Pulse magnetic properties measurement of Fe-based nanocrystalline cores and its application in magnetic switches
-
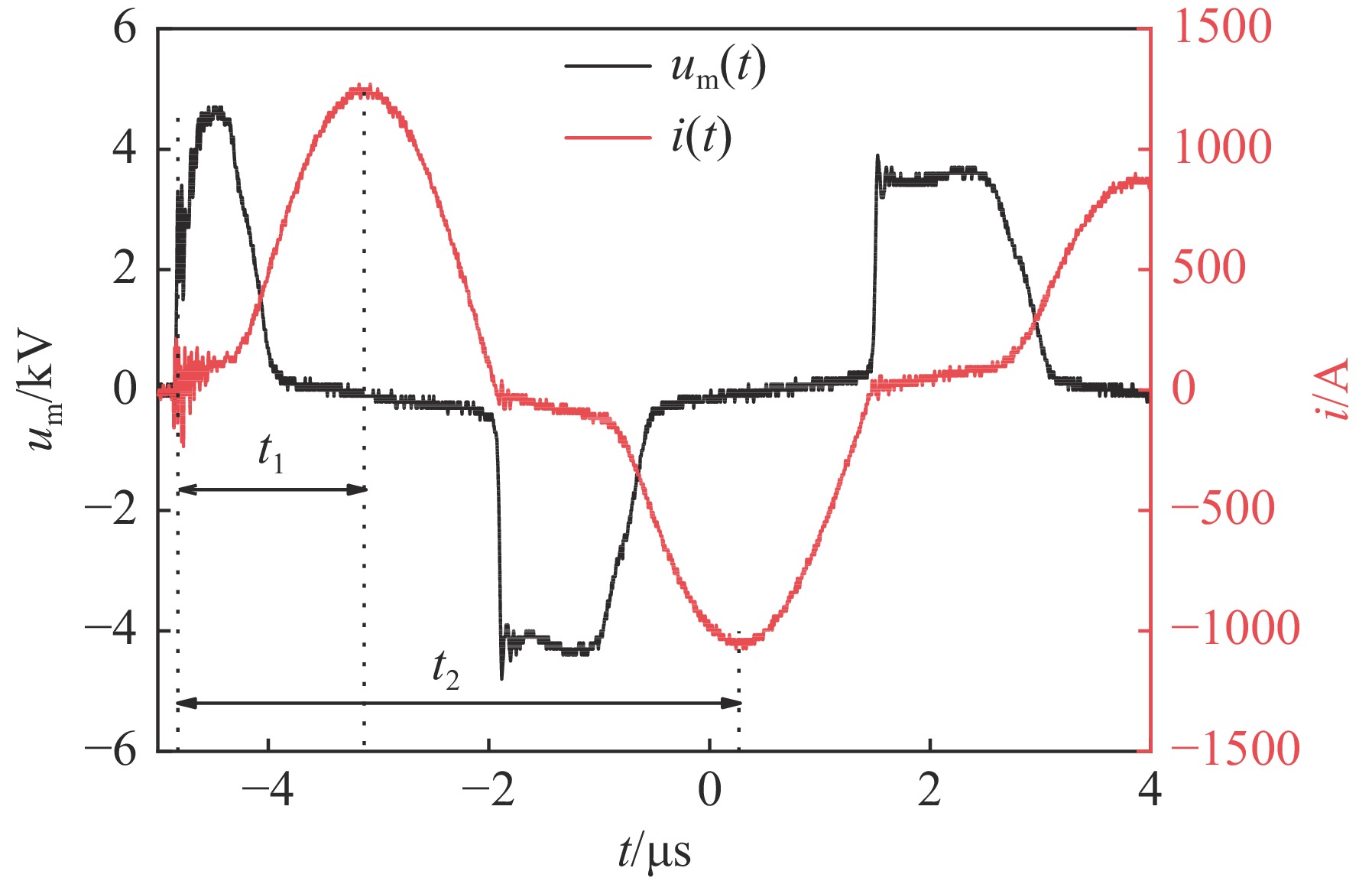
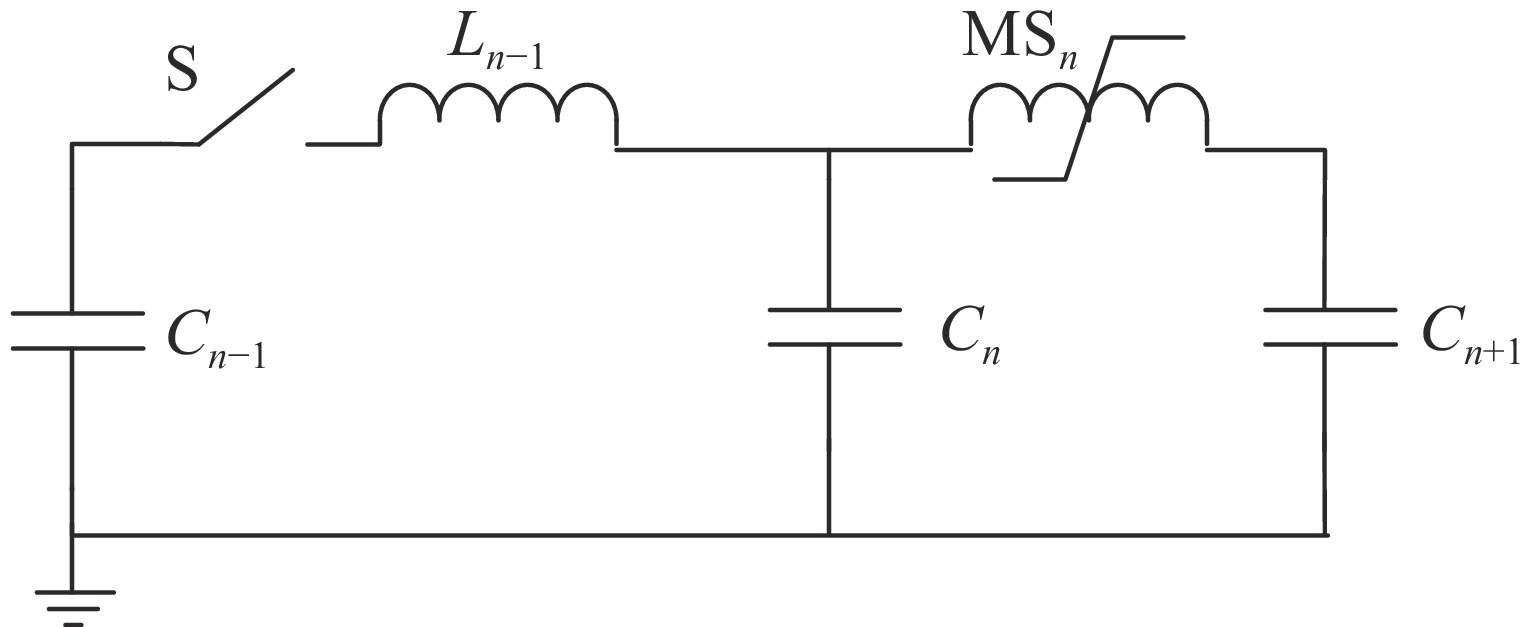
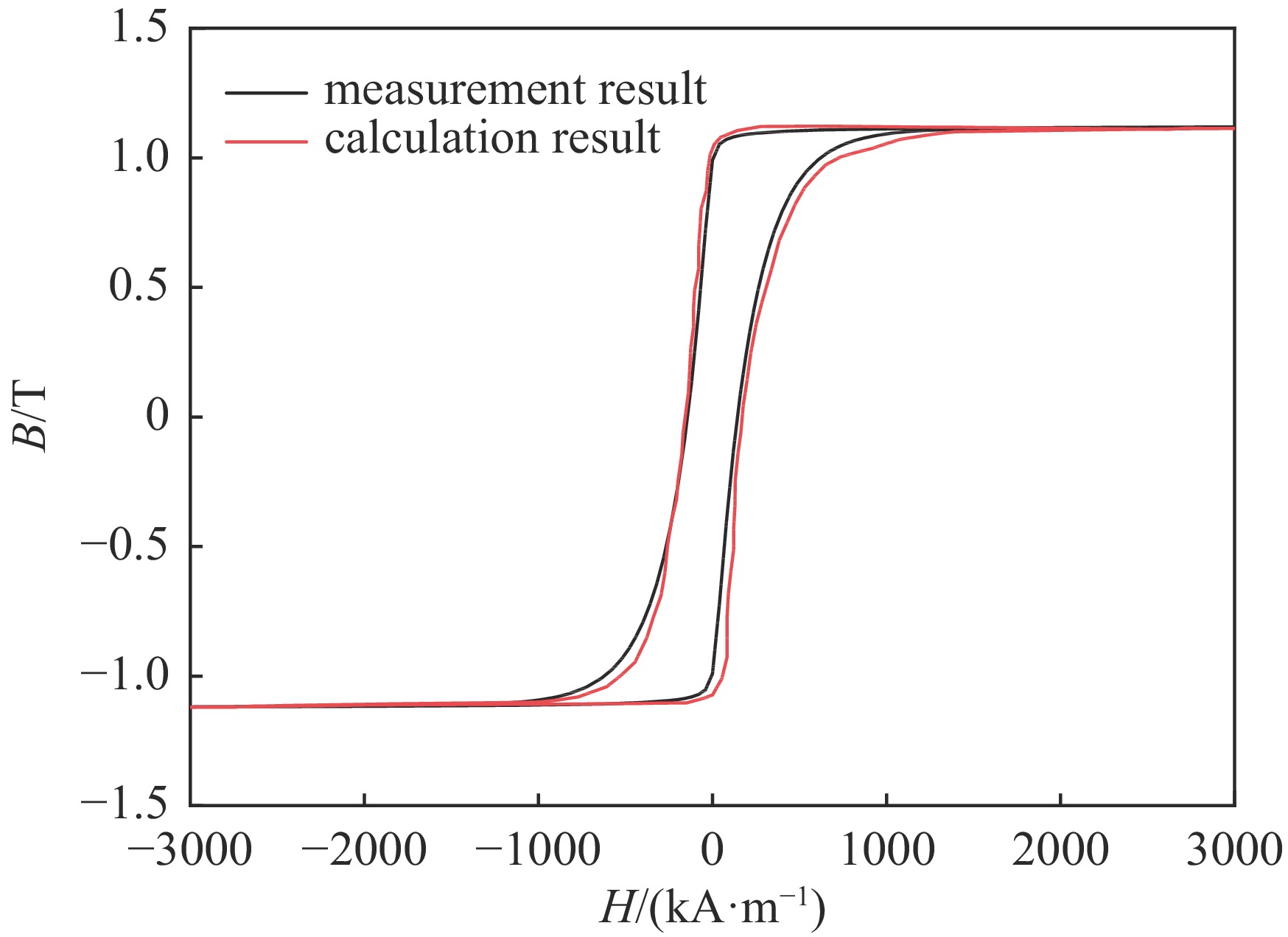
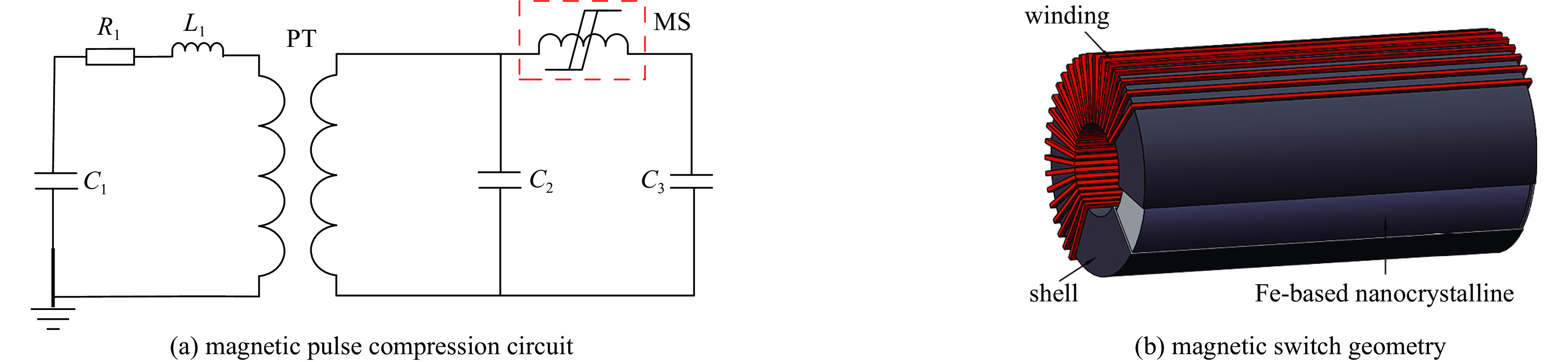
摘要: 磁开关是重复频率脉冲功率系统可选的工作性能优越的开关器件之一。目前磁开关的仿真模型是基于伏秒积分的宏观特性建立起来的纯电路模型,未考虑磁芯饱和过程中磁芯特性的变化,仿真难以准确预测磁开关负载上的预脉冲,波形的前沿误差也较大。测试获得了快脉冲激励下的铁基纳米晶磁芯磁滞回线和初始磁化曲线,利用磁芯磁滞回线的关键参数,提取了脉冲激励下的磁芯J-A参数,用于定义多物理场中磁开关模型的磁芯特性。针对磁开关脉冲压缩电路,利用多物理场仿真软件COMSOL建立了磁脉冲压缩系统电路与磁开关电磁场的场路耦合仿真模型,计算磁脉冲压缩电路的输出波形,与实验结果对比,预脉冲幅值误差为2%,峰值误差为2%,前沿误差为5%,证明了建立的场路耦合仿真模型的有效性和准确性。Abstract: The magnetic switch is one of the switching devices with excellent performance that can be selected for the repetitive frequency pulse power system. At present, the simulation model of the magnetic switch is a pure circuit model established based on the macroscopic characteristics of the volt-second integral, without considering the change of the magnetic core characteristics during the core saturation process, it is difficult to accurately predict the pre-pulse on the magnetic switch load, and the front error of the waveform is also larger. In this paper, the hysteresis loop and initial magnetization curve of the Fe-based nanocrystalline magnetic core under fast pulse excitation are tested and obtained. Using the key parameters of the magnetic core hysteresis loop, the J-A parameter of the magnetic core under pulse excitation is extracted, which is used to define Magnetic core properties for a magnetic switch model in multi-physics field. For the magnetic switch pulse compression circuit, the field-circuit coupling simulation model was established by using the multi-physics simulation software COMSOL, and the output waveform was simulated. Compared with the experimental results, the pre-pulse amplitude error is 2%, the peak error is 2%, and the front error is 5%, which proves the validity and accuracy of the established field-circuit coupling simulation model.
-
表 1 磁芯测试参数
Table 1. Magnetic core test parameters
C/nF U0/kV (dB/dt)/(T·μs−1) f/kHz 2000 1.0 0.3 32 200 4.5 1.5 145 100 6.0 2.0 202 70 7.2 2.4 251 50 9.8 3.3 318 -
[1] 刘锡三. 高功率脉冲技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005Liu Xisan. High pulsed power technology[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2005 [2] 江伟华. 高重复频率脉冲功率技术及其应用: (3)磁开关的作用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(6):1269-1275 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122406.1269Jiang Weihua. Repetition rate pulsed power technology and its applications: (III) the role of magnetic switches[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(6): 1269-1275 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122406.1269 [3] 刘刚, 李黎, 林福昌, 等. 磁开关在强脉冲能源模块中的设计和应用[J]. 高电压技术, 2011, 37(12):2945-2951Liu Gang, Li Li, Lin Fuchang, et al. Design and implementation of magnetic switch for pulsed power conditioning modules[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2011, 37(12): 2945-2951 [4] 李嵩, 钱宝良, 杨汉武, 等. 固态脉冲功率驱动源主磁开关的特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(4):863-867 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122404.0863Li Song, Qian Baoliang, Yang Hanwu, et al. Characteristics of magnetic switch used as main switch of solid-state accelerator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(4): 863-867 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122404.0863 [5] 邱爱慈. 脉冲功率技术应用[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2016Qiu Aici. Pulse power technology application[M]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 2016 [6] Choi J. Introduction of the magnetic pulse compressor (MPC)—fundamental review and practical application[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, 2010, 5(3): 484-492. [7] 邵涛, 章程, 王瑞雪, 等. 大气压脉冲气体放电与等离子体应用[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(3):685-705Shao Tao, Zhang Cheng, Wang Ruixue, et al. Atmospheric-pressure pulsed gas discharge and pulsed plasma application[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(3): 685-705 [8] 米彦, 万佳仑, 卞昌浩, 等. 基于磁脉冲压缩的DBD高频双极性纳秒脉冲发生器的设计及其放电特性[J]. 电工技术学报, 2017, 32(24):244-256Mi Yan, Wan Jialun, Bian Changhao, et al. Design of DBD high-frequency bipolar nanosecond pulse generator based on magnetic pulse compression system and its discharging characteristics[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2017, 32(24): 244-256 [9] 张东东, 严萍, 王珏. 磁脉冲压缩系统的仿真研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2008, 20(3):497-500Zhang Dongdong, Yan Ping, Wang Jue. Simulation on a magnetic pulse compression system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2008, 20(3): 497-500 [10] 时承瑜. 高功率磁开关同步运行技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2019: 9-13Shi Chengyu. Study on the synchronization of high power magnetic switches[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2019: 9-13 [11] 韩毅博, 刘毅, 刘思维, 等. 环形磁芯脉冲磁化特性测量分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(16):4239-4246Han Yibo, Liu Yi, Liu Siwei, et al. Study on the measurement of pulse magnetization characteristics of toroidal magnetic cores[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(16): 4239-4246 [12] 方旭, 丁臻捷, 浩庆松, 等. 磁开关磁芯动态参数测试及分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2017, 29:105001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201729.170166Fang Xu, Ding Zhenjie, Hao Qingsong, et al. Dynamic parameter test and analysis of magnetic switch core[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2017, 29: 105001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201729.170166 [13] 李嵩. 高功率磁脉冲压缩系统及其在长脉冲驱动源中的应用研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2015: 44-45Li Song. High-power magnetic pulse compressor and its application in the long pulse generators[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2015: 44-45 [14] 杨实, 钟辉煌, 杨汉武, 等. 铁基非晶磁环磁开关设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(5):1172-1176 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102205.1172Yang Shi, Zhong Huihuang, Yang Hanwu, et al. Design of magnetic switch based on metglas magnetic core[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(5): 1172-1176 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102205.1172 [15] 杨银辉, 郑义军, 朱子任, 等. 脉冲气体激光器用固态高压开关的研制[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49:20200045 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200045Yang Yinhui, Zheng Yijun, Zhu Ziren, et al. Development of solid-state high voltage switch for pulsed gas laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49: 20200045 doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200045 [16] Jiles D C, Atherton D L. Theory of ferromagnetic hysteresis (invited)[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1984, 55(6): 2115-2120. doi: 10.1063/1.333582 [17] 赵越, 李琳, 刘任, 等. 基于损耗统计理论的动态J-A磁滞模型[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2019, 38(5):90-96Zhao Yue, Li Lin, Liu Ren, et al. New dynamic hysteresis J-A model based on statistical theory of losses[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2019, 38(5): 90-96 [18] Wilson P R, Ross J N, Brown A D. Optimizing the Jiles-Atherton model of hysteresis by a genetic algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2001, 37(2): 989-993. doi: 10.1109/20.917182 -





 下载:
下载: