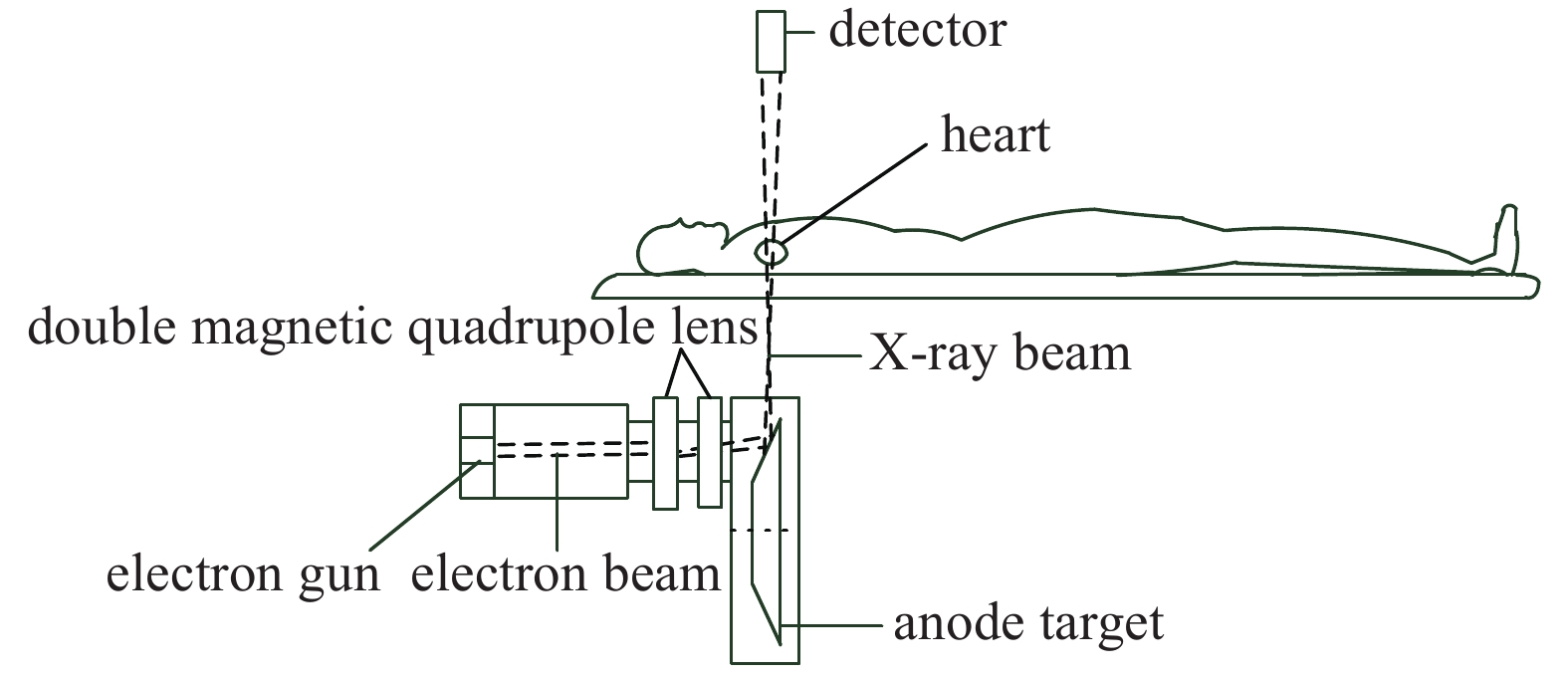
Research of flying focal spot of the CT tube based on dynamic magnetic focusing
-
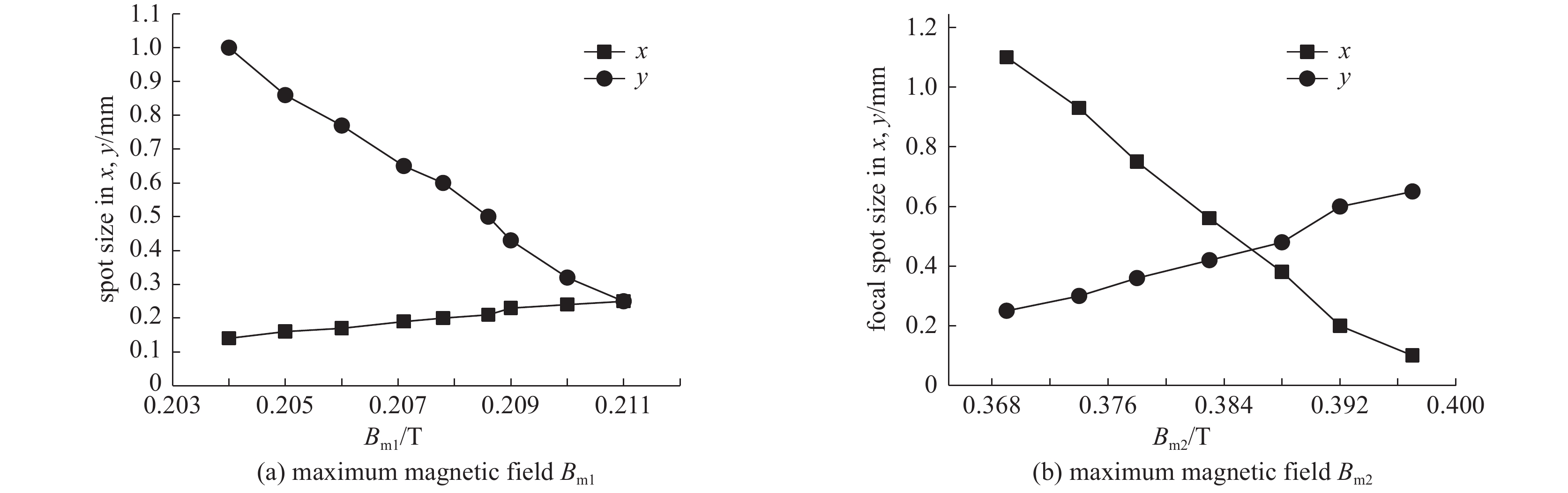
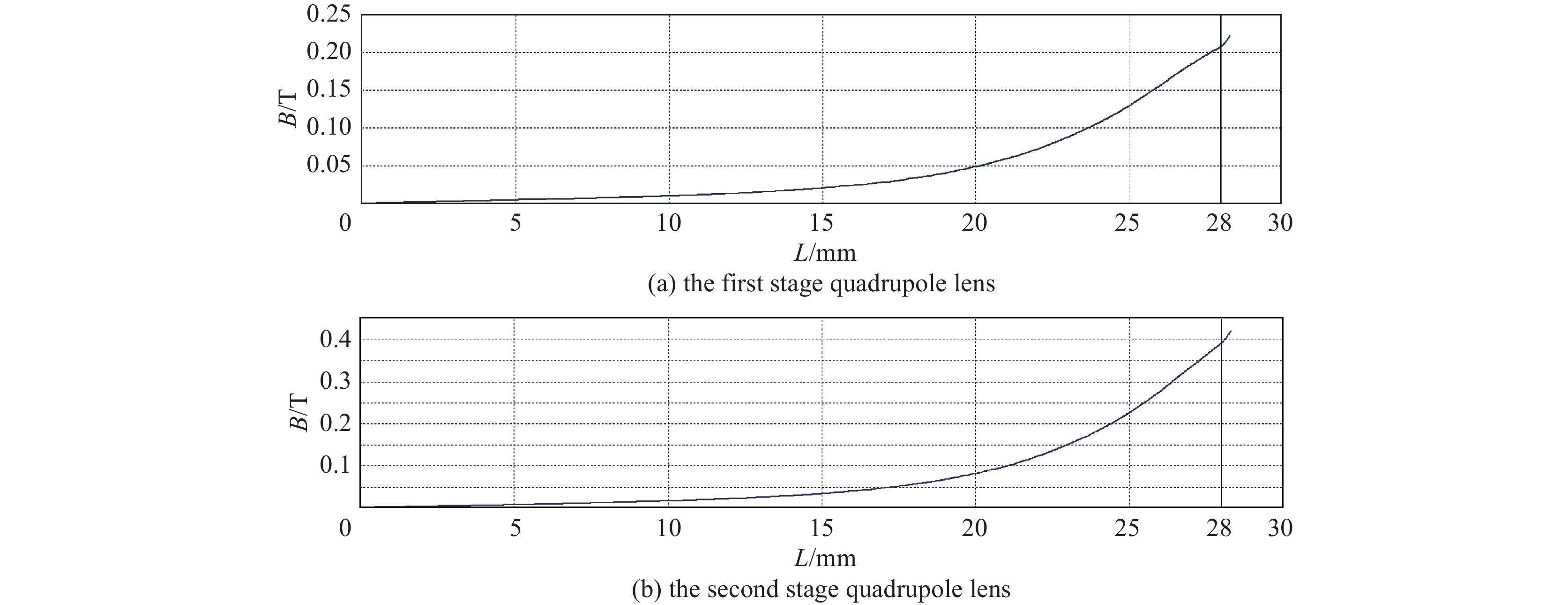
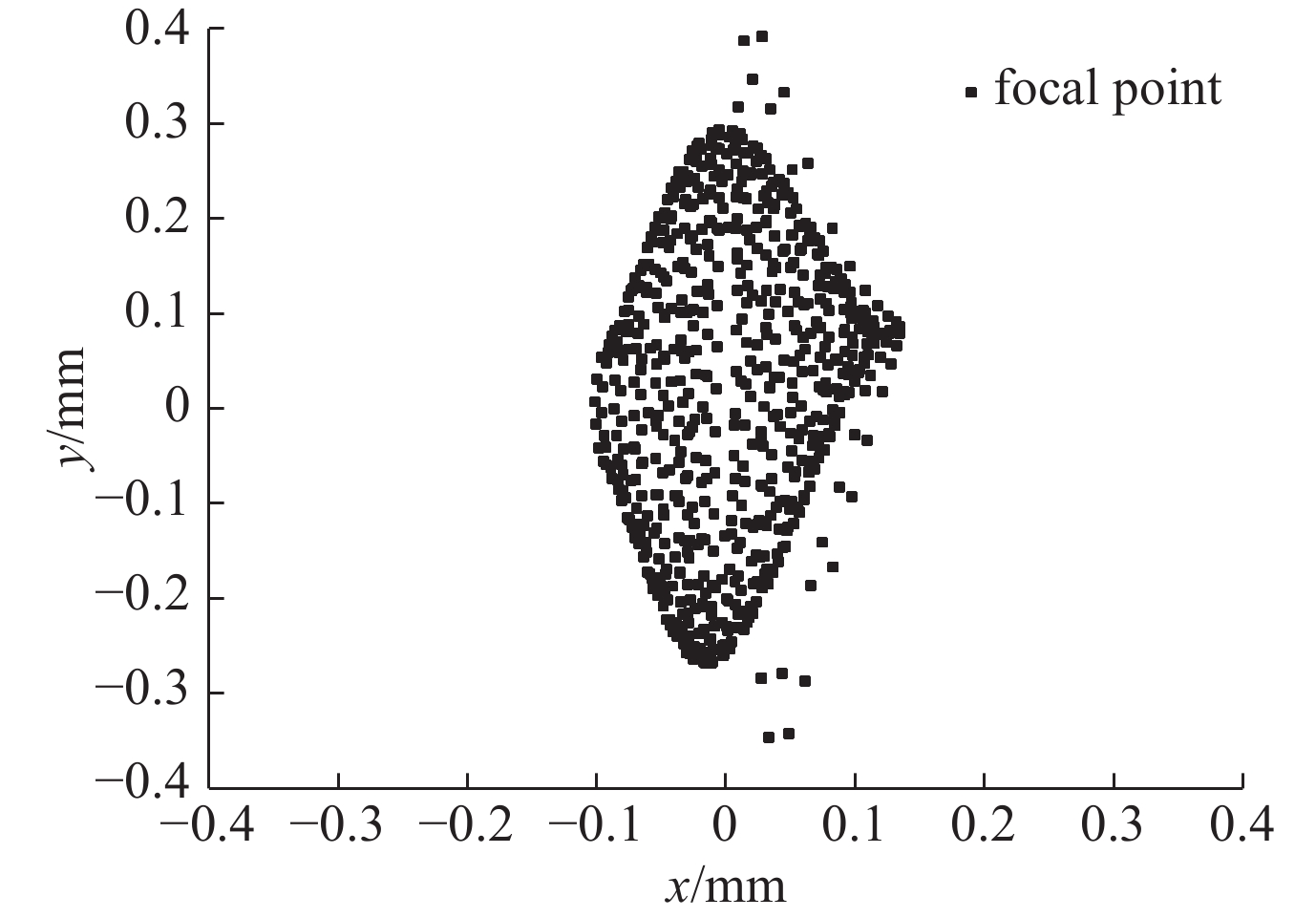
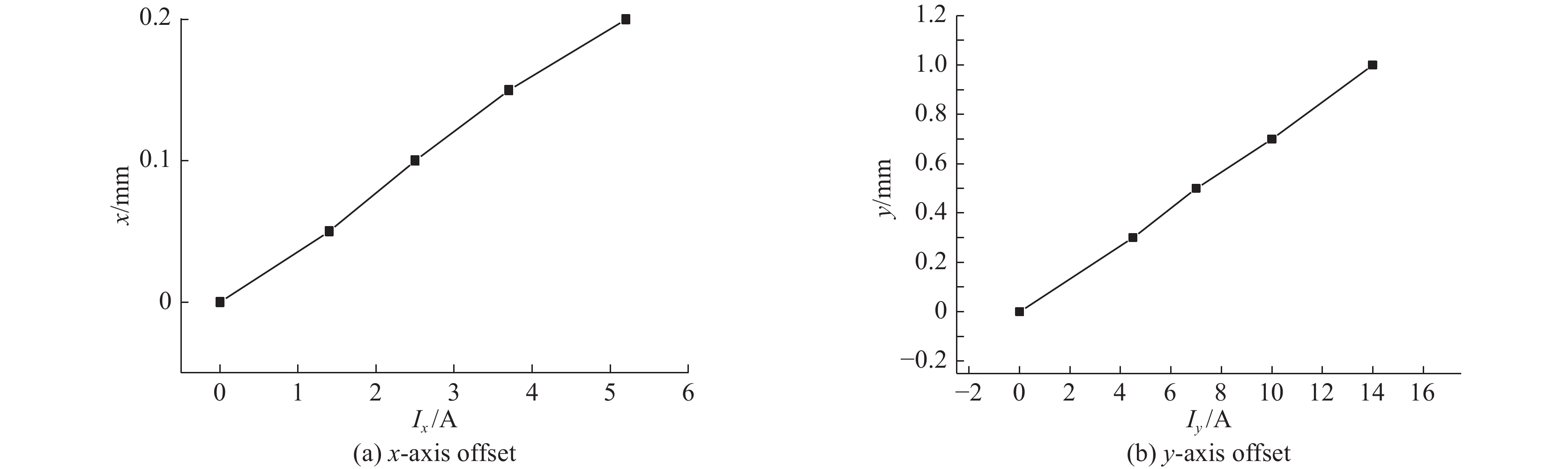
摘要: 作为CT设备的核心器件,CT球管采用动态磁聚焦技术以利于大电流输出时小焦点的实现。飞焦点技术可以多角度记录每次扫描的每个投影,提高采样率,从而大幅改善图像清晰度,提高成像质量。当CT球管为1 A大电流输出时,采用CST软件对双磁四极透镜关键参数进行模拟仿真及优化,满足焦点目标尺寸为0.2 mm×0.6 mm的同时具备飞焦点功能。Abstract: CT tube is the core component of CT equipment. CT tube adopts dynamic magnetic focusing technology to facilitate the realization of small focus when there is large current output. Flying focal spot technology can record each projection of each scan from multiple angles, improve the sampling rate, and greatly improve the image definition and quality. CST software is used to simulate the CT tube based on dynamic magnetic focusing. When the CT tube outputs high current of 1 A, the key parameters of the dual magnetic quadrupole lens are optimized to get the target size of focus of 0.2 mm×0.6 mm and the function of flying focus.
-
Key words:
- core component /
- CT tube /
- dynamic magnetic focusing /
- dual magnetic quadrupole lens /
- flying focal spot
-
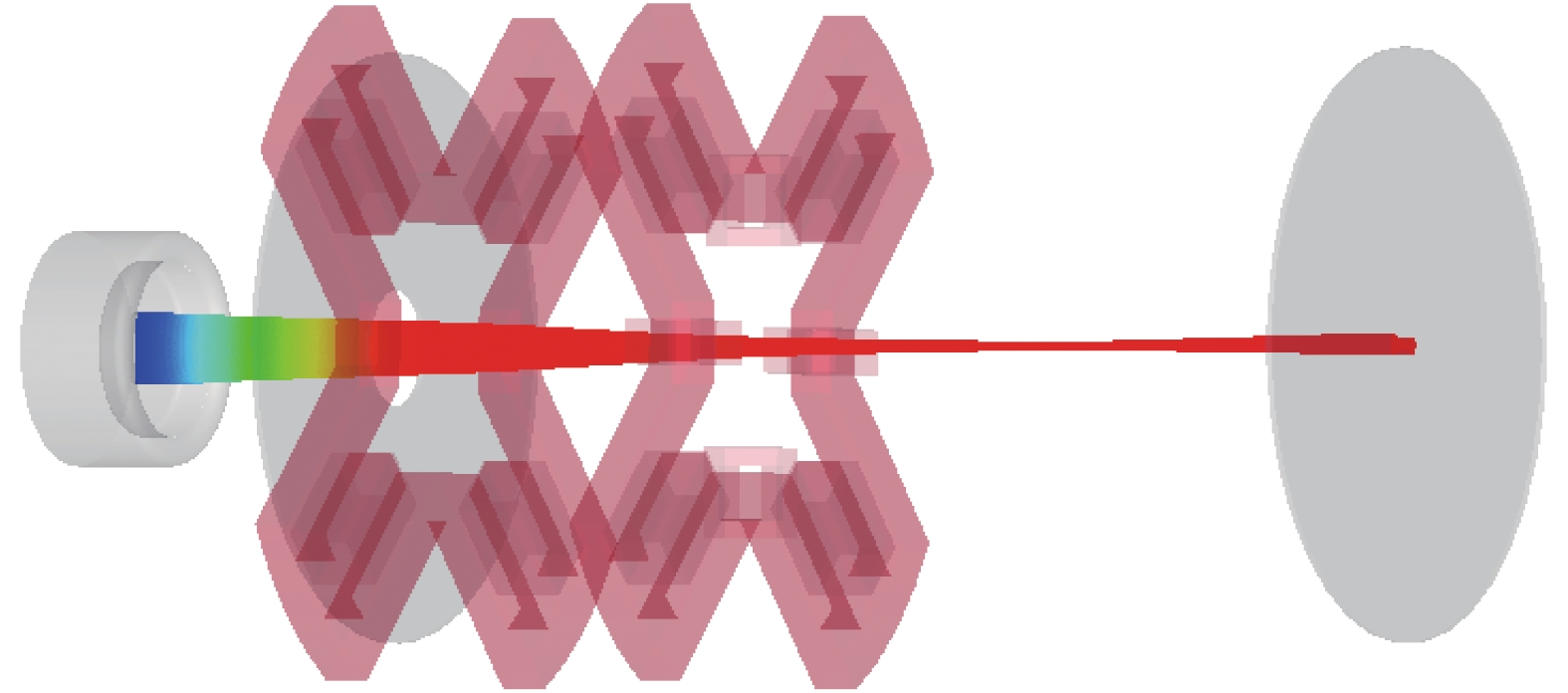
图 4 双磁四极透镜系统CST仿真结构
Figure 4. CST simulation structure of dual magnetic quadrupole lens system
1—focusing electrode; 2—cathode; 3—anode head; 4—first stage quadrupole lens core; 5—first stage quadrupole lens coil; 6—second stage quadrupole lens core; 7—second stage quadrupole lens coil; 8—deflection coil; 9—enclosure; 10—anode target.
表 1 国外部分机构在动态磁聚焦飞焦点技术的应用
Table 1. Application of foreign institutions in dynamic magnetic focusing flying focus technology
number institution CT tube flying focal spot technology image resolution improvement 1 Siemens[7] Straton z-Sharp technology(z-axis double sampling) each probe unit yields two alternately overlapping X-line projections without a dose increase, substantially improving the spatial resolution and imaging quality 2 Philips iMRC precise flying focal spot (SFS,the x-axial and z-axial flying focal spot technology) double sampling rate is obtained in plane and longitudinal direction, which is equivalent to 4 times of detector, and high spatial resolution is obtained in axial position and spiral scanning 3 Dunlee CT5000 xDFS(the x-axial flying focal spot),zDFS(the z-axial flying focal spot) improve imaging quality, provide sharp and clear images, zDFS double the number of slices, and there is no need for detectors with higher spatial resolution -
[1] 逯乐慧, 王颖, 刘艳岚. CT成像纳米探针的设计及应用[C]//中国化学会第30届学术年会摘要集-第三十八分会: 纳米生物效应与纳米药物化学. 2016: 188.Lu Lehui, Wang Ying, Liu Yanlan. Nanoprobe for CT imaging[C]//Summary of the 30th Annual Conference of the Chinese Chemical Society—Chapter 38: Nanobiological Effects and Nanomedicinal Chemistry. 2016: 188. [2] 石灵, 张富治, 王瑞海, 等. 医用CT球管国内外现状及发展趋势[J]. 真空电子技术, 2018(2):61-64,68. (Shi Ling, Zhang Fuzhi, Wang Ruihai, et al. Domestic and foreign situation and development trend of medical CT X-ray tubes[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2018(2): 61-64,68 [3] 余晓锷, 龚剑. CT原理与技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 16Yu Xiao’e, Gong Jian. CT philosophy and technique[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 16 [4] 张富治, 盛兴, 王瑞海, 等. X射线CT球管的研制进展[J]. 真空电子技术, 2016(1):7-10. (Zhang Fuzhi, Sheng Xing, Wang Ruihai, et al. Research development of the X-ray tubes for CT[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2016(1): 7-10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8935.2016.01.003 [5] Braun M. Physics of X-ray tubes for CT scanners[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1979, 26(2): 2840-2844. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1979.4330546 [6] Behling R. Modern diagnostic X-ray sources: technology manufacturing, reliability[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2015: 216. [7] Kachelriess M, Knaup M, Penssel C, et al. Flying focal spot (FFS) in cone-beam CT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2006, 53(3): 1238-1247. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2006.874076 [8] Legge G J F. A history of ion microbeams[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 1997, 130(1/4): 9-19. [9] Gestrin G N, Kuleshov A N, Yefimov B P. Magnetic focusing system for hybrid FEL-based on quadrupole lenses[C]//2004 14th International Crimean Conference “Microwave and Telecommunication Technology”. 2004: 237-238. [10] 李泉凤. 电磁场数值计算与电磁铁设计[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2002: 184Li Quanfeng. Numerical calculation of electro-magnetic field and electromagnet design[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2002: 184 [11] 陈连运. 单粒子束装置束线传输系统的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2002: 21Chen Lianyun. Study on beam transport of the single-ion microbeam facility[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2002: 21 [12] 杜秉初, 汪健如. 电子光学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2002: 305Du Bingchu, Wang Jianru. Electron optics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2002: 305 [13] Chichkine V, Winkler A, Behr K H, et al. Strong pulsed magnetic quadrupole lens[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2002, 12(1): 699-702. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2002.1018497 [14] 窦彦昕. 聚焦型高能离子微束技术的模拟研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018: 29Dou Yanxin. Simulation research on the focused high energy ion microbeam technology[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018: 29 [15] 钱文枢. 大功率辐照加速器X射线转换靶研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2008: 19Qian Wenshu. Research of the bremsstrahlung converter for high-power irradiation linacs[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2008: 19 [16] 赵国骏, 凌宝京, 薛坤兴. 电子离子光学[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1994: 135-146Zhao Guojun, Ling Baojing, Xue Kunxing. Electronic ion optics[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1994: 135-146 -





 下载:
下载: