Design and study of atmospheric pressure microwave plasma jet
-
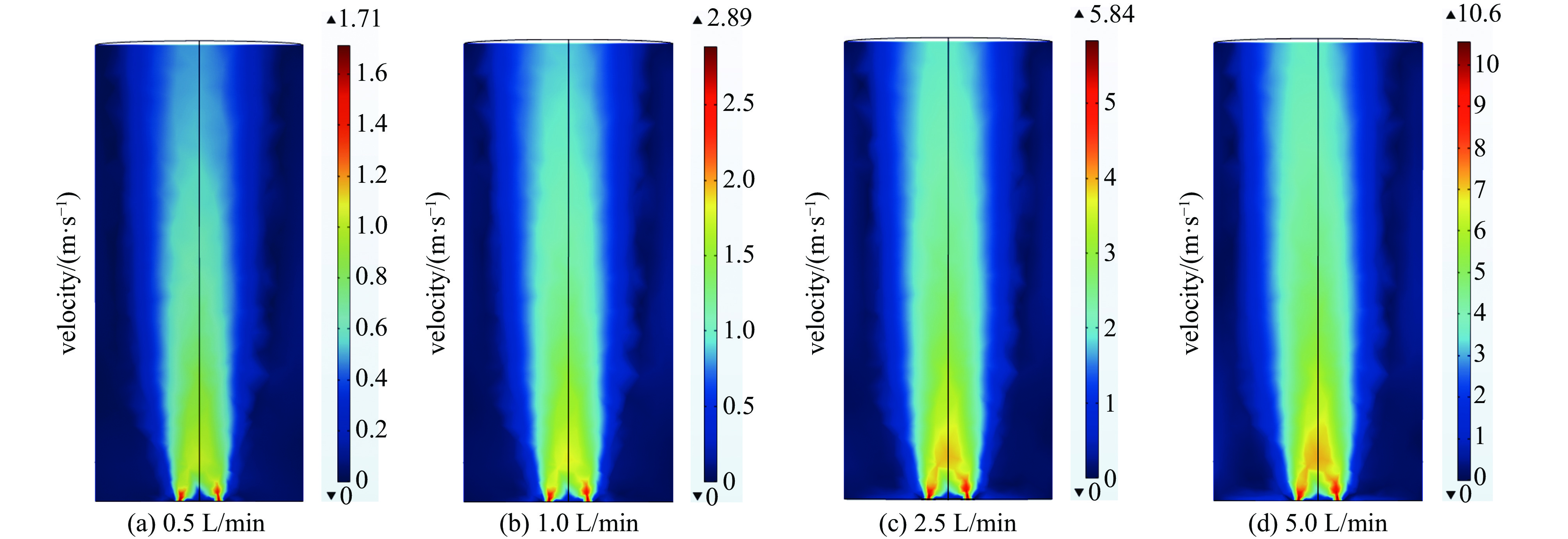
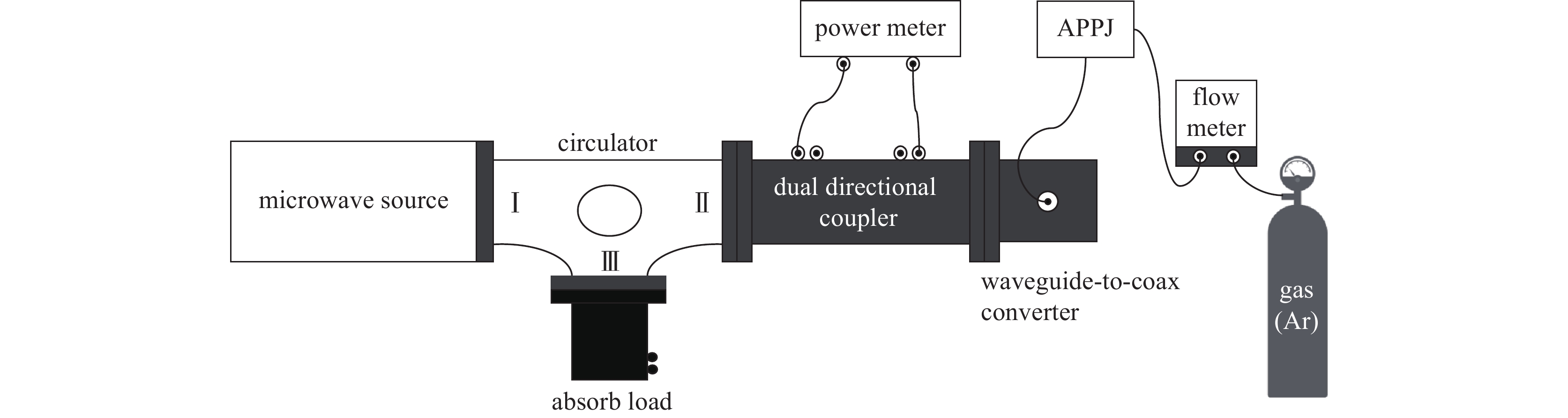
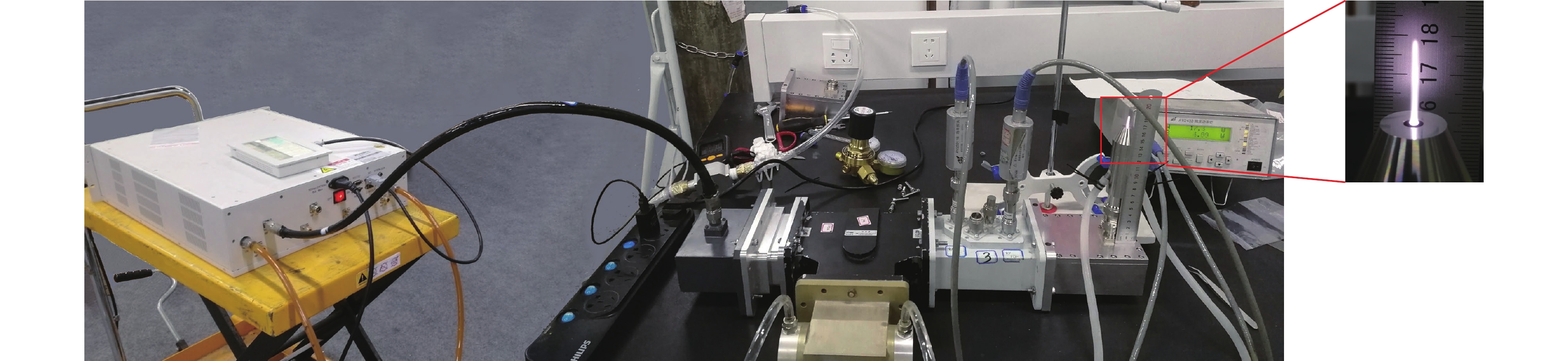
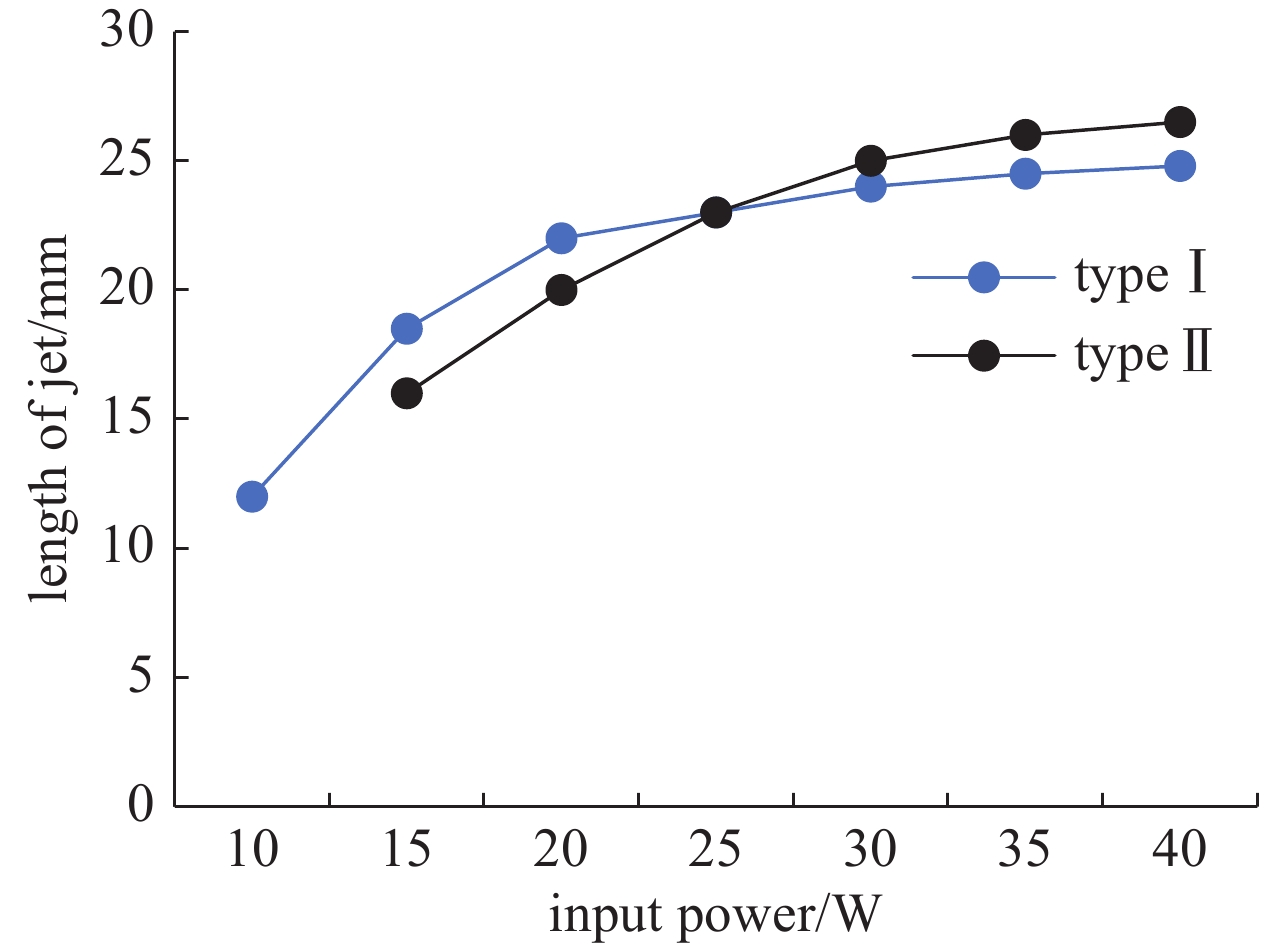
摘要: 基于同轴传输线结构设计了两种不同喷嘴结构的大气压微波等离子体射流(MW-APPJ)装置,其工作频率2.45 GHz,工作气体为氩气,分别研究了两种不同喷嘴结构对等离子体放电特性产生的影响。仿真结果表明,MW-APPJ在气体喷嘴处会产生高强度的电场,经过优化结构,实现在频率2.45 GHz下,喷嘴处的场强满足氩气电离的击穿场强阈值要求。同时,利用多物理场耦合仿真软件对装置的气流分布进行了稳态模拟,并通过实验对比分析了两种喷嘴结构下大气压氩等离子体射流的基本特性。实验结果表明,不同的喷嘴结构会影响等离子体装置的反射系数随输入功率的变化规律,但并不影响等离子体射流长度随输入功率的变化规律和反射功率随进气流量的变化规律;同时,在大气压下,稳态微波等离子体射流呈现出类金属性,等离子体中的电子只能在很薄的区域中吸收微波能量,因而造成微波的反射功率较大。Abstract: Two atmospheric pressure microwave plasma jet (MW-APPJ) devices with different nozzle structures are designed which are based on the coaxial transmission line structure. The frequency is 2.45 GHz and working gas is argon. What's more, the effects of two different nozzle structures on the characteristics of plasma discharge have been studied. Based on the electromagnetic field simulation results, the MW-APPJ generates a high-intensity electric field at the nozzle. After optimizing the structure, the field strength at the nozzle have reached the breakdown field strength required for argon ionization under the frequency of 2.45 GHz. Meanwhile, the simulation of the argon flow distribution was carried out under steady-state using multi-physics coupling simulation software. In addition, the basic characteristics of the atmospheric pressure argon plasma jet under the two nozzle structures were compared and analyzed through experiments. The experimental results show that different nozzle structures can affect the variation of reflection parameter with input power, but do not affect the variation of plasma jet length with input power and the variation of reflected power with inlet flow; at the same time, under atmospheric pressure, the steady-state microwave plasma jet exhibits metal-like property and the electrons in the plasma can only absorb microwave energy in a very thin area, which causes large reflected power of the microwave.
-
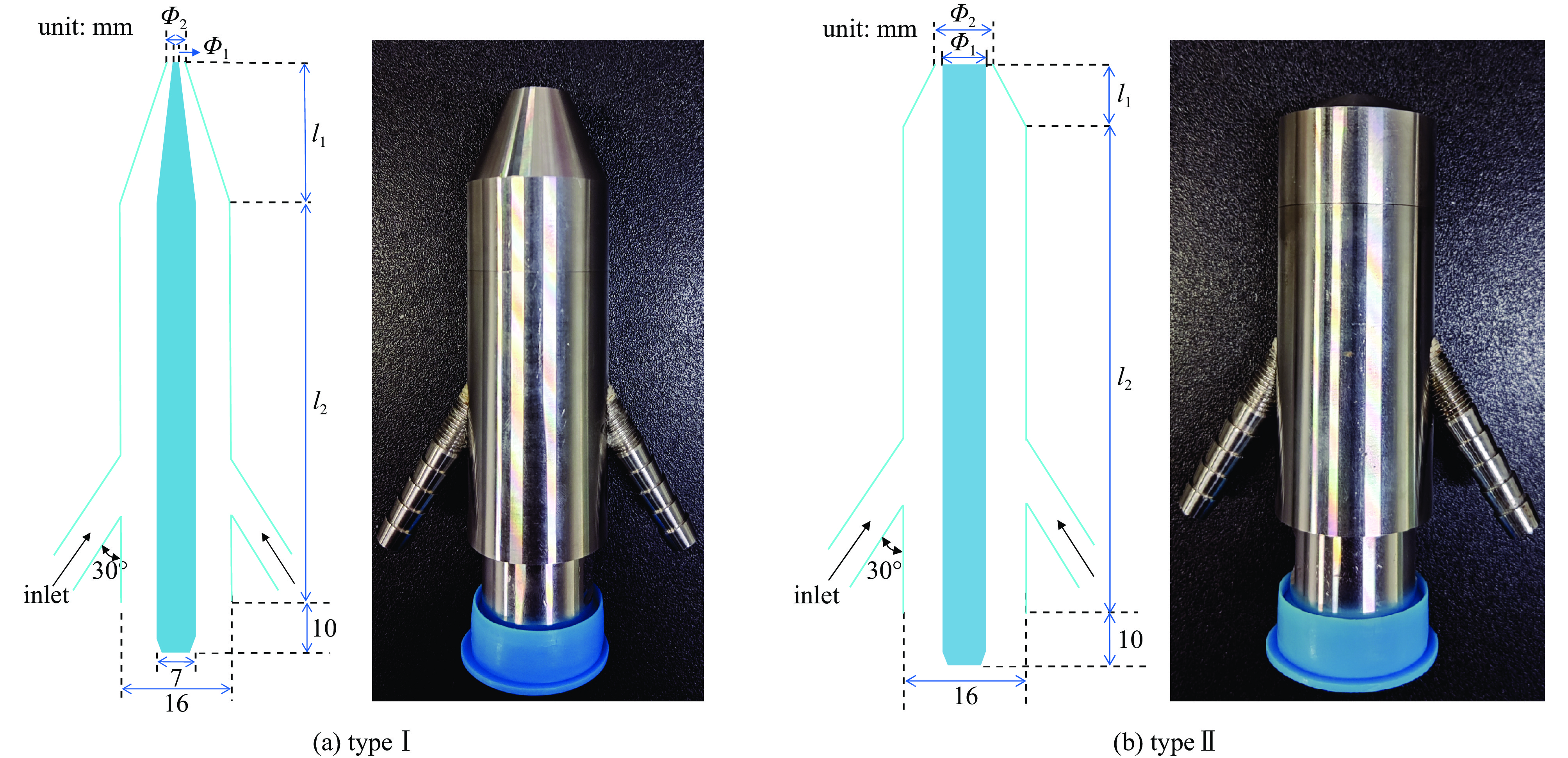
表 1 优化结构尺寸
Table 1. Optimized structure size
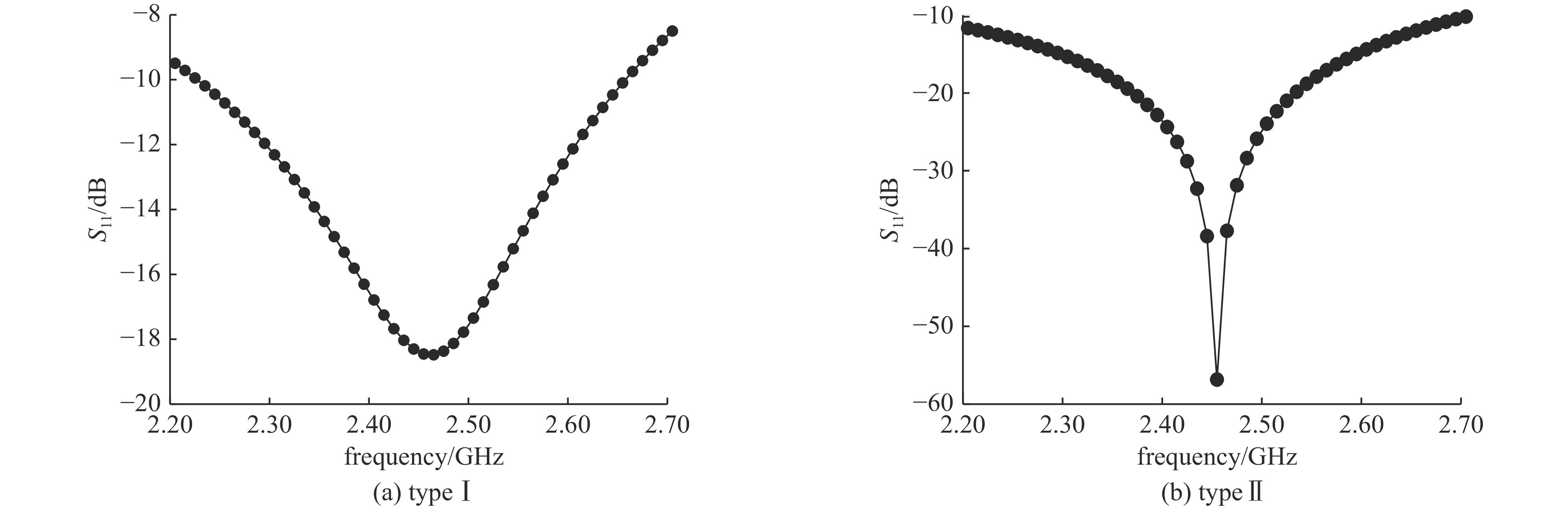
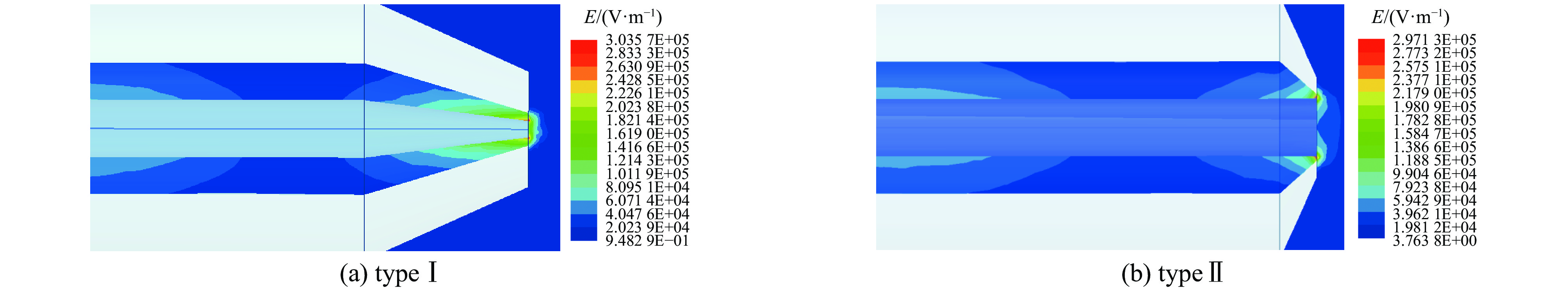
item Φ1/mm Φ2/mm l1/mm l2/mm typeⅠ 2 4 20 77 typeⅡ 7 9 4.5 77.5 表 2 仿真结果
Table 2. Results of simulation
item f/GHz S11/dB Emax/(V·m−1) typeⅠ 2.45 −18.45 3.04×105 typeⅡ 2.45 −56.84 2.97×105 -
[1] 李文浩, 褚向前, 赵世奇, 等. 大气压宽径向空气等离子体射流装置的设计、实验和仿真研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2019, 39(5):420-428. (Li Wenhao, Chu Xiangqian, Zhao Shiqi, et al. Modification of atmospheric pressure air plasma jet: a simulation and experimental study[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2019, 39(5): 420-428 [2] Onyshchenko I, De Geyter N, Morent R. Improvement of the plasma treatment effect on PET with a newly designed atmospheric pressure plasma jet[J]. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 2017, 14: 1600200. doi: 10.1002/ppap.201600200 [3] Lehmann A, Pietag F, Arnold T. Human health risk evaluation of a microwave-driven atmospheric plasma jet as medical device[J]. Clinical Plasma Medicine, 2017, 7/8: 16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cpme.2017.06.001 [4] Fu Wenjie, Zhang Chaoyang, Nie Cong, et al. A high efficiency low-temperature microwave-driven atmospheric pressure plasma jet[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2019, 114: 254106. doi: 10.1063/1.5108538 [5] 李和平, 于达仁, 孙文廷, 等. 大气压放电等离子体研究进展综述[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(12):3697-3727. (Li Heping, Yu Daren, Sun Wenting, et al. State-of-the-art of atmospheric discharge plasmas[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(12): 3697-3727 [6] Park G Y, Park S J, Choi M Y, et al. Atmospheric-pressure plasma sources for biomedical applications[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2012, 21: 043001. doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/21/4/043001 [7] Choi J, Iza F, Do H J, et al. Microwave-excited atmospheric-pressure microplasmas based on a coaxial transmission line resonator[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2009, 18: 025029. doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/18/2/025029 [8] Kim J, Katsurai M, Kim D, et al. Microwave-excited atmospheric-pressure plasma jets using a microstrip line[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93: 191505. doi: 10.1063/1.3025841 [9] 张庆, 张贵新, 王黎明, 等. 大气压微波等离子体炬的仿真设计与实验[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(2):315-318. (Zhang Qing, Zhang Guixin, Wang Liming, et al. Design and experiment of an atmospheric pressure microwave plasma torch[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(2): 315-318 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102202.0315 [10] Wang Yaoyao, Wang Zhongli, Wu Dajun, et al. Design of a fully automatic microwave plasma torch system[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019, 90: 055112. doi: 10.1063/1.5097182 [11] 任昊. 基于COMSOL的MPT离子化源等离子体建模仿真[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014Ren Hao. Modeling and simulation of MPT ionization source based on COMSOL[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014 [12] Li Shouzhe, Xu Maochun, Zhang Xin, et al. A pulse-modulated nonequilibrium atmospheric-pressure microwave argon plasma discharge preionized by a kilohertz excited plasma jet[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100: 174101. doi: 10.1063/1.4705433 [13] Lu Xinpei, Naidis G V, Laroussi M, et al. Reactive species in non-equilibrium atmospheric-pressure plasmas: generation, transport, and biological effects[J]. Physics Reports, 2016, 630: 1-84. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.03.003 [14] 张冠军, 詹江杨, 邵先军, 等. 大气压氩气等离子体射流长度的影响因素[J]. 高电压技术, 2011, 37(6):1432-1438. (Zhang Guanjun, Zhan Jiangyang, Shao Xianjun, et al. Influence factor analysis on jet length of atmospheric pressure argon plasma jets[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2011, 37(6): 1432-1438 [15] Yue Yuanfu, Pei Xuekai, Lu Xinpei. Comparison on the absolute concentrations of hydroxyl and atomic oxygen generated by five different nonequilibrium atmospheric-pressure plasma jets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2017, 1(6): 541-549. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2017.2757037 [16] Woo W, DeGroot J S. Microwave absorption and plasma heating due to microwave breakdown in the atmosphere[J]. The Physics of Fluids, 1984, 27(475): 475-487. [17] 刘繁, 汪建华, 王秋良, 等. 常压微波等离子体炬装置的模拟与设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(6):1504-1508. (Liu Fan, Wang Jianhua, Wang Qiuliang, et al. Numerical modeling and design of atmospheric pressure microwave plasma jet[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(6): 1504-1508 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112306.1504 [18] 刘文正, 贾凌云, 孔飞, 等. 阵列式等离子体射流特性的研究[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2011, 35(2):105-108. (Liu Wenzheng, Jia Lingyun, Kong Fei, et al. Study on the characteristics of array plasma jet[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2011, 35(2): 105-108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0291.2011.02.019 -




 下载:
下载: