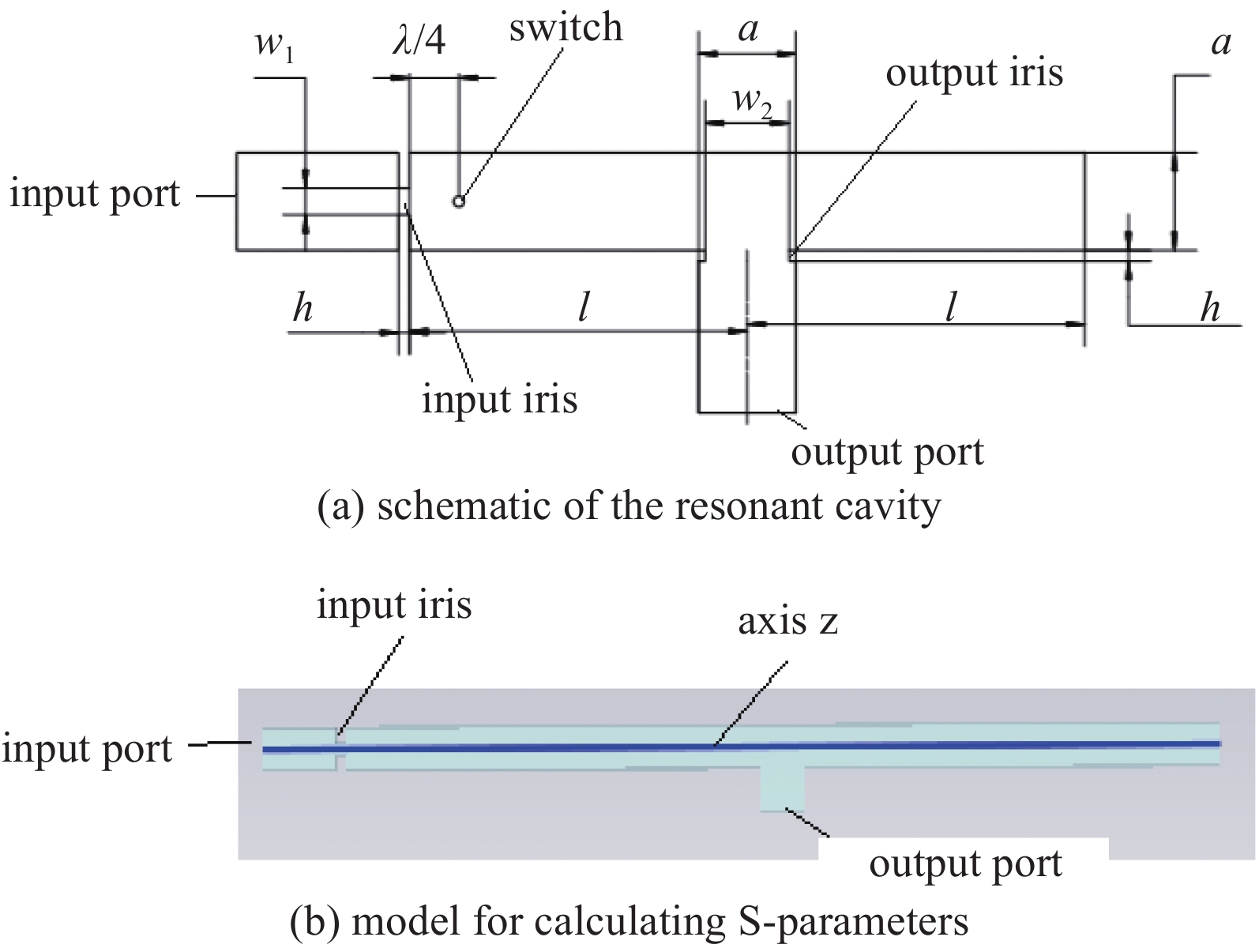
摘要: 为了计算高品质因数谐振腔的储能过程和泄能过程,将高品质因数谐振腔的输入膜片和输出结构分别建模为一个二端口网络和一个三端口网络,根据高品质因数谐振腔的信号流图,提出了一种基于递推的数值计算方法。用该方法设计了一个工作在2.92 GHz附近的基于BJ32波导的高品质因数谐振腔,给出了谐振腔的储能过程和泄能过程。当输入膜片开口宽度取20 mm、输出膜片开口宽度取60 mm时,计算得出的谐振频率为2.9198 GHz,饱和储能时间为2.6 μs,输出脉冲宽度6.82 ns,输出峰值增益为129.6,能量效率为0.169。Abstract: In order to calculate the storing process and dumping process of energy in high quality factor resonant cavity, the input iris and the output coupling structure are modeled as a 2-port net and a 3-port net respectively, and an algorithm based on iteration is proposed according to the signal flow graph of the high quality factor resonant cavity. The algorithm is then used to design a high quality factor resonant cavity working around 2.92 GHz and based on rectangular waveguide of type BJ32. When the width of the input iris takes 20 mm and the width of the output iris takes 60 mm, the resonant frequency, the storing time, the pulse width of the output pulse, the peak output power gain and the energy efficiency are calculated to be 2.9198 GHz, 2.6 μs, 6.82 ns, 129.6 and 0.169, respectively.
-
表 1
${w_{\rm{1}}}$ 取不同值时谐振腔参数计算结果Table 1. Calculated parameters of the resonant cavity when
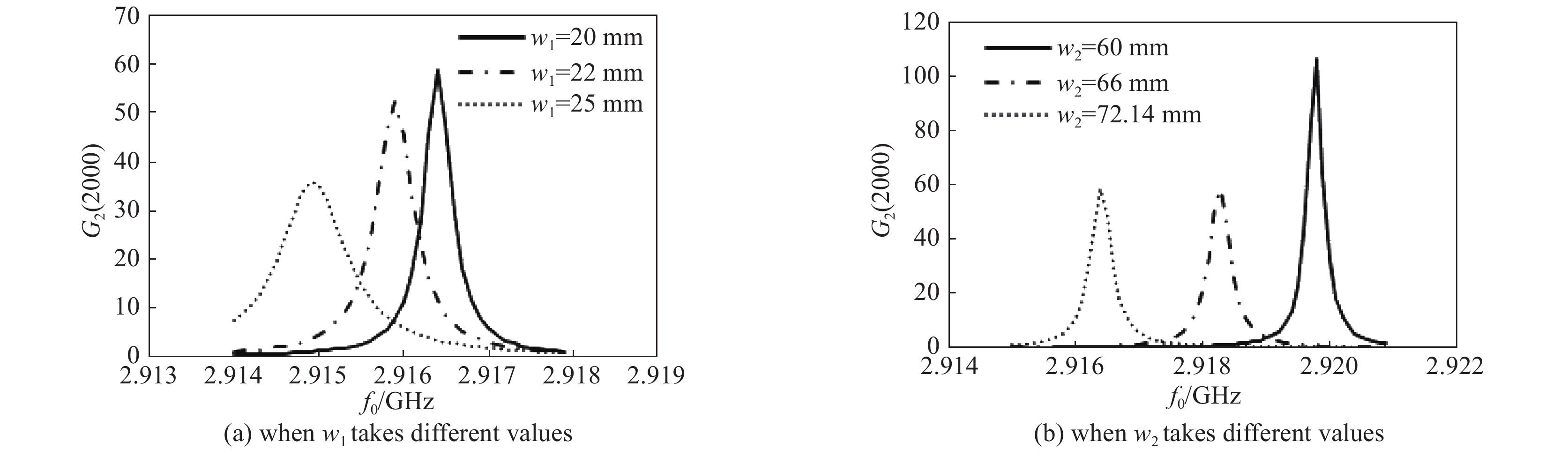
${w_{\rm{1}}}$ takes different values${w_1}$/mm $\Delta \lambda $/mm ${f_0}$/GHz $\left| {{S_{11}}} \right|$/dB $\left| {{S_{{2}1}}} \right|$/dB ${P_ + }$/W ${G_ + }$ ${Q_0}$ ${Q_{\rm{e}}}$ 20 1.08 2.9194 −25.33 −5.86 26.8 53.6 18501 52019 22 1.08 2.9189 −16.39 −4.58 23.1 46.2 18488 31304 25 1.08 2.9179 −8.69 −3.52 15.1 30.2 18460 13376 表 2
${w_{2}}$ 取不同值时谐振腔参数计算结果Table 2. Calculated parameters of the resonant cavity when
${w_{2}}$ takes different values${w_{2}}$/mm $\Delta \lambda $/mm ${f_0}$/GHz $\left| {{S_{11}}} \right|$/dB $\left| {{S_{{2}1}}} \right|$/dB ${P_ + }$/W ${G_ + }$ ${Q_0}$ ${Q_{\rm{e}}}$ 60 1.08 2.9229 −26.1 −6.25 28.7 57.4 18502 58721 66 1.08 2.9213 −26.1 −6.01 27.5 55 18503 54612 72.14 1.08 2.9194 −25.33 −5.86 26.8 53.6 18501 52019 表 3 输入膜片的S参数
Table 3. S-parameters of the input iris
${w_{\rm{1}}}$/mm Si11 Si12 20 −0.9881+0.0748j 0.0098+0.1290j 22 −0.9781+0.1180j 0.0201+0.1663j 25 −0.9499+0.1964j 0.0487+0.2355j 表 4 输出结构的S参数
Table 4. S-parameters of the output structure
${w_{2}}$/mm So11 So12 So13 So33 60 −0.2319−0.0767j 0.7514−0.2568j 0.47+0.2962j −0.1047+0.6096j 66 −0.2428−0.0301j 0.7252−0.2794j 0.5105+0.2729j −0.0158+0.5731j 72.12 −0.2405+0.0165j 0.7040−0.3105j 0.5228+0.2556j 0.0294+0.5481j 表 5 输出峰值增益
Table 5. Peak gain at the output port
${w_{2}}$/mm $\left| {{S_{{\rm{o}}13}}} \right|$ ${G_ + }$ ${G_{\rm{S}}}$ ${G_{6{\rm{p}}}}$ $\eta $ 60 0.5555 57.4 70.86 129.6 0.169 66 0.5555 55 67.90 77.34 0.101 72.12 0.5555 53.6 66.17 77.95 0.102 -
[1] 钱宝良. 国外高功率微波技术的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 真空电子技术, 2015(2):2-7. (Qian Baoliang. The research status and developing tendency of high power microwave technology in foreign countries[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2015(2): 2-7 [2] 张颜颜, 陈宏, 鄢振麟, 等. 高功率微波反无人机技术[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2020, 35(4):39-43. (Zhang Yanyan, Chen Hong, Yan Zhenlin, et al. The technology of high power microwave anti-bee swarm drone[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2020, 35(4): 39-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2020.04.009 [3] 杨丽娜, 曹泽阳, 韩耀锋. 高功率微波反无人机蜂群系统能力需求分析[J]. 军事运筹与系统工程, 2020, 34(2):26-32. (Yang Li’na, Cao Zeyang, Han Yaofeng. Analysis on the demand for the capability of high power microwave anti-bee swarm drone system[J]. Military Operations Research and Systems Engineering, 2020, 34(2): 26-32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8211.2020.02.005 [4] Chumerin P Y, Yushkov Y G. A shaper of gigawatt nanosecond microwave pulses with time domain compression of magnetron radiation energy[J]. Instruments and Experimental Techniques, 2000, 43(3): 363-365. doi: 10.1007/BF02759036 [5] Manko A N, Slinko V N, Chumerin P Y, et al. A facility with resonant pulse compression for generating high-power Ku-band microwave pulses[J]. Instruments and Experimental Techniques, 2004, 47(3): 372-375. doi: 10.1023/B:INET.0000032906.57420.0e [6] Avgustinovich V A, Artemenko S N, Kaminskii V L, et al. A two-step system for compression of microwave pulses in series-coupled resonators[J]. Instruments and Experimental Techniques, 2007, 50(2): 233-236. doi: 10.1134/S002044120702011X [7] Avgustinovich V A, Artemenko S N, D’yachenko V F, et al. A study of the switching of the microwave compressor switch in a circular waveguide[J]. Instruments and Experimental Techniques, 2009, 52(4): 547-550. doi: 10.1134/S0020441209040137 [8] Artemenko S N, Yushkov Y G. Compression of microwave pulses in a resonant system based on two waveguide T-joints[J]. Radioelectronics and Communications Systems, 2011, 54(5): 281-283. doi: 10.3103/S0735272711050086 [9] Artemenko S N, Gorev S A, Igumnov V S, et al. Formation of long nanosecond rectangular pulses in the active RF pulse compression system with a compact resonant cavity[J]. Journal of Physics, 2016, 755: 011001. [10] Savaidis S P, Mitilineos S A, Ioannidis Z C, et al. Experiments on the pulse repetition frequency optimization of 1.3-GHz, 100-kW microwave pulse compressor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(6): 2374-2381. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.2978046 [11] 宁辉, 方进勇, 李平, 等. 高功率微波脉冲压缩技术实验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2001, 13(4):471-474. (Ning Hui, Fang Jinyong, Li Ping, et al. Experimental research on HPM pulse compression[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2001, 13(4): 471-474 [12] 谢苏隆, 曹学军. X波段过模圆柱腔脉冲压缩技术理论研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2006, 18(4):639-642. (Xie Shulong, Cao Xuejun. Theoretic research of X-band excessive modes cylindrical cavity pulse compression technology[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2006, 18(4): 639-642 [13] 方进勇, 黄惠军, 张治强, 等. 基于圆柱谐振腔的高功率微波脉冲压缩系统[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60:048404. (Fang Jinyong, Huang Huijun, Zhang Zhiqiang, et al. High power microwave pulse compression system based on cylindrical resonant cavity[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60: 048404 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.048404 [14] Jiang Tao, Yang Meng, Xiong Zhengfeng, et al. An X-band switched energy storage microwave pulse compression system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2019, 47(10): 4525-4529. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2019.2920739 [15] 廖承恩. 微波技术基础[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 1994.Liao Cheng’en. Basis of microwave technology[M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 1994) [16] Altman J L. Microwave Circuits[M]. Canada: D. Van Nostrand Company Ltd, 1964. -




 下载:
下载: