Investigating surface damage characteristics in DKDP crystals by laser irradiation at 355 nm and 1064 nm
-
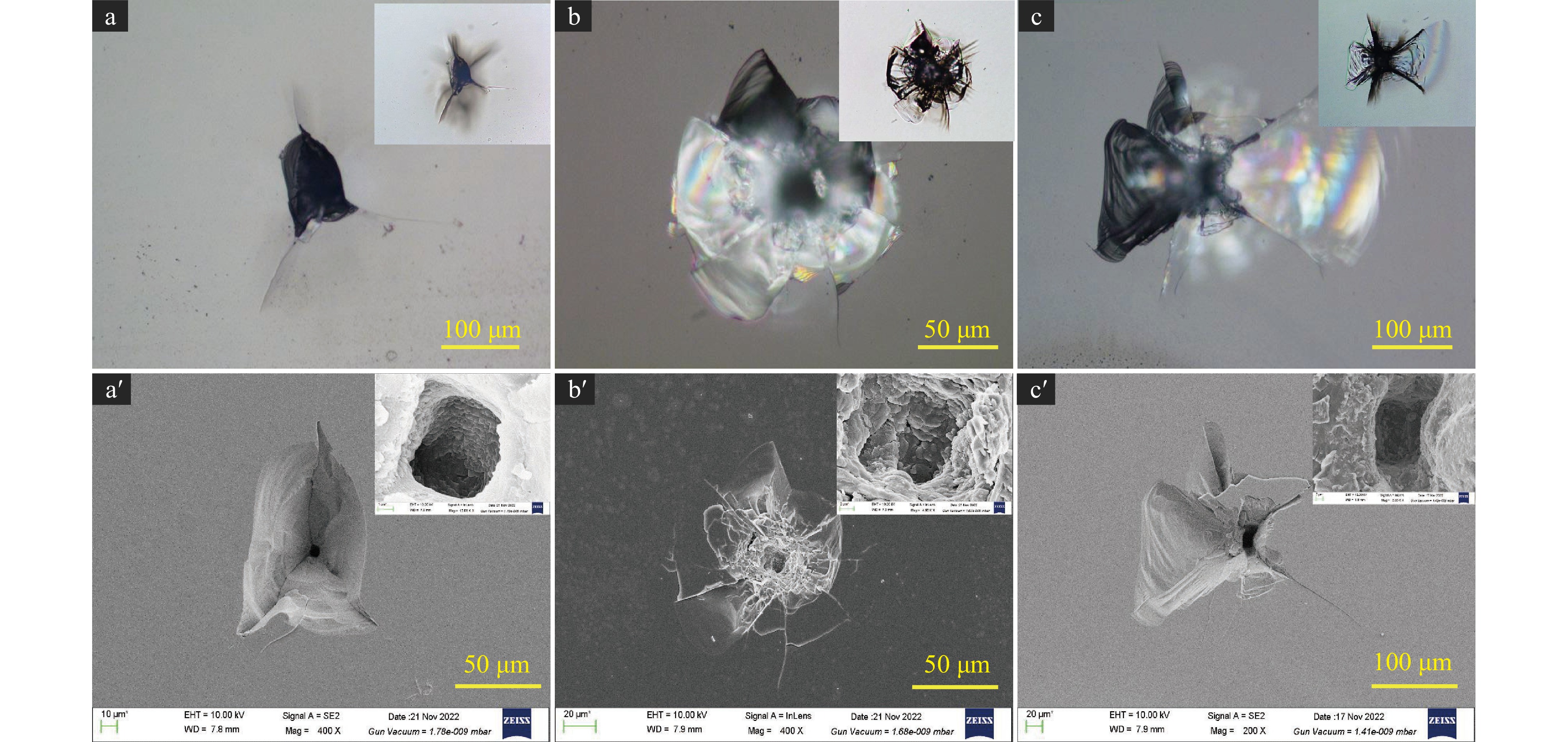
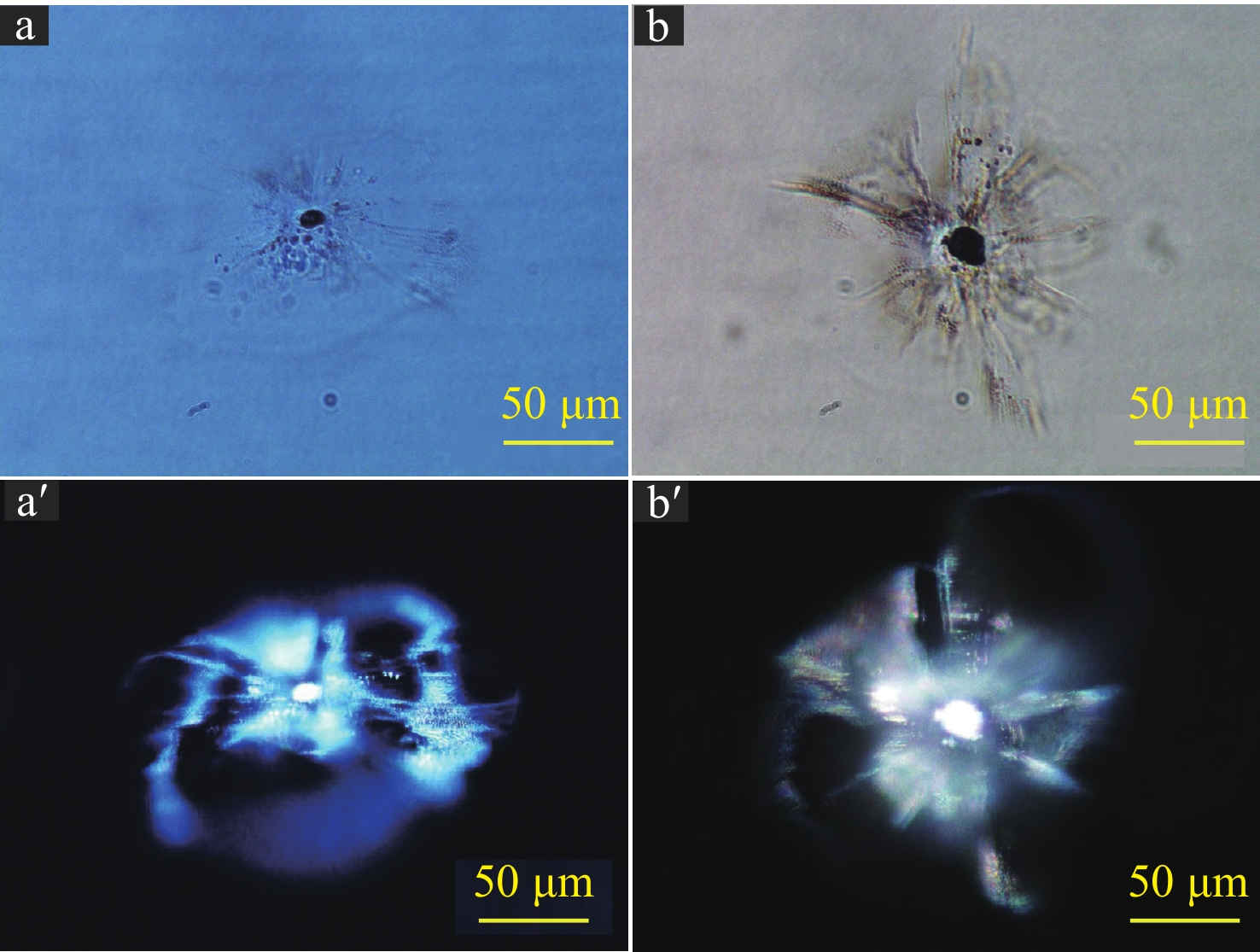
摘要: 利用Nd:YAG激光器研究了DKDP晶体元件在激光辐照下的表面损伤特性,对比研究了355 nm和1064 nm激光辐照下晶体元件的表面损伤形貌,分析了每种损伤形貌对应的前驱体和损伤机制。研究结果表明:相对于体损伤,晶体的表面损伤更加复杂,在脉宽约10 ns、损伤概率小于等于50%的激光能量密度辐照下,DKDP晶体的表面损伤主要有带坑底空腔损伤坑、表面损伤裂纹、平底损伤坑、表面烧蚀四种典型形貌。通过光学显微镜和扫描电子显微镜的成像和分析发现:带坑底空腔损伤坑和表面损伤裂纹的前驱体都是晶体体缺陷,平底损伤坑的前驱体则可能是表面加工裂纹、裂纹内碎屑、表层体缺陷等中的一种或多种,表面烧蚀主要由表面污染和浅表层缺陷形成。与熔石英光学元件一样,表面损伤仍然是晶体元件抗激光辐照损伤的薄弱环节。Abstract: The surface damage characteristics in DKDP crystals under laser irradiation at 355 nm and 1064 nm were studied and compared by using a Nd: YAG laser. The damage precursors and mechanisms corresponding to each damage morphologies were analyzed. The damage results reveal that the surface damage in DKDP crystal is more complex than that in bulk damage. Under the irradiation laser corresponding to the pulse width of 10 ns and the damage probability at 0% − 50%, surface damage morphology in DKDP crystals mainly contained four typical damage morphology: crater with cavity, crater with flat bottom, surface damage crack, and surface ablation. Through the comparison and analysis of the imaging of optical microscope and scanning electron microscope, damage precursors that induced damage craters with bottom cavity and surface cracks were mainly bulk defects, which were the same as the precursors forming the internal damage points (pinpoints). The precursors that induced damage craters with flat bottom were relatively complex, which could be the surface contamination, surface cracks, machining defects, and shallow surface bulk defects. For surface ablation, it was mainly caused by surface contamination and surface absorption defects. Surface damage is still one of the important factors limiting the laser damage resistance of KDPD crystals.
-
表 1 表面损伤形貌的特征数据
Table 1. Characteristic data of surface damage morphology
depth of damage
crater/μmsize of damage
crater/μmprobability of
occurrence/%damage precursor crater with cavity 15~100 50~300 ~30 crystal bulk defect crater with flat bottom 5~50 50~200 ~60 surface cracks and surface defect surface damage crack 20~100 50~200 ~5 crystal bulk defect surface ablation and others − 30~500 ~5 surface contamination and surface defect -
[1] Manes K R, Spaeth M L, Adams J J, et al. Damage mechanisms avoided or managed for NIF large optics[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 146-249. doi: 10.13182/FST15-139 [2] 柴向旭, 李富全, 王圣来, 等. 氘含量对DKDP晶体横向受激拉曼散射增益系数的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64:034213 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.034213Chai Xiangxu, Li Fuquan, Wang Shenglai, et al. Influence of deuteration degree on the transverse stimulated Raman scattering gain coefficient of DKDP crystal[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64: 034213 doi: 10.7498/aps.64.034213 [3] Spaeth M L, Manes K R, Kalantar D H, et al. Description of the NIF laser[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 25-145. doi: 10.13182/FST15-144 [4] 刘畅, 巨新, 刘宝安, 等. 大口径DKDP元件的辐照损伤分布特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:111013 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210198Liu Chang, Ju Xin, Liu Baoan, et al. Irradiation damage distribution characteristics of DKDP in large-aperture high-energy laser[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 111013 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210198 [5] 赵元安, 邵建达, 刘晓凤, 等. 光学元件的激光损伤问题[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:011004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210331Zhao Yuanan, Shao Jianda, Liu Xiaofeng, et al. Tracking and understanding laser damage events in optics[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 011004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.210331 [6] Huang Jin, Wu Zhiqing, Wang Fengrui, et al. Initial damage and damage growth of KDP crystals induced by 355 nm pulse laser[J]. Crystal Research & Technology, 2018, 53: 1700269. [7] 徐子媛, 王岳亮, 赵元安, 等. 不同脉冲宽度355 nm波长激光诱导DKDP晶体损伤特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:091004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190164Xu Ziyuan, Wang Yueliang, Zhao Yuanan, et al. Laser damage behaviors of DKDP crystals dominated by laser pulse duration[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 091004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190164 [8] Wang Yueliang, Zhao Yuanan, Xie Xiaoyi, et al. Laser damage dependence on the size and concentration of precursor defects in KDP crystals: view through differently sized filter pores[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(7): 1534-1537. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001534 [9] Cheng Jian, Wang Janghe, Peng Enhong, et al. Combined modulation of incident laser light by multiple surface scratches and their effects on the laser damage properties of KH2PO4 crystal[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(6): 8764-8782. doi: 10.1364/OE.388741 [10] 陈明君, 姜伟, 庞启龙, 等. KDP晶体微纳米加工表层缺陷对其激光损伤阈值的影响[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(1):159-164 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102201.0159Chen Mingjun, Jiang Wei, Pang Qilong, et al. Simulation of micro—nano processing induced surface defects influencing KDP laser damage threshold[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(1): 159-164 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102201.0159 [11] Gao Wei, Ji Jianwei, Wang Chao, et al. Mitigation of subsurface damage in potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) crystals with a novel abrasive-free jet process[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2018, 8(9): 2625-2635. doi: 10.1364/OME.8.002625 [12] Yang Hao, Cheng Jian, Chen Mingjun, et al. Optimization of morphological parameters for mitigation pits on rear KDP surface: experiments and numerical modeling[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(15): 18332-18345. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.018332 [13] Liu Zhichao, Geng Feng, Li Yaguo, et al. Study of morphological feature and mechanism of potassium dihydrogen phosphate surface damage under a 351 nm nanosecond laser[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(35): 10334-10341. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.010334 [14] Wang Shengfei, Wang Jian, Xu Qiao, et al. Influences of surface defects on the laser-induced damage performances of KDP crystal[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(10): 2638-2646. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.002638 [15] Han Wei, Zhou Lidan, Xiang Yong, et al. Characteristics of laser-induced surface and bulk damage of large-aperture deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate at 351 nm[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2016, 33: 027803. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/33/2/027803 [16] Yang Hao, Cheng Jian, Liu Zhichao, et al. Dynamic behavior modeling of laser-induced damage initiated by surface defects on KDP crystals under nanosecond laser irradiation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57300-2 [17] Papernov S, Schmid A W. Laser-induced surface damage of optical materials: absorption sources, initiation, growth, and mitigation[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 7132, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2008. 2008: 71321J. [18] Wang Shengfei, Wang Jian, Lei Xiangyang, et al. Investigation of the laser-induced surface damage of KDP crystal by explosion simulation[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(11): 15142-15158. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.015142 [19] 赵元安, 胡国行, 刘晓凤, 等. 激光预处理技术及其应用[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(12):2938-2947 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162412.2938Zhao Yuanan, Hu Guohang, Liu Xiaofeng, et al. Laser conditioning technology and its applications[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(12): 2938-2947 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162412.2938 [20] Li Ting, Zhao Yuanan, Lian Yafei, et al. Optimizing sub-nanosecond laser conditioning of DKDP crystals by varying the temporal shape of the pulse[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(22): 35993-36004. doi: 10.1364/OE.441918 [21] 刘志超, 许乔, 雷向阳, 等. 大口径氘化磷酸二氢钾晶体离线亚纳秒激光预处理技术[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70:074208 doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20201524Liu Zhichao, Xu Qiao, Lei Xiangyang, et al. Off-line sub-nanosecond laser conditioning on large aperture deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystal[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70: 074208 doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20201524 [22] Sun Wei, Qi Hongji, Fang Zhou, et al. 1064 nm nanosecond laser induced concentric rings and periodic ripples structures at the exit surface of fused silica[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 309: 79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.04.179 [23] Chambonneau M, Rullier J L, Grua P, et al. Wavelength dependence of the mechanisms governing the formation of nanosecond laser-induced damage in fused silica[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(17): 21819-21830. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.021819 [24] 胡国行. KDP/DKDP晶体和熔石英激光损伤及抑制技术研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院研究生院, 2011: 48-76Hu Guoxing. Laser induced damage and suppression techniques for KDP/DKDP crystal and fused silica [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011 [25] Carr C W, Feit M D, Johnson M A, et al. Complex morphology of laser-induced bulk damage in K2H(2-x)DxPO4 crystals[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89: 131901. doi: 10.1063/1.2345254 [26] Wang Ke, Ma Bin, Han Jiaqi, et al. Morphological and damage growth characteristics of shell-type damage of fused silica optics induced by ultraviolet laser pulses[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(32): 8882-8888. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.008882 -





 下载:
下载: